
Acacia murrayana is a tree in the family Fabaceae. It has numerous common names, including sandplain wattle, Murray's wattle, fire wattle, colony wattle and powder bark wattle that is endemic to arid areas in every mainland State except Victoria.
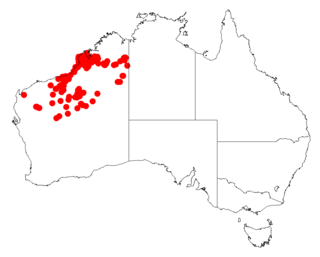
Acacia eriopoda, commonly known as the Broome pindan wattle and the narrow-leaf pindan wattle, is a species of wattle in the legume family that is native to northern Western Australia. It is also known as Yirrakulu to the Nyangumarta peoples.

Acacia monticola, commonly known as red wattle, gawar, curly-bark wattle, curly-bark tree and hill turpentine, is a species of plant in the legume family that is native to northern Australia.

Acacia adoxa, commonly known as the grey-whorled wattle, is a species of plant in the legume family that is native to northern Australia.

Acacia spondylophylla, commonly known as curry wattle or spine-leaf wattle, is a small, flat topped shrub native to central and western Australia. The leaves, which are arranged on spaced whorls around the stem, have a distinctive curry-like smell.

Acacia acradenia, commonly known as Velvet Hill wattle and silky wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to northern and central Australia. The Indigenous Australian group the Nyangumarta peoples know it as walypuna the Alyawarr call it ampwey, the Jaminjung and Ngaliwurru know it as Mindiwirri, the Jaru as binbali or gundalyji, the Kaytetye as ampweye or arwele and the Warlpiri as ngardurrkura.

Acacia ancistrocarpa, commonly known as fitzroy wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. The shrub is also known as fish hook wattle, pindan wattle and shiny leaved wattle.

Acacia clelandii, also known as umbrella mulga, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to arid parts of central Australia.

Acacia elachantha is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to arid parts of central and northern Australia.

Acacia minyura is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae endemic to arid parts of central Australia.

Acacia orthocarpa, also commonly known as Pilbara weeping wattle, needle-leaf wattle or straight-podded wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to tropical parts of northern Australia. The indigenous Nyangumarta peoples know it as yartupu.

Acacia ptychophylla is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae the is endemic to arid areas of north western Australia.

Acacia rhodophloia, commonly known as minni ritchi or western red mulga, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to a large area of arid central western Australia. The Indigenous group the Kurrama peoples know the plant as mantaru.

Acacia sibirica, commonly known as bastard mulga or false witchetty bush, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to arid areas of Australia.

Acacia dictyophleba, also known as the sandhill wattle, waxy wattle and feather veined wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae. The Nyangumarta peoples know the plant as Langkur or Lungkun and the Thalanyji know it as Jabandi.

Acacia jensenii is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to north western Australia.

Acacia melleodora, commonly known as scented wax wattle, waxy wattle, honey wattle or honey scented wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to arid parts of central Australia.

Acacia prainii, commonly known as Prain's wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae endemic to Australia.

Acacia validinervia also commonly known as nyalanyalara, nyala nyala, alumaru or blue wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae endemic to arid areas of inland Australia.

Acacia abrupta is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to arid parts of central and western Australia.























