The long chain fatty acyl-CoA ligase is an enzyme of the ligase family that activates the oxidation of complex fatty acids. Long chain fatty acyl-CoA synthetase catalyzes the formation of fatty acyl-CoA by a two-step process proceeding through an adenylated intermediate. The enzyme catalyzes the following reaction,
In enzymology, sarcosine dehydrogenase (EC 1.5.8.3) is a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction N-demethylation of sarcosine to give glycine. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the CH-NH group of donor with other acceptors. The systematic name of this enzyme class is sarcosine:acceptor oxidoreductase (demethylating). Other names in common use include sarcosine N-demethylase, monomethylglycine dehydrogenase, and sarcosine:(acceptor) oxidoreductase (demethylating). Sarcosine dehydrogenase is closely related to dimethylglycine dehydrogenase, which catalyzes the demethylation reaction of dimethylglycine to sarcosine. Both sarcosine dehydrogenase and dimethylglycine dehydrogenase use FAD as a cofactor. Sarcosine dehydrogenase is linked by electron-transferring flavoprotein (ETF) to the respiratory redox chain. The general chemical reaction catalyzed by sarcosine dehydrogenase is:
In enzymology, a phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (EC 1.1.1.44) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.4.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NADPH—hemoprotein reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ADP-L-glycero-D-manno-heptose 6-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a dTDP-4-dehydrorhamnose 3,5-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a L-ribulose-5-phosphate 4-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of ribulose 5-phosphate and xylulose 5-phosphate in the oxidative phase of the Pentose phosphate pathway.
In enzymology, an UDP-arabinose 4-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
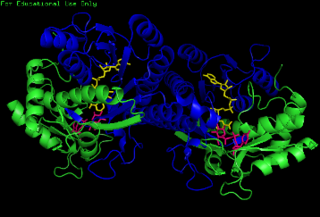
The enzyme UDP-glucose 4-epimerase, also known as UDP-galactose 4-epimerase or GALE, is a homodimeric epimerase found in bacterial, fungal, plant, and mammalian cells. This enzyme performs the final step in the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, catalyzing the reversible conversion of UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose. GALE tightly binds nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a co-factor required for catalytic activity.
In enzymology, an UDP-glucuronate 4-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Casein kinase II subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CSNK2B gene. It is a ubiquitous protein kinase which regulates metabolic pathways, signal transduction, transcription, translation, and replication. The enzyme localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus.
The enzyme lysophospholipase (EC 3.1.1.5) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a dolichyl-phosphate beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucosyl-DNA beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction in which a beta-D-glucosyl residue is transferred from UDP-glucose to a glucosylhydroxymethylcytosine residue in DNA. This enzyme resembles DNA beta-glucosyltransferase in that respect.

In enzymology, a nicotinate-nucleotide-dimethylbenzimidazole phosphoribosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a riboflavin kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Laminin subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LAMA1 gene.
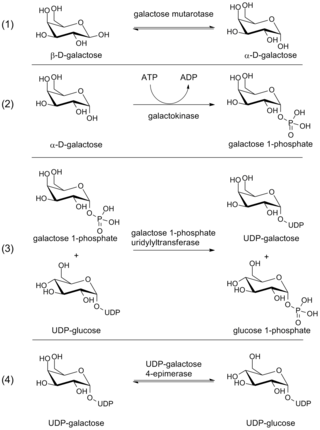
The Leloir pathway is a metabolic pathway for the catabolism of D-galactose. It is named after Luis Federico Leloir, who first described it.
N-acetylneuraminate epimerase is an enzyme with systematic name N-acetyl-alpha-neuraminate 2-epimerase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction












