The History of Pakistan prior to its independence in 1947 spans several millennia and covers a vast geographical area known as the Greater Indus region. Anatomically modern humans arrived in what is now Pakistan between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Stone tools, dating as far back as 2.1 million years, have been discovered in the Soan Valley of northern Pakistan, indicating early hominid activity in the region. The earliest known human remains in Pakistan are dated between 5000 BCE and 3000 BCE. By around 7000 BCE, early human settlements began to emerge in Pakistan, leading to the development of urban centres such as Mehrgarh, one of the oldest in human history. By 4500 BCE, the Indus Valley Civilization evolved, which flourished between 2500 BCE and 1900 BCE along the Indus River. The region that now constitutes Pakistan served both as the cradle of a major ancient civilization and as a strategic gateway connecting South Asia with Central Asia and the Near East.

Sind was a province of British India from 1 April 1936 to 1947 and Dominion of Pakistan from 14 August 1947 to 14 October 1955. Under the British, it encompassed the current territorial limits excluding the princely state of Khairpur. Its capital was Karachi. After Pakistan's creation, the province lost the city of Karachi, as it became the capital of the newly created country. It became part of West Pakistan upon the creation of the One Unit Scheme.

Lahore is the capital and largest city of the Pakistani province of Punjab. It is the second largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and 26th largest in the world, with a population of over 13 million. Located in central-eastern Punjab, along the River Ravi, it is the largest Punjabi-speaking city in the world. Lahore is one of Pakistan's major industrial, educational and economic hubs. It has been the historic capital and cultural centre of the wider Punjab region, and is one of Pakistan's most socially liberal, progressive, and cosmopolitan cities.

Multan is a city in Punjab, Pakistan, located on the bank of river Chenab. It is one of the five largest urban centres of Pakistan in 2024 and is the administrative centre of Multan Division. It is a major cultural, religious and economic centre of Punjab region, Multan is one of the oldest cities of Asia with a history stretching deep into antiquity.

Mughal architecture is the type of Indo-Islamic architecture developed by the Mughals in the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries throughout the ever-changing extent of their empire in the Indian subcontinent. It developed from the architectural styles of earlier Muslim dynasties in India and from Iranian and Central Asian architectural traditions, particularly Timurid architecture. It also further incorporated and syncretized influences from wider Indian architecture, especially during the reign of Akbar. Mughal buildings have a uniform pattern of structure and character, including large bulbous domes, slender minarets at the corners, massive halls, large vaulted gateways, and delicate ornamentation; examples of the style can be found in modern-day Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India and Pakistan.

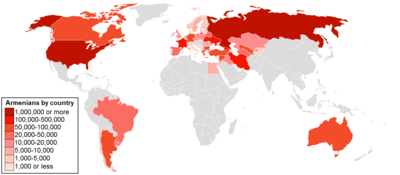
The association of Armenians with India and the presence of Armenians in India are very old, and there has been a mutual economic and cultural association of Armenians with India. Today there are about a hundred, most of whom currently live in or around Kolkata.

The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods:

Mujra is a dance performance by man/woman in a format that emerged during Mughal rule in India, where the elite class and local rulers like the nawabs of the Indian society used to frequent tawaifs (courtesans) for their entertainment.

Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, popularly known as Akbar the Great, and also as Akbar I, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expand and consolidate Mughal domains in the Indian subcontinent. He is generally considered one of the greatest emperors in Indian history and led a successful campaign to unify the various kingdoms of Hindūstān or India proper.
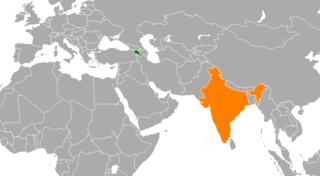
International relations between Armenia and India have been described as friendly. The two countries share a strong burgeoning relationship in economics, culture, military and technology. In 2022, it was reported that the two nations were exploring possibilities of long-term military cooperation. Armenia has an embassy in New Delhi. India has an embassy in Yerevan.

The Mughal Empire was an early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of present-day Assam and Bangladesh in the east, and the uplands of the Deccan Plateau in South India.

Christians form 0.7% of the total population numbering around 120,000 in Punjab, India as per as the 2021 census. Many converts to Christianity keep their original identity to exploit the benefits of reservation. John Lowrie and William Reed were missionaries who went there in 1834. The Diocese of Amritsar of the Church of North India has its seat in Punjab as does the Roman Catholic diocese of Jalandhar. There are thousands of settlements with a Christian congregation.From 2018 to 2024 the Christian population of the Punjab,India decreased by 44%.
Christianity is the second-largest religion in Punjab Province of Pakistan comprising 1.9% of its population. Most Christians (81%) of Pakistan live in Punjab province. There are 2,458,924 Christians in Punjab province as of 2023, up from 1,699,843 in 1998.
The siege of Kandahar lasted from November 1605 to January 1606 and was led by Safavids to capture the Mughal frontier city of Kandahar. After two months of constant assaults, the relief army forced the Persians to retreat. Thus, resulted in a decisive victory for the Mughal Empire.
Mirza Zulqarnain or Mirza Zul-Qarnain was a diwan and faujdar of Armenian descent in the court of the Mughal Empire.

Punjabi Christians are adherents of Christianity who identify ethnically, linguistically, culturally, and genealogically as Punjabis. They are mainly found in the Pakistani province of Punjab, forming the largest religious minority. They are one of the four main ethnoreligious communities of the Punjab region with the others being Muslims, Sikhs and Hindus. Punjabi Christians are traditionally divided into various castes, and are largely descendants of Hindus who converted to Christianity during the British Raj in colonial India.

The Subah of Lahore was one of the three subahs (provinces) of the Mughal Empire in the Punjab region, alongside Multan and Delhi subahs, encompassing the northern, central and eastern Punjab. It was created as one of the original 12 Subahs of the Mughal Empire under the administrative reforms carried by Akbar in 1580. The province ceased to exist after the death of its last viceroy, Adina Beg in 1758, with large parts being incorporated into Durrani Empire. Collectively, Lahore and Multan subahs, and parts of Delhi subah, comprised Mughal Punjab.

The Subah of Multan was one of the three subahs (provinces) of the Mughal Empire in the Punjab region, alongside Lahore and Delhi subahs. It was also amongst the original twelve Mughal provinces, encompassing southern parts of Punjab, stretching towards parts of the regions of Pashtunistan and Balochistan, bordering Kandahar Province and the Persian Safavid Empire. It was one of the largest and most important provinces of the Mughal Empire.

The foreign relations of the Mughal Empire were characterized by competition with the Persian Empire to the west, the Marathas and others to the south, and the British to the east. Steps were taken by successive Mughal rulers to secure the western frontiers of India. The Khyber Pass along the Kabul- Qandahar route was the natural defence for India, and their foreign policy revolved around securing these outposts, as also balancing the rise of powerful empires in the region.