| Aspartate dehydrogenase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 1.4.1.21 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 37278-97-0 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
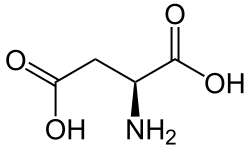
Aspartate dehydrogenase (EC 1.4.1.21) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The three substrates of this enzyme are L-aspartic acid, water, and oxidised nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+}. Its products are oxaloacetic acid, ammonia, reduced NADH, and a proton. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate can be used as an alternative cofactor. [1] [2] [3]
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the CH-NH2 group of donors with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is L-aspartate:NAD(P)+ oxidoreductase (deaminating). Other names in common use include NAD-dependent aspartate dehydrogenase, NADH2-dependent aspartate dehydrogenase, and NADP+-dependent aspartate dehydrogenase. This enzyme participates in nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism. [4]