
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides, and it is a normal component of urine. High blood concentrations of uric acid can lead to gout and are associated with other medical conditions, including diabetes and the formation of ammonium acid urate kidney stones.
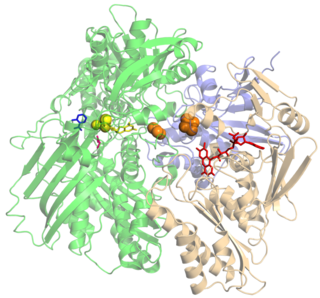
Xanthine oxidase is a form of xanthine oxidoreductase, a type of enzyme that generates reactive oxygen species. These enzymes catalyze the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and can further catalyze the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid. These enzymes play an important role in the catabolism of purines in some species, including humans.

The enzyme urate oxidase (UO), uricase or factor-independent urate hydroxylase, absent in humans, catalyzes the oxidation of uric acid to 5-hydroxyisourate:
Purine metabolism refers to the metabolic pathways to synthesize and break down purines that are present in many organisms.

Guanosine monophosphate synthetase, also known as GMPS is an enzyme that converts xanthosine monophosphate to guanosine monophosphate.

Xanthine dehydrogenase, also known as XDH, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the XDH gene.

In enzymology, a homoserine dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ureidoglycolate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.154) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Alanine dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a ferredoxin—nitrate reductase (EC 1.7.7.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an allantoate deiminase (EC 3.5.3.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aminoacylase (EC 3.5.1.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an ureidoglycolate hydrolase (EC 3.5.3.19) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Carnitine O-acetyltransferase also called carnitine acetyltransferase is an enzyme that encoded by the CRAT gene that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 3-deoxy-8-phosphooctulonate synthase (EC 2.5.1.55) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
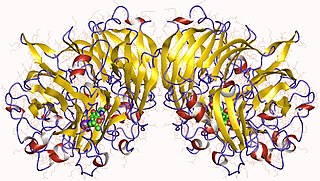
Methanol dehydrogenase (cytochrome c) (EC 1.1.2.7, methanol dehydrogenase, MDH) is an enzyme with systematic name methanol:cytochrome c oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Catalase-peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.21, katG (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name donor:hydrogen-peroxide oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
- donor + H2O2 ⇌ oxidized donor + 2 H2O
- 2 H2O2 ⇌ O2 + 2 H2O
Beta-carotene 3-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.129, beta-carotene 3,3'-monooxygenase, CrtZ) is an enzyme with systematic name beta-carotene,NADH:oxygen 3-oxidoreductase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Phospholipase C (EC 3.1.4.3, lipophosphodiesterase I, Clostridium welchii α-toxin, Clostridium oedematiens β- and γ-toxins, lipophosphodiesterase C, phosphatidase C, heat-labile hemolysin, α-toxin) is an enzyme with systematic name phosphatidylcholine cholinephosphohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
The enzyme exo-(1→4)-α-D-glucan lyase (EC 4.2.2.13, α-(1→4)-glucan 1,5-anhydro-D-fructose eliminase, α-1,4-glucan exo-lyase, α-1,4-glucan lyase, GLase) is an enzyme with systematic name (1→4)-α-D-glucan exo-4-lyase (1,5-anhydro-D-fructose-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction










