
Beer is a relatively small lunar impact crater located on the Mare Imbrium, to the east of the crater Timocharis. It was named after German astronomer Wilhelm W. Beer. Just to the northwest is the matching twin Feuillée.

Sampson is a relatively tiny lunar impact crater located near the central part of the Mare Imbrium. It was named after British astronomer Ralph Allan Sampson. To the northeast is the crater Landsteiner and to the southeast lies Timocharis. East of this crater is the Dorsum Grabau, a wrinkle ridge in the mare.

Wallach is a tiny lunar impact crater located in the eastern Mare Tranquillitatis. It was named after German chemist and Nobel laureate Otto Wallach. It is a circular, bowl-shaped feature with a negligible interior floor; the inner walls just slope down to the midpoint of the crater. Wallach is located to the northeast of the crater Maskelyne, near some low ridges in the lunar mare. It was previously identified as Maskelyne H before being given a name by the IAU.

Deseilligny is a small lunar impact crater in the southern part of the Mare Serenitatis. It was named after French selenographer Jules Deseilligny. It is located to the east-southeast of the crater Bessel. Deseilligny is a bowl-shaped crater with a low rim. It is otherwise undistinguished.

Abbot is a small lunar impact crater that lies on the rugged ground between the Mare Fecunditatis in the south and west, and the Mare Crisium to the north. It is a circular crater with a cup-shaped interior. The inner walls slope downward to the midpoint, and no impacts of significant mark the interior or the rim.

Beketov is a small lunar impact crater that lies in the northern reaches of the Mare Tranquillitatis. It is named after Russian chemist Nikolay Beketov. To the south is the ghost crater Jansen R. Northeast of Beketov, along the edge of the mare, is the crater Vitruvius. Beketov was previously designated Jansen C before being named by the IAU. The flooded crater Jansen itself lies to the south.

Crile is a tiny lunar impact crater. It is roughly circular and cup-shaped, with interior walls that slope down to the midpoint. The crater lies in the Palus Somni, between the Mare Crisium to the east and Mare Tranquillitatis to the west.

Curtis is a very small lunar impact crater that lies in the western Mare Crisium, to the east of the crater Picard. It is a circular, cup-shaped formation that is otherwise undistinguished. It was named after American astronomer Heber D. Curtis in 1973. In the past it was designated Picard Z.

Auzout is a lunar impact crater that is located to the southeast of the Mare Crisium, near the eastern limb of the Moon. It is named after French astronomer Adrien Auzout."Auzout (crater)". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program. Attached to the southern rim is the smaller crater van Albada. To the east-northeast is the large Condorcet. This crater is not especially notable, although it does possess a central mountain. This crater is designated 'Azout' in some sources.

Bonpland is the remains of a lunar impact crater that is attached to the walled plain Fra Mauro to the north and Parry to the east. The intersection of their rims forms a three-pointed mountainous rise. To the southeast is the small crater Tolansky. Bonpland lies on the eastern edge of Mare Cognitum. It is named after Aimé Bonpland, a French explorer and botanist.
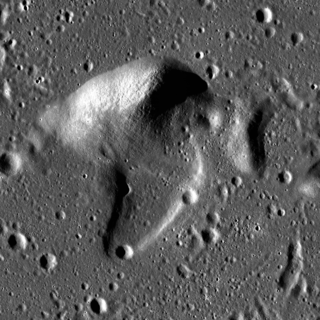
Fedorov is a lunar geologic feature located in the western Mare Imbrium. It was named after Russian rocket scientist A. P. Fyodorov. It lies east-northeast of the crater Diophantus, and southeast of Delisle. About 20 kilometers to the south-southeast is the slightly larger formation of Artsimovich.

Maskelyne is a solitary lunar impact crater that lies in the southeast part of the Mare Tranquillitatis. Its diameter is 22 km. It was named after British astronomer Nevil Maskelyne. The outer rim has a somewhat polygonal shape, although it is generally circular. The inner walls are terraced and there is a low central rise at the midpoint of the floor.

Atwood is a small lunar impact crater that is located on the Mare Fecunditatis, to the northwest of the prominent crater Langrenus. It forms a triple-crater formation with Naonobu attached to the north rim and Bilharz near the west rim.

Sinas is a small lunar impact crater that lies in the eastern part of the Moon on the Mare Tranquillitatis. Its diameter is 12 km. It was named after the Greek magnate Simon Sinas. This is an isolated formation that is located very near the midpoint of the lunar mare. Sinas is circular and bowl-shaped, with a small floor at the midpoint. A wrinkle ridge intersects the east edge of the crater, and several lunar domes lie to the north.

Condorcet is a lunar impact crater that is located in the eastern part of the Moon's near side, to the southeast of the Mare Crisium. It was named after French mathematician Marquis de Condorcet. To the northeast of Condorcet are the craters Hansen and Alhazen.
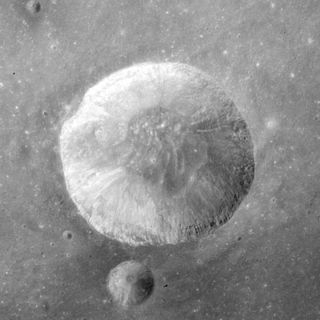
Carmichael is a lunar impact crater that is located along the eastern edge of the Sinus Amoris, in the northeastern quadrant of the Moon's near side. Its diameter is 20 km. It was named after American psychologist Leonard Carmichael. It lies within a couple of crater diameters south-southwest of the smaller crater Hill. Further to the east-northeast is the prominent crater Macrobius. Carmichael was designated Macrobius A before being given its current name by the IAU.

Glaisher is a lunar impact crater that is located in the region of terrain that forms the southwest border of Mare Crisium. It lies to the southwest of the lava-flooded crater Yerkes, and west-northwest of the Greaves–Lick crater pair. It is surrounded by a ring of satellite craters of various dimensions, the larger companions generally being arranged to the south of Glaisher.

Feuillée is a small lunar impact crater in the eastern part of the Mare Imbrium. It was named after French natural scientist Louis Feuillée. It lies less than a half crater diameter to the northwest of Beer, and the two formations form a nearly matched pair. To the west is the small but prominent crater Timocharis.

Fabbroni is a small lunar impact crater that lies along the northern edge of the Mare Tranquillitatis, at the eastern edge of the gap where the lunar mare joins Mare Serenitatis to the north. To the southeast is the crater Vitruvius.

Mons Vinogradov is a rugged massif that is located on the lunar mare where Oceanus Procellarum to the southwest joins Mare Imbrium to the east. There are three primary peaks in this formation, which rise to altitudes of 1.0–1.4 km above the surface. To the east of this rise is the crater Euler, and to the southeast is an area of rugged ground that reaches the Montes Carpatus range. The Carpatus mountain range forms the southwest boundary of the Mare Imbrium.


























