
Tabebuia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Bignoniaceae. Tabebuia consists almost entirely of trees, but a few are often large shrubs. A few species produce timber, but the genus is mostly known for those that are cultivated as flowering trees.

Bignoniaceae is a family of flowering plants in the order Lamiales commonly known as the bignonias or trumpet vines. It is not known to which of the other families in the order it is most closely related.

In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. These can be activated by enzyme hydrolysis, which causes the sugar part to be broken off, making the chemical available for use. Many such plant glycosides are used as medications. Several species of Heliconius butterfly are capable of incorporating these plant compounds as a form of chemical defense against predators. In animals and humans, poisons are often bound to sugar molecules as part of their elimination from the body.

Plantago lanceolata is a species of flowering plant in the plantain family Plantaginaceae. It is known by the common names ribwort plantain, narrowleaf plantain, English plantain, ribleaf, lamb's tongue, and buckhorn. It is a common weed on cultivated or disturbed land.

Junonia coenia, known as the common buckeye or buckeye, is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found in the United States east of the Rocky Mountains and in Mexico. Its habitat is open areas with low vegetation and some bare ground. Its original ancestry has been traced to Africa, which then experiences divergence in Asia. The species Junonia grisea, the gray buckeye, is found west of the Rocky Mountains and was formerly a subspecies of Junonia coenia.

Bignonia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Bignoniaceae. Its genus and family were named after Jean-Paul Bignon by his protégé Joseph Pitton de Tournefort in 1694, and the genus was established as part of modern botanical nomenclature in 1753 by Carl Linnaeus. Species have been recorded from the southern USA, Central to most of South America.

Lamium album, commonly called white nettle or white dead-nettle, is a flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae. It is native throughout Europe and Asia, growing in a variety of habitats from open grassland to woodland, generally on moist, fertile soils.
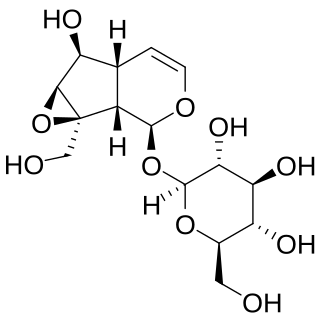
Catalpol is an iridoid glucoside. This natural product falls in the class of iridoid glycosides, which are simply monoterpenes with a glucose molecule attached.

Verbascoside is a caffeoyl phenylethanoid glycoside in which the phenylpropanoid caffeic acid and the phenylethanoid hydroxytyrosol form an ester and an ether bond respectively, to the rhamnose part of a disaccharide, namely β-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1→3)-β-D-(4-O-caffeoyl)-glucopyranoside.

Castilleja levisecta is a rare species of flowering plant in the family Orobanchaceae known by the common name golden paintbrush, or golden Indian paintbrush, listed under the Endangered Species Act in 1997. It is native to British Columbia and Washington, where it is known from eleven remaining populations. It occurred in Oregon but all natural occurrences there have been extirpated. It has been reintroduced to a few areas in Oregon, but it remains to be seen if the plants will survive. The plant is a federally listed endangered species of Canada and was listed as threatened in the United States in 1997. On June 30, 2021, the plant was proposed for delisting due to recovery.

Euphydryas editha taylori, the Whulge checkerspot or Taylor's checkerspot, is a butterfly native to an area of the northwestern United States and Vancouver Island.

Stachytarpheta mutabilis is a species of flowering plant in the verbena family known by the common names changeable velvetberry, coral porterweed, pink snakeweed, red snakeweed, and pink rat tail. It is native to Mexico, the Caribbean, and South America. It can be found in many other places as an introduced species. It is cultivated as an ornamental plant.

Phenylethanoids are a type of phenolic compounds characterized by a phenethyl alcohol structure. Tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol are examples of such compounds.

Handroanthus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Bignoniaceae. It consists of 30 species of trees, known in Latin America by the common names poui, pau d'arco, or ipê. The latter sometimes appears as epay or simply ipe (unaccented) in English. The large timber species are sometimes called lapacho or guayacan, but these names are more properly applied to the species Handroanthus lapacho and Handroanthus guayacan, respectively.

Astianthus is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the Bignoniaceae family. The sole species is Astianthus viminalis. It is known by the common names achuchil in Mexico and chilca in Guatemala and Honduras.

Amphilophium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Bignoniaceae, native to South America. Amphilophium crucigerum has escaped from cultivation elsewhere, and has become an invasive weed in Australia.

Tanaecium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Bignoniaceae, native to south and Central America.

Dolichandra is a genus of flowering plants in the family Bignoniaceae, native to Latin America and the Caribbean. They are climbing lianas with trifid and uncate tendrils. The best-known species is Dolichandra unguis-cati.
Xylophragma is a genus of flowering plants in the family Bignoniaceae, native to dry forests of Mexico, Central America, Trinidad and northern South America. They are lianas or scandent shrubs.

Heterophragma is a genus of two species of tree, constituting part of the plant family Bignoniaceae. The species are found in Southeast Asia and India.



















