
Zingiberaceae or the ginger family is a family of flowering plants made up of about 50 genera with a total of about 1600 known species of aromatic perennial herbs with creeping horizontal or tuberous rhizomes distributed throughout tropical Africa, Asia, and the Americas. Members of the family Zingiberaceae including turmeric, ginger, Javanese ginger, and galangal have been used for centuries in traditional medicine. Preclinical studies of Zingiberaceae extracts have shown analgesic properties.

Cardamom, sometimes cardamon or cardamum, is a spice made from the seeds of several plants in the genera Elettaria and Amomum in the family Zingiberaceae. Both genera are native to the Indian subcontinent and Indonesia. They are recognized by their small seed pods: triangular in cross-section and spindle-shaped, with a thin, papery outer shell and small, black seeds; Elettaria pods are light green and smaller, while Amomum pods are larger and dark brown.

Amomum subulatum, also known as Black cardamom, hill cardamom, Bengal cardamom, greater cardamom, Indian cardamom, Nepal cardamom, winged cardamom, big cardamon, or brown cardamom, is a perennial herbaceous plant in the family Zingiberaceae. Its seed pods have a strong, camphor-like flavour, with a smoky character derived from the method of drying. In Hindi it is called बड़ी इलाइची.

Cypress is a common name for various coniferous trees or shrubs of northern temperate regions that belong to the family Cupressaceae. The word cypress is derived from Old French cipres, which was imported from Latin cypressus, the latinisation of the Greek κυπάρισσος (kyparissos).

Aframomum melegueta is a species in the ginger family, Zingiberaceae, and closely related to cardamom. Its seeds are used as a spice ; it imparts a pungent, black-pepper-like flavor with hints of citrus. It is commonly known as grains of paradise, melegueta pepper, alligator pepper, Guinea grains, ossame, or fom wisa. The term Guinea pepper has also been used, but is most often applied to Xylopia aethiopica.

Malagueta pepper, a variety of Capsicum frutescens, is a type of chili pepper widely used in Brazil, the Caribbean, Portugal, Mozambique, Angola, and São Tomé and Príncipe. It is heavily used in the Bahia state of Brazil. It apparently got its name from the unrelated melegueta pepper from West Africa, because of a similar level of piquancy.
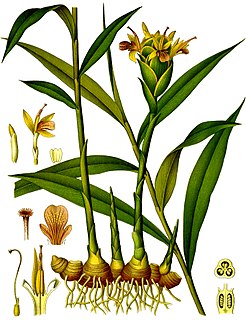
The genus Zingiber is native to Southeast Asia especially in Thailand, China, the Indian Subcontinent, and New Guinea. It contains the true gingers, plants grown the world over for their medicinal and culinary value. The most well known are Z. officinale and Z. mioga, two garden gingers.

Apocynum, commonly known as dogbane or Indian hemp, is a small genus of the flowering plant family Apocynaceae. Its name comes from Ancient Greek ἀπόκυνον apókunon, from ἀπο- apo- "away" and κύων kúōn "dog", referring to dogbane, which was used to poison dogs. The genus is native to North America, temperate Asia, and southeastern Europe.

Cornus amomum, the silky dogwood, is a species of dogwood native to the eastern United States, from Michigan and Vermont south to Alabama and Florida. Other names for this dogwood have included red willow, silky cornel, kinnikinnick, and squawbush.

Alligator pepper is a West African spice made from the seeds and seed pods of Aframomum danielli, A. citratum or A. exscapum. It is a close relative of grains of paradise, obtained from the closely related species, Aframomum melegueta or "grains of paradise". Unlike grains of paradise, which are generally sold as only the seeds of the plant, alligator pepper is sold as the entire pod containing the seeds.

Aframomum corrorima is a species of flowering plant in the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. The spice, known as Ethiopian cardamom, false cardamom, or korarima, is obtained from the plant's seeds, and is extensively used in Ethiopian and Eritrean cuisine. It is an ingredient in berbere, mitmita, awaze, and other spice mixtures, and is also used to flavor coffee. Its flavor is comparable to that of the closely related Elettaria cardamomum or green cardamom. In Ethiopian herbal medicine, the seeds are used as a tonic, carminative, and laxative.

Aframomum is a genus in the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It is widespread across tropical Africa as well as on some islands of the Indian Ocean. It is represented by approximately 50 species. It is larger than other genera in its family. Its species are perennials and produce colorful flowers.

Spikenard, also called nard, nardin, and muskroot, is a class of aromatic amber-colored essential oil derived from Nardostachys jatamansi, a flowering plant in the honeysuckle family which grows in the Himalayas of Nepal, China, and India. The oil has been used over centuries as a perfume, a traditional medicine, or in religious ceremonies across a wide territory from India to Europe. Historically, the name nard has also referred to essential oils derived from several other species, including some species in the closely related valerian genus and Spanish lavender, which have also been used in perfume-making and sometimes to adulterate true spikenard using more common, less valued materials.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to herbs and spices:

Wurfbainia villosa, also known by its basionym Amomum villosum, is a plant in the ginger family that is grown throughout Southeast Asia and in South China. Similar to cardamom, the plant is cultivated for its fruits, which dry into pods when mature and contain strongly aromatic seeds. W. villosa is an evergreen plant in the ginger family, grow in the shade of the tree, 1.5 to 3.0 m high, whose branches and leaves are similar to ginger's. W. villosa has a characteristic that flowers spread on the ground can bear fruit while flowers on the branches can not. Its flowers bloom in March and April and are the colour of white jade.

Spices have been around in conjunction with human use for millennia, with many civilizations in antiquity that have used a variety of spices for their common qualities. The variety of spices were used for common purposes across the ancient world, and they were also used to create a variety of products designed to enhance or suppress certain sensations. Spices were also associated with certain rituals to perpetuate a superstition or fulfill a religious obligation, among other things.
Amomum ovoideum is a widespread shade-demanding rhizomatous herb of the ginger family (Zingiberaceae) native to Southeast Asia. It is perennial, producing leafy stems up to 3 m (9.8 ft) tall from a subterranean, long, and much-branched rhizome. The plant bears fruits up to 2 cm (0.79 in) long, covered by slender, soft, red spines. When dried, the fruit produces cardamom seedpods similar to other cardamom spice plants.
Wurfbainia uliginosa is the type species of the recently reconstituted plant genus Wurfbainia in the ginger family. Its native range is from Indo-China to Sumatra.
Aframomum daniellii, also known as African cardamom, is a species in the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It was first described by Joseph Dalton Hooker, and got its current name from Karl Moritz Schumann.















