
Acacia conniana is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to the southern coast of western Australia.

Acacia desertorum is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia filamentosa is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to north western Australia.
Acacia gibsonii, commonly known as Gibson's wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae.
Acacia incongesta, also known as Peak Charles wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to a small area in south western Australia

Acacia limbata is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic across northern Australia.

Acacia multispicata, commonly known as spiked wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia neurocarpa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to northern Australia.

Acacia sessilispica is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae native to Western Australia.

Acacia iteaphylla, commonly known as Flinders Range wattle, Port Lincoln wattle, winter wattle and willow-leaved wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to South Australia.

Acacia nigripilosa is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to Western Australia.
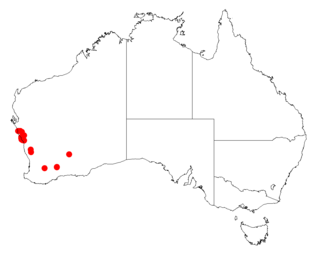
Acacia oxyclada is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia robiniae, commonly known as Robin's wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.
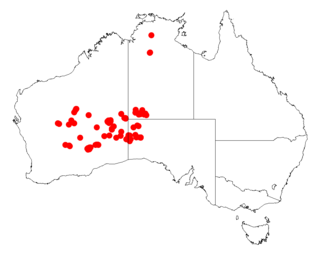
Acacia helmsiana, commonly known as Helm's wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to arid areas of central and western Australia.
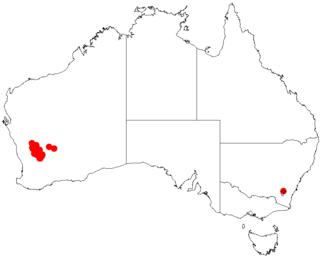
Acacia obtecta is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in south western Australia.

Acacia hamiltoniana, commonly known as Hamilton's wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to parts of eastern Australia.

Acacia kybeanensis, commonly known as kybean wattle or kybeyan wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south eastern Australia.

Acacia linearifolia, commonly known as stringybark wattle or narrow-leaved wattle, is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia cretata is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia curranii, also known as curly-bark wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia. It is listed as vulnerable under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.


















