
In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a P–O–P linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate (Na2H2P2O7) and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7), among others. Often pyrophosphates are called diphosphates. The parent pyrophosphates are derived from partial or complete neutralization of pyrophosphoric acid. The pyrophosphate bond is also sometimes referred to as a phosphoanhydride bond, a naming convention which emphasizes the loss of water that occurs when two phosphates form a new P–O–P bond, and which mirrors the nomenclature for anhydrides of carboxylic acids. Pyrophosphates are found in ATP and other nucleotide triphosphates, which are important in biochemistry. The term pyrophosphate is also the name of esters formed by the condensation of a phosphorylated biological compound with inorganic phosphate, as for dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. This bond is also referred to as a high-energy phosphate bond.

Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate is an isoprenoid precursor. It is a product of both the mevalonate pathway and the MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. It is an isomer of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and exists in virtually all life forms. The enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase catalyzes isomerization between DMAPP and IPP.

Isopentenyl pyrophosphate is an isoprenoid precursor. IPP is an intermediate in the classical, HMG-CoA reductase pathway and in the non-mevalonate MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. Isoprenoid precursors such as IPP, and its isomer DMAPP, are used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids.
Farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), also known as farnesyl diphosphate (FDP), is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids such as sterols and carotenoids. It is also used in the synthesis of CoQ, as well as dehydrodolichol diphosphate.
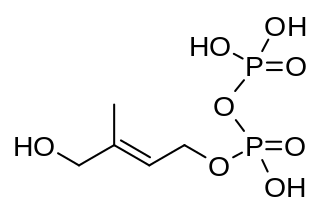
(E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (HMBPP or HMB-PP) is an intermediate of the MEP pathway (non-mevalonate pathway) of isoprenoid biosynthesis. The enzyme HMB-PP synthase (GcpE, IspG) catalyzes the conversion of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) into HMB-PP. HMB-PP is then converted further to isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) by HMB-PP reductase (LytB, IspH).

Isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase, also known as Isopentenyl-diphosphate delta isomerase, is an isomerase that catalyzes the conversion of the relatively un-reactive isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) to the more-reactive electrophile dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP). This isomerization is a key step in the biosynthesis of isoprenoids through the mevalonate pathway and the MEP pathway.
In enzymology, an adenylate dimethylallyltransferase (EC 2.5.1.27) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a chrysanthemyl diphosphate synthase is an enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of terpenoids. This enzyme is also known as CPPase. It catalyzes the chemical reaction shown below :
In enzymology, a farnesyltranstransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a geranyltranstransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a lavandulyl diphosphate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a naringenin 8-dimethylallyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tryptophan dimethylallyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
4-Hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate reductase (EC 1.17.1.2, isopentenyl-diphosphate:NADP+ oxidoreductase, LytB, (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate reductase, HMBPP reductase, IspH, LytB/IspH) is an enzyme in the non-mevalonate pathway. It acts upon (E)-4-Hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (or "HMB-PP").
Trihydroxypterocarpan dimethylallyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name dimethylallyl-diphosphate:(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan dimethylallyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Leachianone-G 2''-dimethylallyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name dimethylallyl-diphosphate:leachianone-G 2''-dimethylallyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
TRNA dimethylallyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name dimethylallyl-diphosphate: tRNA dimethylallyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
7-dimethylallyltryptophan synthase is an enzyme with systematic name dimethylallyl-diphosphate:L-tryptophan 7-dimethylallyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
(2Z,6Z)-farnesyl diphosphate synthase is an enzyme with systematic name dimethylallyl-diphosphate:isopentenyl-diphosphate cistransferase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Fumigaclavine A dimethylallyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name dimethylallyl-diphosphate:fumigaclavine A dimethylallyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction






