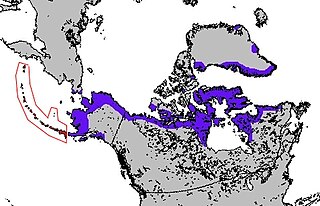
Chukchi Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the Long Strait, off Wrangel Island, and in the east by Point Barrow, Alaska, beyond which lies the Beaufort Sea. The Bering Strait forms its southernmost limit and connects it to the Bering Sea and the Pacific Ocean. The principal port on the Chukchi Sea is Uelen in Russia. The International Date Line crosses the Chukchi Sea from northwest to southeast. It is displaced eastwards to avoid Wrangel Island as well as the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug on the Russian mainland.

Scoresby Sund is a large fjord system of the Greenland Sea on the eastern coast of Greenland. It has a tree-like structure, with a main body approximately 110 km (68 mi) long that branches into a system of fjords covering an area of about 38,000 km2 (14,700 sq mi). The longest of the fjords extends 340–350 km inland from the coastline. The depth is 400–600 m in the main basin, but depths increase to up to 1,450 m (4,760 ft) in some fjords. It is one of the largest and longest fjord systems in the world.

Belkovsky Island is the westernmost island of the Anzhu Islands subgroup of the New Siberian Islands archipelago in the Laptev Sea.

Walrus Island is a small islet located 15 km east of Saint Paul Island, Alaska in the Bering Sea. It is part of the Pribilof Islands group. Its length is 2,130 feet (650 m) and its area is 50.3 acres (0.2036 km²). There is no resident population.

Ayon Island is an island in the coast of Chukotka in the East Siberian Sea. The island itself consists mainly of low-lying tundra, and is primarily populated by the Chukchi people, who use the tundra as pasture for their reindeer herds.

McClintok Island or MacKlintok Island is an island in Franz Josef Land, Russia.
Payer Island is an island in Franz Josef Land, Russia.

The Walrus Islands are a group of craggy coastal islands in the Bering Sea, close to the northern shores of Bristol Bay, Alaska at the entrance to Togiak Bay. They are located 18 km to the east of Hagemeister Island, and are protected as the Walrus Islands State Game Sanctuary by the state. A part of the island group is also of archaeological importance, with numerous deeply stratified sites covering 6,000 years of human use. For this reason, Crooked Island, Summit Island and Round Island were designated the Walrus Islands Archeological District, a National Historic Landmark District comprising 14 historical sites, in December 2016.
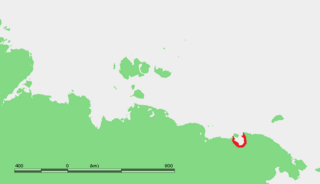
The Routan Islands are two islands in the eastern coast of the Chaunskaya Bay of the East Siberian Sea. They are located directly off Pevek, separated from the shore of the Pevek Peninsula by a 4.7 km wide sound. Ayon Island lies on the other side of the Chaunskaya Bay, 24 km to the west.

Idlidlya Island is a small island in the Chukchi Sea. It is close to the coast, being only 2 km (1.2 mi) away from the shores of the Chukotka Peninsula in the area of the coastal landspits enclosing Neskynpil'gyn Lagoon.

The Shelonsky Islands is an island group in the Laptev Sea. It is located in the coastal lowlands of the Yana Bay, east of the mouths of the Yana river.

Trety Island or Treti Island is a relatively large island in the western shores of the Shelikhov Bay, at the northern end of the Sea of Okhotsk. It is located 4 km to the south of a peninsula that encloses a small bay in an area that is largely uninhabited.
The Saint Lawrence Bay is a bay in the Bering Sea on the eastern coast of the Chukotka Peninsula, Russian Federation.

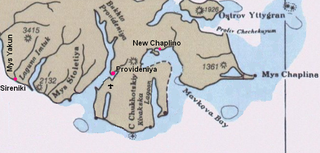
Providensky District is an administrative and municipal district (raion), one of the six in Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia. It is located in the northeast of the autonomous okrug, in the southern half of the Chukchi Peninsula with a northwest extension reaching almost to the Kolyuchinskaya Bay on the Arctic. It borders with Chukotsky District in the north, the Bering Sea in the east and south, and with Iultinsky District in the west. The area of the district is 26,800 square kilometers (10,300 sq mi). Its administrative center is the urban locality of Provideniya. Population: 3,923 (2010 Census); 4,660 (2002 Census); 9,778 (1989 Census). The population of Provideniya accounts for 50.2% of the district's total population.

Ptichy Island is a small island in the Sea of Okhotsk. It lies close to the mainland off the western coast of the Kamchatka Peninsula.

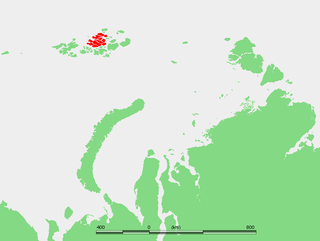
The Geography of Franz Josef Land refers to an island group belonging to Arkhangelsk Oblast of Russia. It is situated in the Barents Sea of the Arctic, north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard. At latitudes between 80.0° and 81.9° north, it is the most northerly group of islands associated with Eurasia. The extreme northernmost point is Cape Fligely on Rudolf Island. The archipelago consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a total area of 16,134 km2 (6,229 sq mi). It is currently uninhabited. The archipelago is only 900 to 1,110 km from the North Pole, and the northernmost islands are closer to the Pole than any other land except for Canada's Ellesmere Island and Greenland. The largest island is Zemlya Georga which measures 110 km (68 mi) from end to end. The highest point in the archipelago is on Ostrov Viner-Neyshtadt which reaches 620 m (2,034 ft) above sea level. The central cluster of large islands in the midst of the archipelago forms a compact whole, known as Zichy Land, where islands are separated from each other by very narrow sounds that are frozen most of the year.

Sam Ford Fiord is an isolated, elongated Arctic fjord on Baffin Island's northeastern coast in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. The Inuit settlement of Pond Inlet is 320 km (200 mi) to the northwest and Clyde River is 80 km (50 mi) to the east.