
Senecio is a genus of flowering plants in the daisy family (Asteraceae) that includes ragworts and groundsels.

Adenostyles is a genus of flowering plants in the sunflower family Asteraceae, and of the tribe Senecioneae. It was described as a genus in 1816. Adenostyles occur in the temperate climates of the northern hemisphere, mainly in Europe and Asia Minor.

Senecioneae is the largest tribe of the Asteraceae, or the sunflower family, comprising over 150 genera and over 3,500 species. Almost one-third of the species in this tribe are placed in the genus Senecio. Its members exhibit probably the widest possible range of form to be found in the entire plant kingdom, and include annuals, minute creeping alpines, herbaceous and evergreen perennials, shrubs, climbers, succulents, trees, and semi-aquatic plants.

Bougainvillea is a genus of thorny ornamental vines, bushes, and trees belonging to the four o' clock family, Nyctaginaceae. It is native to eastern South America, found from Brazil, west to Peru, and south to southern Argentina. Different authors accept from 4 to 22 species in the genus. The inflorescence consists of large colourful sepal-like bracts which surround three simple waxy flowers, gaining popularity for the plant as an ornamental.

The Passifloraceae are a family of flowering plants, containing about 750 species classified in around 27 genera.

The Combretaceae, often called the white mangrove family, are a family of flowering plants in the order Myrtales. The family includes about 530 species of trees, shrubs, and lianas in ca 10 genera. The family includes the leadwood tree, Combretum imberbe. Three genera, Conocarpus, Laguncularia, and Lumnitzera, grow in mangrove habitats (mangals). The Combretaceae are widespread in the subtropics and tropics. Some members of this family produce useful construction timber, such as idigbo from Terminalia ivorensis. The commonly cultivated Quisqualis indica is now placed in the genus Combretum. Many plants in the former Quisqualis genus contain the excitotoxin quisqualic acid, a potent AMPA agonist.

Bombax is a genus of mainly tropical trees in the mallow family. They are native to western Africa, the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, and the subtropical regions of East Asia and northern Australia. It is distinguished from the genus Ceiba, which has whiter flowers.

Echinocereus is a genus of ribbed, usually small to medium-sized, cylindrical shaped cacti, comprising about 70 species native to the southern United States and Mexico in very sunny, rocky places. Usually the flowers are large and the fruit edible.

Pericallis is a small genus of 15 species of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae, native to the Canary Islands, Madeira and Azores. The genus includes herbaceous plants and small subshrubs. In the past, the genus was often included in either Cineraria or Senecio.

Nyctaginaceae, the four o'clock family, is a family of around 33 genera and 290 species of flowering plants, widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions, with a few representatives in temperate regions. The family has a distinctive fruit type called an accessory fruit or anthocarp, and many genera have extremely large pollen grains.

Jacobaea is a genus of flowering plants in the tribe Senecioneae and the family Asteraceae. Its members used to be placed in the genus Senecio, but have been separated into the segregate genus Jacobaea on the basis of molecular phylogenetics in order to maintain genera that are monophyletic.

Syncarpha is a genus of herbaceous flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. The flowers are known by the common name: everlastings. The genus is endemic to the fynbos of the Eastern and Western Cape in South Africa.

Limonia acidissima is the only species within the monotypic genus Limonia. Common names for the species in English include wood-apple and elephant-apple. It is sometimes also called monkey fruit.

Aequatorium is a genus of flowering plants in the aster family. It was described as a genus in 1978. It is a member of the tribe Senecioneae and native to South America.

Rune Bertil Nordenstam is a Swedish botanist and professor emeritus at the Swedish Museum of Natural History in the Department of Phanerogamic Botany. He has worked with Colchicaceae, Senecioneae and Calenduleae, was the editor of Compositae Newsletter newsletter since 1990, and is a Tribal Coordinator for The International Compositae Alliance with responsibility for the tribes Calenduleae and Senecioneae.

Elekmania is a genus of the tribe Senecioneae and the family Asteraceae.

Wurmbea is a genus of perennial herbs in the family Colchicaceae, native to Africa and Australia. There are about 50 species, with about half endemic to each continent.
Acrisione denticulata is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae, native to southern Argentina and central and southern Chile.
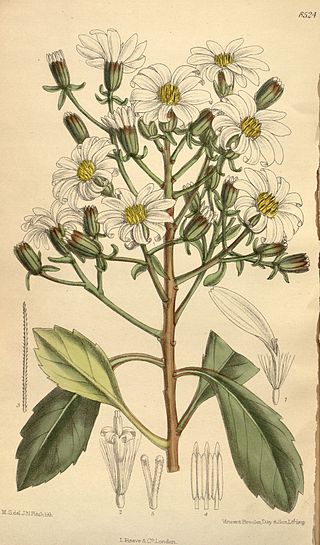
Urostemon is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Asteraceae. The genus is monotypic, being represented by the single species Urostemon kirkii found in New Zealand. Endemic to North Island, usually growing as a small epiphytic bush. It is classified as nationally vulnerable.

Osteospermum tomentosum, the woolly boneseed, is species in the genus Osteospermum native to the Cape Province region of South Africa. In the past it was under the monospecific genus Inuloides as Inuloides tomentosa.



















