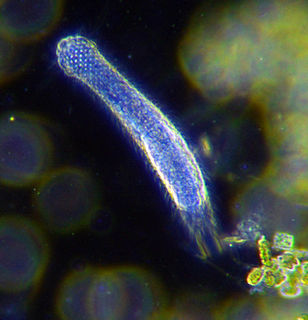
The gastrotrichs, commonly referred to as hairybellies or hairybacks, are a group of microscopic (0.06-3.0 mm), worm-like, pseudocoelomate animals, and are widely distributed and abundant in freshwater and marine environments. They are mostly benthic and live within the periphyton, the layer of tiny organisms and detritus that is found on the seabed and the beds of other water bodies. The majority live on and between particles of sediment or on other submerged surfaces, but a few species are terrestrial and live on land in the film of water surrounding grains of soil. Gastrotrichs are divided into two orders, the Macrodasyida which are marine, and the Chaetonotida, some of which are marine and some freshwater. Nearly 800 species of gastrotrich have been described.
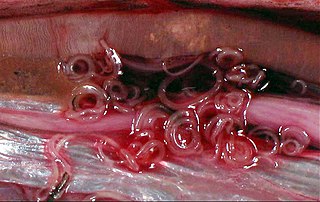
The Chromadorea are a class of the roundworm phylum, Nematoda. They contain a single subclass (Chromadoria) and several orders. With such a redundant arrangement, the Chromadoria are liable to be divided if the orders are found to form several clades, or abandoned if they are found to constitute a single radiation.
Aphelenchus avenae is a mycophagous nematode capable of feeding on plant tissue in culture.

The Anisakidae are a family of intestinal nematodes (roundworms). The larvae of these worms can cause anisakiasis when ingested by humans, in raw or insufficiently cooked fish.

The nematodes or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda, with plant-parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Taxonomically, they are classified along with insects and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike flatworms, have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but as their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, it shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum.

Bursaphelenchus is a genus of nematodes (roundworms) in the order Aphelenchida. Most are obligate mycophages, but some feed on wood, with two species, the red ring nematode and the pine wood nematode, economically significant as pests of coconut palms and of pine trees, respectively. Given that Bursaphelenchus species are usually hard to distinguish from one another except by trained nematologists with access to microscopes or DNA sequence analysis, the entire genus is put under quarantine in some countries. Where this is not the case however, these nematodes are becoming established as model organisms for nematode developmental biology, ecology and genetics.
Laxus is a genus of nematode worms from the subfamily Stilbonematinae of the family Desmodoridae. Like other members of this subfamily, they are covered by a layer of symbiotic sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, which in Laxus are coccoid in shape. They are distinguished from other stilbonematine genera by the finely-annulated somatic cuticle, thickened cephalic cuticle, small and coiled amphidial fovea, and lack of male structures. There are at least five species in the genus.

Huffmanela is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Trichosomoididae.
Aphelenchoididea is a nematode superfamily in the order Rhabditida. Its members can be found inside bodies of species from the families Lepidoptera and Blattodea.
Qudsia Tahseen is a Professor of Zoology at Aligarh Muslim University and teaches Animal Ecology as well as Nematology to the students of the Masters programme. Her areas of research include taxonomy and developmental biology of terrestrial and aquatic nematodes. Her thrust areas are Biodiversity, Taxonomy, Ecology and developmental biology of soil and fresh water nematodes. She is a fellow of two national science academies of India.

Cucullanus is a genus of parasitic nematodes. The genus includes more than 100 species.
Plectus parvus is a species of nematode (roundworm) found in freshwater and terrestrial environments. It has been sampled in Europe and New Zealand. Along with the similar nematode Panagrolaimus detritophagus, in 2018 it was the first species of multicellular eukaryote to be thawed into a living state after prolonged cryopreservation. Female worms of this species were found in Pleistocene permafrost in the Kolyma River lowland. They were mobile and ate, after being frozen for 30–40 thousand years.
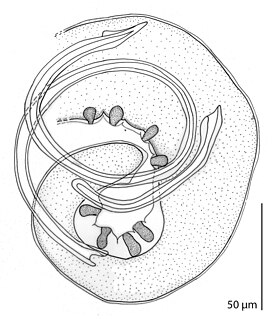
Cystidicolidae is a family of spirurian nematodes. It was created by Skrjabin in 1946. All members of the family are parasites of fish.
Sabatieria furcillata is a nematode in the family Comesomatidae ranking. It was described in 1954 by the Austrian zoologist Wolfgang Wieser.

Ascarophis is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Ascarophis are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of marine and estuarine fishes.

Ascarophisnema is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Ascarophisnema are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of fish. According to the World Register of Marine Species, the genus currently (2019) includes a single species, Ascarophisnema tridentatum.
Metabronemoides is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Metabronemoides are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of fish.
Prospinitectus is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Prospinitectus are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of Tuna fish.
István Andrássy was a Hungarian nematologist. Starting with his first publication in 1952 on the nematode fauna of Mount Bükk, over his dissertation in 1973 on the evolution of nematodes to his last days he was a very prolific scientist, publishing more than 200 manuscripts, chapters and books on the class of Nematoda. He described 530 taxa of nematodes and at least 60 nematode taxa are named after him, which shows the huge respect he had in the nematologists world.
Raphidascarididae is a family of roundworms in the order Ascaridida. It encompasses nine genera, including Hysterothylacium, which parasitize marine fish, and Raphidascaris. The family contains over 190 species.









