
Udawalawe National Park is a national park on the boundary of Sabaragamuwa and Uva Provinces in Sri Lanka. The park was created to provide a sanctuary for wild animals displaced by the construction of the Udawalawe Reservoir on the Walawe River, as well as to protect the catchment of the reservoir. The reserve covers 30,821 hectares (119.00 sq mi) of land area and was established on 30 June 1972.

Ficus religiosa or sacred fig is a species of fig native to the Indian subcontinent and Indochina that belongs to Moraceae, the fig or mulberry family. It is also known as the bodhi tree, peepul tree, peepal tree, pipala tree or ashvattha tree. The sacred fig is considered to have a religious significance in four major religions that originated on the Indian subcontinent: Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism and Jainism. Hindu and Jain ascetics consider the species to be sacred and often meditate under it. Gautama Buddha is believed to have attained enlightenment under a tree of this species. The sacred fig is the state tree of the Indian states of Odisha, Bihar and Haryana.

Couroupita guianensis, known by a variety of common names including cannonball tree, is a deciduous tree in the flowering plant family Lecythidaceae. It is native to the tropical forests of Central and South America, and it is cultivated in many other tropical areas throughout the world because of its fragrant flowers and large fruits, which are brownish grey. There are potential medicinal uses for many parts of Couroupita guianensis, and the tree has cultural and religious significance in South and Southeast Asia. In Sri Lanka and India, the cannonball tree has been widely misidentified as the Sal tree, after its introduction to the island by the British in 1881, and has been included as a common item in Buddhist temples as a result.

Mesua ferrea, the Ceylon ironwood, or cobra saffron, is a species in the family Calophyllaceae native to the Indomalayan realm. This slow-growing tree is named after the heaviness and hardness of its timber. It is widely cultivated as an ornamental for its graceful shape, grayish-green foliage with a beautiful pink to red flush of drooping young leaves, and large, fragrant white flowers. It is the national tree of Sri Lanka, as well as the state tree of Mizoram and state flower of Tripura in India.

Borassus is a genus of five species of fan palms, native to tropical regions of Africa, Asia, and Papua New Guinea.
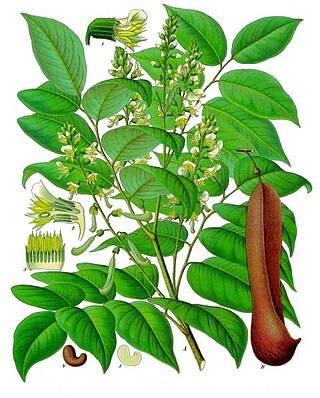
Myroxylon is a genus of Fabaceae native to Latin America.

The Deccan thorn scrub forests are a xeric shrubland ecoregion of south India and northern Sri Lanka. Historically this area was covered by tropical dry deciduous forest, but this only remains in isolated fragments. The vegetation now consists of mainly of southern tropical thorn scrub type forests. These consist of open woodland with thorny trees with short trunks and low, branching crowns; spiny and xerophytic shrubs; and dry grassland. This is the habitat of the great Indian bustard and blackbuck, though these and other animals are declining in numbers; this area was at one time home to large numbers of elephants and tigers. Almost 350 species of bird have been recorded here. The remaining natural habitat is threatened by overgrazing and invasive weeds, but there are a number of small protected areas which provide a haven for the wildlife. Trees in these forests have adapted to not require much water.
Chandigarh Golf Club, established in 1962, the Chandigarh Golf Club is a non-profit registered golf club located in Chandigarh, India. The club nestled under the Sivalik Hills, the club features an 18-hole course spanning 6.5 kilometers. Founded in 1962, the clubhouse was originally laid out by Dharam Vira in 1969, seven years after the founding of the course. The club has been home to some professional golfers, the most known being Jeev Milkha Singh.

Alstonia macrophylla, the hard alstonia, hard milkwood or big-leaved macrophyllum, is a species of plant in the family Apocynaceae.

Tetrameles is a genus of flowering plants in the family Tetramelaceae with one species, Tetrameles nudiflora. It grows as a large deciduous tree and is found across southern Asia from India through southeast Asia, Malesia, and into northern Australia.

Caryota urens is a species of flowering plant in the palm family, native to Sri Lanka, India, Myanmar and Malaysia, where they grow in fields and rainforest clearings, it is regarded as introduced in Cambodia. The epithet urens is Latin for "stinging" alluding to the chemicals in the fruit. Common names in English include solitary fishtail palm, kitul palm, toddy palm, wine palm, sago palm and jaggery palm. Its leaf is used as fishing rod after trimming the branches of the leaf and drying. According to Monier-Williams, it is called moha-karin in Sanskrit. It is one of the sugar palms.

Udawattakele Forest Reserve often spelled as Udawatta Kele, is a historic forest reserve on a hill-ridge in the city of Kandy. It is 104 hectares large. During the days of the Kandyan kingdom, Udawattakele was known as "Uda Wasala Watta" in Sinhalese meaning "the garden above the royal palace". The sanctuary is famous for its extensive avifauna. The reserve also contains a great variety of plant species, especially lianas, shrubs and small trees. There are several giant lianas. Many of small and medium size mammals that inhabit Sri Lanka can be seen here. Several kinds of snakes and other reptiles might be seen. Udawattakele was designated as a forest reserve in 1856, and it became a sanctuary in 1938.
Angammedilla National Park is one of the new national parks in Sri Lanka. The region was designated national park on 6 June 2006. Originally Angammedilla was a forest reserve within the Minneriya-Girithale Sanctuary declared on 12 February 1988. The park is declared mainly to protect the drainage basin of Parakrama Samudra. Angammedilla also secures the drainage basins of Minneriya and Girithale irrigation tanks, water sources in Sudu Kanda and habitats and wildlife of the adjacent forests. It is located 225 kilometres (140 mi) away from Colombo in Polonnaruwa District.
Dandeli National Park is a protected area in the Western Ghats, India.

Terminalia arjuna is a tree of the genus Terminalia. It is commonly known as arjuna or arjun tree in English. It is used as a traditional medicinal plant.
Gelioya is a town located in Udunuwara Divisional Secretariat, Kandy District, Central Province, Sri Lanka. It is situated approximately 14 kilometers east of Kandy, the district capital.

Rhizophora mucronata is a species of mangrove found on coasts and river banks in East Africa and the Indo-Pacific region.
Lankascincus taylori, commonly known as Taylor's tree skink, is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to the island of Sri Lanka.

Commiphora caudata, the hill mango or green commiphora, is the most abundant Asian species of Commiphora of flowering plants in the frankincense and myrrh family, Burseraceae. It can be found in Southern India and Sri Lanka, usually growing in the full sun on hilly granite rock outcrops in dry zone areas. It is a small to medium-sized deciduous tree which is said to be able to reach height of 10-20m, but usually is less high. The tree has a smooth, succulent green bark, which partly flakes off with age, giving rise to a characteristic patchwork of green and brown patches. Its sap has a strong resinous scent. The tree has medicinal properties. The fruit is a globose fleshy drupe with 2 to 6 valves and 1 seed that is black and has 4 wings. Remnants of branches can form a kind of thorns on the trunk. The flowers have a greenish to cream-yellow pedestal with pink to red petals.
Telangana has special climatic conditions due to its unique location in the heart of the Deccan Plateau. It is considered suitable for the developing flora and fauna. There are famous wildlife sanctuaries all over the region.The state of Telangana harbors a total of 2,800 taxa belonging to 1,051 genera under 185 families with its diverse ecosystems and varied agro-climatic regions, is home to a rich and vibrant flora. The state's flora encompasses a wide range of plant species, including both native and cultivated varieties.Telangana tropical rainy type of climate prevails, The State has a wide variety of soils and they form into three broad categories - red, black and laterite with Tropical moist deciduous forests, Southern dry deciduous forests, Northern mixed dry deciduous forests.


















