Histone deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.98, HDAC) are a class of enzymes that remove acetyl groups (O=C-CH3) from an ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on a histone, allowing the histones to wrap the DNA more tightly. This is important because DNA is wrapped around histones, and DNA expression is regulated by acetylation and de-acetylation. Its action is opposite to that of histone acetyltransferase. HDAC proteins are now also called lysine deacetylases (KDAC), to describe their function rather than their target, which also includes non-histone proteins.
Vorinostat (rINN) also known as Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid is a member of a larger class of compounds that inhibit histone deacetylases (HDAC). Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDI) have a broad spectrum of epigenetic activities.
Histone acetylation and deacetylation are the processes by which the lysine residues within the N-terminal tail protruding from the histone core of the nucleosome are acetylated and deacetylated as part of gene regulation.

Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HDAC1 gene.
Histone deacetylase inhibitors are chemical compounds that inhibit histone deacetylases.

Histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HDAC2 gene. It belongs to the histone deacetylase class of enzymes responsible for the removal of acetyl groups from lysine residues at the N-terminal region of the core histones. As such, it plays an important role in gene expression by facilitating the formation of transcription repressor complexes and for this reason is often considered an important target for cancer therapy.

Histone deacetylase 3 is an enzyme encoded by the HDAC3 gene in both humans and mice.

Paired amphipathic helix protein Sin3a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIN3A gene.

Histone-binding protein RBBP4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBBP4 gene.

Histone deacetylase 6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HDAC6 gene.
Histone-binding protein RBBP7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBBP7 gene.

Histone deacetylase 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HDAC5 gene.

Histone deacetylase 9 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HDAC9 gene.
Histone deacetylase 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HDAC7 gene.
Histone deacetylase 8 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HDAC8 gene.

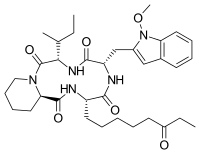
Romidepsin, also known as Istodax, is an anticancer agent used in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) and other peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCLs). Romidepsin is a natural product obtained from the bacterium Chromobacterium violaceum, and works by blocking enzymes known as histone deacetylases, thus inducing apoptosis. It is sometimes referred to as depsipeptide, after the class of molecules to which it belongs. Romidepsin is branded and owned by Gloucester Pharmaceuticals, now a part of Celgene.
In the field of molecular biology, the Mi-2/NuRDcomplex, is a group of associated proteins with both ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling and histone deacetylase activities. As of 2007, Mi-2/NuRD was the only known protein complex that couples chromatin remodeling ATPase and chromatin deacetylation enzymatic functions.
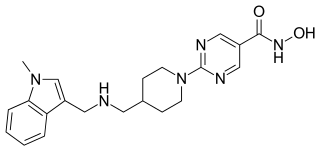
Quisinostat is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of cancer. It is a "second generation" histone deacetylase inhibitor with antineoplastic activity. It is highly potent against class I and II HDACs.

3-Deazaneplanocin A is a drug which acts as both a S-adenosylhomocysteine synthesis inhibitor and also a histone methyltransferase EZH2 inhibitor. Studies have shown that it has in vitro against a variety of different tumor cell lines.
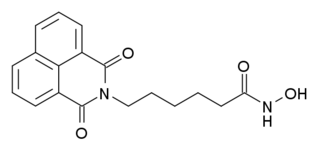
Scriptaid is a drug which acts as a histone deacetylase inhibitor, and was one of the first compounds discovered via high-throughput screening that acts at this target. Scriptaid itself was never developed for medical applications, but led to the development of structurally related drugs such as vorinostat, which have been accepted into clinical use. Most early research using these compounds focused on their anti-cancer activity, but more recent research has found scriptaid to be useful in other applications such as cloning and research into regulation of metabolism.