
Aleutians West Census Area is a census area located in the U.S. state of Alaska. As of the 2010 census, the population was 5,561. It is part of the Unorganized Borough and therefore has no borough seat. Its largest city is Unalaska. It contains most of the Aleutian Islands, from Attu Island in the west to Unalaska Island in the east, as well as the Pribilof Islands, which lie north of the Aleutians in the Bering Sea.

Atka is a small city located on the east side of Atka Island, in Aleutians West Census Area, Alaska, United States. The population was 61 at the 2010 census, down from 92 in 2000.

Umnak is one of the Fox Islands of the Aleutian Islands. With 686.01 square miles (1,776.76 km2) of land area, it is the third largest island in the Aleutian archipelago and the 19th largest island in the United States. The island is home to a large volcanic caldera on Mount Okmok and the only field of geysers in Alaska. It is separated from Unalaska Island by Umnak Pass. In 2000, Umnak was permanently inhabited by only 39 people.

Atka Island is the largest island in the Andreanof Islands of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. The island is 50 miles (80 km) east of Adak Island. It is 65 miles (105 km) long and 2–20 miles (3–30 km) wide with a land area of 404.6 square miles (1,048 km2), making it the 22nd largest island in the United States. The northeast of Atka Island contains the Korovin volcano which reaches a peak of 5,030 feet (1,533 m). Oglodak Island is located 3.4 miles off Cape Kigun, Atka's westernmost point.
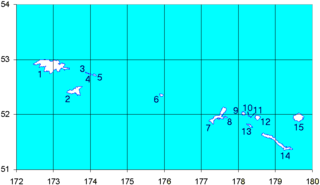
Shemya or Simiya is a small island in the Semichi Islands group of the Near Islands chain in the Aleutian Islands archipelago southwest of Alaska, at 52°43′27″N174°07′08″E. It has a land area of 5.903 sq mi (15.29 km2), and is about 1,200 miles (1,900 km) southwest of Anchorage, Alaska. It is 2.73 miles (4.39 km) wide and 4.32 miles (6.95 km) long.

The Delarof Islands are a group of small islands at the extreme western end of the Andreanof Islands group in the central Aleutian Islands, Alaska. The Delarofs consist of 11 named islands: Amatignak, Gareloi, Ilak, Kavalga (Qavalĝa), Ogliuga (Aglaga), Skagul (Sxaĝulax̂), the Tags (Tagachaluĝis), Tanadak (Tanaadax̂), Ugidak (Qagan-tanax̂), Ulak, and Unalga (Unalĝa).

Derbin Island is located in the Krenitzin Islands, a subgroup of the Fox Islands in the eastern Aleutian Islands, Alaska, United States. Derbin is a small island and is situated near the southwestern shore of Tigalda Island. It is measuring 840 metres (0.52 mi) long and 204 metres (0.127 mi) wide. It was named in 1935 by the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey because of its proximity to Derbin Strait, the channel between Avatanak and Tigalda islands. Derbin Strait, in turn, is derived from "Derbenskoy," the Russian name published by Father Veniaminov (1840).

Pancake Rock is an island in the Fox Islands group in the eastern Aleutian Islands, Alaska. It is approximately 2,000 feet (610 m) across and is located about 1.9 miles (3.1 km) off the west coast of Umnak Island. The island measuring 1.48 kilometres (0.92 mi) long and 2.06 kilometres (1.28 mi) wide.

Poa Island is an islet located about 0.99 miles (1.59 km) off the south coast of Akun Island in the Fox Islands group of the eastern Aleutian Islands, Alaska. The island is 0.62 miles (1.00 km) long and reaches a maximum elevation of about 200 feet (61 m) above sea level. It was named for a genus of grasses in 1888 by the U.S. Bureau of Fisheries. Captain Tebenkov (1852) called it "Ostrov Tumannyi," meaning "foggy island."

Amlia is an island in the Aleutian Islands. It is located near the eastern end of the Andreanof Islands and is situated between Atka Island and Seguam Island.

Islands of Four Mountains is an island grouping of the Aleutian Islands in Alaska, United States. The chain includes, from west to east, Amukta, Chagulak, Yunaska, Herbert, Carlisle, Chuginadak, Uliaga, and Kagamil islands. This island chain is located between Amukta Pass and the Andreanof Islands to the west, and Samalga Pass and the Fox Islands to the east. These islands have a total land area of 210.656 sq mi (545.596 km²) and have no permanent population. The two largest islands are Yunaska and Chuginadak. Chuginadak is mainly made up of the active volcano Mount Cleveland.

Egg Island is a small island in the Fox Islands subgroup of the Aleutian Islands in the U.S. state of Alaska. It lies off the eastern end of Unalaska Island and just off the northeastern tip of Sedanka Island. It is the easternmost island in the Aleutians West Census Area of Alaska. The island has a land area of 311.12 acres (1.259 km²) and is uninhabited. It is 19.3 kilometres (12.0 mi) long and 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) wide.

Rootok Island (also called Aektok, Aiaktak, Ouektock, Aiaiepta, Veniaminof, or Goloi is the smallest member of the Krenitzin Islands, a subgroup of the Fox Islands in the eastern Aleutian Islands in Alaska, United States. The island's common spelling of Rooktok appears to have arisen from Aektok. Deviations in compass readings of up to 3 degrees from normal have been observed off the island's north-western side. The island was set aside to house a lighthouse on January 4, 1901; though no navigation aids were ever constructed. The island is uninhabited and it is 6.3 kilometres long and 6.2 kilometres wide.

Adugak Island is a small island in the Fox Islands group in the Aleutian Islands of southwestern Alaska. It is about 1.2 miles (2 km) long and is located 5.0 miles (8 km) off the northwest coast of Umnak Island. The island has been protected as a rookery for the endangered Steller sea lion, which has been observed during the winter feeding on the fish that inhabit the water nearby. The island reaches an elevation of about 102 feet (31 m) above sea level and the area around the island is extremely hazardous to ships because of the numerous rocks that lie just below the surface of the water.

Aziak Island is a small island in the Andreanof Islands group in the Aleutian Islands of southwestern Alaska. The name "Aziak" is derived from the Aleut word ha-azax - "ten," and in many books and charts published before 1920, it was often used to refer to Sledge Island, located 930 miles (1,500 km) to the northeast off the Seward Peninsula, or to a native settlement on that island. This practice apparently became rarer as the twentieth century progressed and today Aziak is used almost exclusively to refer the Andreanof-group island. Aziak Island is approximately 1.1 miles (1.8 km) long and reaches a maximum elevation of 190 feet (58 m). Very little is known about the island and it is uninhabited.

Anangula Island is a small island in the Fox Islands group of the Aleutian Islands of southwestern Alaska. The 1.4-mile (2.3 km)-long island is separated from Umnak Island by a channel about 0.93 miles (1.50 km) wide and consists of a mostly barren tundra landscape of volcanic ash.

Akutan Island is an island in the Fox Islands group of the eastern Aleutian Islands in the Aleutians East Borough of Alaska.
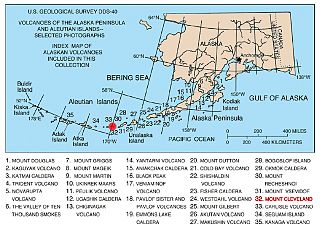
The Aleutian Arc is a large volcanic arc in the U.S. state of Alaska. It consists of a number of active and dormant volcanoes that have formed as a result of subduction along the Aleutian Trench. Although taking its name from the Aleutian Islands, this term is a geologic grouping rather than a geographic one, and the Aleutian Arc extends through the Alaska Peninsula following the Aleutian Range to the Aleutian Islands.









