
Acacia catenulata, commonly known as bendee, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to some arid areas in Australia.

Acacia hopperiana is a small tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia lirellata is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to south western Australia.
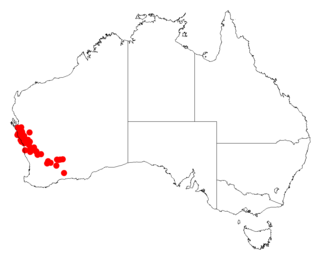
Acacia signata is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia umbraculiformis, commonly known as western umbrella wattle, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae native to western Australia.

Acacia leptospermoides is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae and is endemic to a large area of south western Australia.
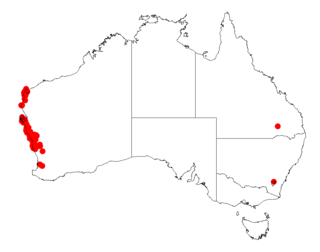
Acacia spathulifolia commonly known as Gold carpet or the Gold carpet wattle is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to coastal parts of western Australia.

Acacia sphacelata is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.
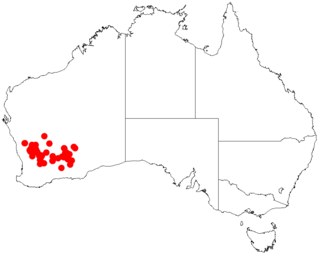
Acacia inceana is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia juncifolia, commonly known as rush-leaf wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to north eastern Australia.
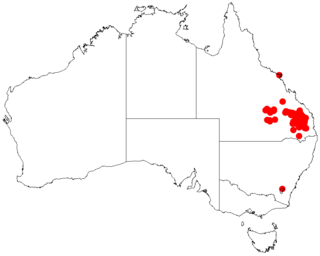
Acacia pustula is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia blakei, commonly known as Blake's wattle or Wollomombi wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia brassii is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia caroleae, also known as Carol's wattle or narrow leaf currawong, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia cretata is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia sparsiflora, also known as currawong or currawang, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to a large area in eastern Australia.

Acacia striatifolia is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia torulosa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia pycnostachya, also known as Bolivia wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to eastern Australia.

Acacia rhodoxylon, also known as rosewood, ringy rosewood or spear wattle, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.





















