
Phyllota is an Australian genus from the family Fabaceae, a biological grouping of flowering plants.

Dioscorea villosa is a species of twining tuberous vine which is native to eastern North America. It is commonly known as wild yam, colic root, rheumatism root, devil's bones, and fourleaf yam,. It is common and widespread in a range stretching from Texas and Florida north to Minnesota, Ontario and Massachusetts.

Armeria is a genus of flowering plants. These plants are sometimes known as "lady's cushion", "thrift", or "sea pink". The genus counts over a hundred species, mostly native to the Mediterranean, although Armeria maritima is an exception, being distributed along the coasts of the Northern Hemisphere, including Ireland, parts of the United Kingdom such as Cornwall, and the Pembrokeshire Coast National Park in Wales.

Nepenthes villosa, or the villose pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Mount Kinabalu and neighbouring Mount Tambuyukon in northeastern Borneo. It grows at higher elevations than any other Bornean Nepenthes species, occurring at elevations of over 3,200 m (10,500 ft). Nepenthes villosa is characterised by its highly developed and intricate peristome, which distinguishes it from the closely related N. edwardsiana and N. macrophylla.

Nepenthes × kinabaluensis, or the Kinabalu pitcher-plant, is the natural hybrid between N. rajah and N. villosa. It was first collected near Kambarangoh on Mount Kinabalu, Borneo by Lilian Gibbs in 1910 and later mentioned by John Muirhead Macfarlane as "Nepenthes sp." in 1914. Although Macfarlane did not formally name the plant, he noted that "[a]ll available morphological details suggest that this is a hybrid between N. villosa and N. rajah". It was finally described in 1976 by Shigeo Kurata as N. × kinabaluensis. The name was first published in Nepenthes of Mount Kinabalu, but was a nomen nudum at the time as it lacked an adequate description and information on the type specimen. The name was subsequently published validly by Kurata in 1984.

Nepenthes edwardsiana, or the splendid pitcher-plant, is a carnivorous tropical pitcher plant endemic to Mount Kinabalu and neighbouring Mount Tambuyukon in Sabah, Malaysian Borneo. It is considered one of the most spectacular of all Nepenthes, producing some of the largest pitchers and the most highly developed peristome ribs of any species in the genus.

Vicia villosa, known as the hairy vetch, fodder vetch or winter vetch, is a plant native to some of Europe and western Asia. It is a legume, grown as a forage crop, fodder crop, cover crop, and green manure. Although non-native, it occurs in all US states and is considered invasive by some states, such as Alaska, Florida, Georgia, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Oregon, and Washington state — as well as in Japan and some parts of Europe where it is not native. It is also found in most Canadian provinces.

Nepenthes × harryana is the natural hybrid between N. edwardsiana and N. villosa. Its two parent species are very closely related and so N. × harryana, which is intermediate in form, may be difficult to distinguish from either of them.

Ulmus villosa, the cherry-bark elm or Marn elm, is one of the more distinctive Asiatic elms, and a species capable of remarkable longevity. It is endemic to the valleys of the Kashmir at elevations of 1200–2500 m but has become increasingly rare owing to its popularity as cattle fodder, and mature trees are now largely restricted to temples and shrines where they are treated as sacred. Some of these trees are believed to be aged over 800 years.

Monardella villosa is a plant in the mint family which is known by the common name coyote mint.

Gentiana villosa, the striped gentian, is a herbaceous perennial plant belonging to the genus Gentiana. It is found mainly in the Eastern United States and is used medicinally by Native American tribes.

Thapsia villosa, commonly known as the villous deadly carrot, is a species of poisonous herbaceous plants in the genus Thapsia. It grows to about 70 to 190 cm in height. It has pinnate hairy leaves with sheath-like petioles. The flowers are yellow in color and borne on compound umbels. They develop into fruits with four wings characteristic of the genus. It is native to southwestern Europe and northwestern Africa surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. The plant was used extensively for traditional medicine since around the 3rd century BC.

Heterotheca villosa, called the hairy goldenaster, is a North American species of flowering plant in the aster family. It widespread across the central and western parts of the continent, from Ontario west to British Columbia and south as far as Illinois, Kansas, Nuevo León, Guanajuato, and northern Baja California.

Chrysothemis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Gesneriaceae.
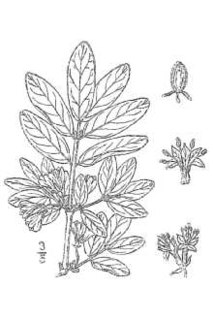
Lonicera villosa, also known as mountain fly honeysuckle, is a species of honeysuckle native to North America.

Serruria villosa, the golden spiderhead, is a flower-bearing shrub that belongs to the genus Serruria and forms part of the fynbos. The plant is native to the Western Cape, where it occurs only on the Cape Peninsula and just south of Constantia. The shrub is erect and grows only 50 cm tall and bears flowers from April to July.

Babiana villosa is a species of geophyte of 10–20 cm (3.9–7.9 in) high that is assigned to the family Iridaceae. It has mauve-pink, purple or scarlet star-symmetrical wide chalice-shaped flowers with narrow tube, large, blackish or dark purple anthers, and velvety hairy, lance-shaped, laterally compressed leaves, set in a fan. Flowers occur during August and September. Its grows between Malmesbury and Wellington in the Western Cape province of South Africa. It is commonly called red babiana in English and rooibobbejaantjie in Afrikaans.

Athroismeae is a tribe of flowering plants in the subfamily Asteroideae of the family Asteraceae.

















