
Tetraodontidae is a family of primarily marine and estuarine fish of the order Tetraodontiformes. The family includes many familiar species variously called pufferfish, puffers, balloonfish, blowfish, blowers, blowies, bubblefish, globefish, swellfish, toadfish, toadies, toadle, honey toads, sugar toads, and sea squab. They are morphologically similar to the closely related porcupinefish, which have large external spines.

Coelacanths are an ancient group of lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) in the class Actinistia. As sarcopterygians, they are more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods than to ray-finned fish.
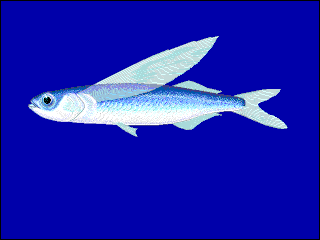
Beloniformes is an order composed of six families of freshwater and marine ray-finned fish:

Menticirrhus is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Sciaenidae, the drums or croakers. They are commonly known as kingcroakers or kingfish. These fish are found in the Western Atlantic and Eastern Pacific Oceans.

Acropomatidae is a family of ray-finned fish in the order Acropomatiformes, commonly known as lanternbellies. Acropoma species are notable for having light-emitting organs along their undersides. They are found in all temperate and tropical oceans, usually at depths of several hundred meters. There are about 32 species in as many as 9 genera, although some authorities recognise fewer genera than Fishbase does.

Sebastes is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae part of the family Scorpaenidae, most of which have the common name of rockfish. A few are called ocean perch, sea perch or redfish instead. They are found in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.

The cornetfishes or flutemouths are a small family, the Fistulariidae, of extremely elongated fishes in the order Syngnathiformes. The family consists of a single genus, Fistularia, with four species, found worldwide in tropical and subtropical marine environments.

Oplegnathus is currently the sole recognized genus in the knifejaw family (Oplegnathidae) of marine centrarchiform ray-finned fishes. The largest, the Cape knifejaw, can reach a maximum length around 90 cm (35 in). Knifejaws have teeth fused into a parrot-like beak in adulthood. They feed on barnacles and mollusks, and are fished commercially. They are native to the Indian and Pacific Oceans.

Jack mackerels or saurels are marine ray-finned fish in the genus Trachurus of the family Carangidae. The name of the genus derives from the Greek words trachys ("rough") and oura ("tail"). Some species, such as T. murphyi, are harvested in purse seine nets, and overfishing has sometimes occurred.

Chelmon is a genus of marine ray-finned fish in the family Chaetodontidae, the butterflyfishes. They are tropical species native to the western Pacific Ocean.

Lithognathus is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Sparidae, which includes the seabreams and porgies. Species in this genus are given the common name of steenbras. The genus is found in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean from southwestern Europe to South Africa and into the southwestern Indian Ocean.

Zaniolepis, the combfishes, is a genus of marine ray-finned fish, it is one of two genera in the family Zaniolepididae. These fishes are native to the eastern Pacific Ocean. Z. frenata that was a source of food to the Native American inhabitants of San Nicolas Island off the coast of southern California, United States during the Middle Holocene.

Chalcidichthys is an extinct genus of prehistoric manefish. It contains a single species, C. malacapterygius, that lived during the Upper Miocene of Southern California. It is known from the Modelo Formation in Los Angeles County, and specimens were found during construction of a tunnel on Sepulveda Boulevard. It is assumed to have preyed on siphonophores, like its living relatives.

Lophar miocaenus is an extinct bony fish almost identical in form to the living bluefish, Pomatomus saltatrix, differing in its dentition, which consisted of "thick, conical subequal teeth" instead of the sharp, slender teeth and canines seen in bluefish. L. miocaenus lived during the Upper Miocene subepoch of Southern California.

Absalomichthys velifer is an extinct, prehistoric manefish that lived during the Upper Miocene of what is now Southern California in the United States. Its dorsal fin was huge in comparison with living species. It is known from the Modelo Formation of Los Angeles County.
Cyttoides is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish that lived during the early Oligocene epoch in the seas over Europe. It contains a single species, C. glaronensis from Canton Glarus, Switzerland. It was a zeiform related to the extant genus Cyttus.

Asthenocormus is an extinct genus of large marine pachycormiform ray-finned fish. It contains a single species, A. titanius. A member of the edentulous suspension feeding clade within the Pachycormiformes, fossils have been found in the Upper Jurassic plattenkalks of Bavaria, Germany.

Plethodus is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish. It is the type genus of the family Plethodidae.
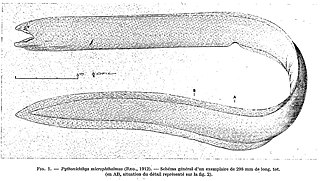
Pythonichthys is a genus of eels of the family Heterenchelyidae that occur in tropical waters of the eastern Pacific Ocean off of Panama and in the Atlantic Ocean near the Caribbean Sea and the west coast of Africa. It contains the following described species:

Augustynolophus is an extinct genus of herbivorous saurolophine hadrosaur dinosaur which was discovered in the Moreno Formation in California, dating to the late Maastrichtian age, making it one of the last dinosaurs known from the fossil record before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.




















