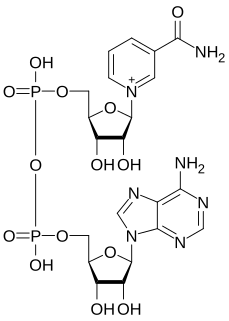
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively.

In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a redox-active coenzyme associated with various proteins, which is involved with several enzymatic reactions in metabolism. A flavoprotein is a protein that contains a flavin group, which may be in the form of FAD or flavin mononucleotide (FMN). Many flavoproteins are known: components of the succinate dehydrogenase complex, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, and a component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
Shikimic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form shikimate, is a cyclohexene, a cyclitol and a cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. It is an important biochemical metabolite in plants and microorganisms. Its name comes from the Japanese flower shikimi, from which it was first isolated in 1885 by Johan Fredrik Eykman. The elucidation of its structure was made nearly 50 years later.

Guanosine monophosphate synthetase, also known as GMPS is an enzyme that converts xanthosine monophosphate to guanosine monophosphate.

NAD+ kinase (EC 2.7.1.23, NADK) is an enzyme that converts nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) into NADP+ through phosphorylating the NAD+ coenzyme. NADP+ is an essential coenzyme that is reduced to NADPH primarily by the pentose phosphate pathway to provide reducing power in biosynthetic processes such as fatty acid biosynthesis and nucleotide synthesis. The structure of the NADK from the archaean Archaeoglobus fulgidus has been determined.

Malate dehydrogenase (oxaloacetate-decarboxylating) (NADP+) (EC 1.1.1.40) or NADP-malic enzyme (NADP-ME) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction in the presence of a bivalent metal ion:

In enzymology, a glutamate synthase (NADPH) (EC 1.4.1.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) (EC 1.6.5.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NADPH—hemoprotein reductase (EC 1.6.2.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Sulfite reductases (EC 1.8.99.1) are enzymes that participate in sulfur metabolism. They catalyze the reduction of sulfite to hydrogen sulfide and water. Electrons for the reaction are provided by a dissociable molecule of either NADPH, bound flavins, or ferredoxins.
Sulfite reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.8.1.2, sulfite (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) reductase, NADPH-sulfite reductase, NADPH-dependent sulfite reductase, H2S-NADP oxidoreductase, sulfite reductase (NADPH2)) is an enzyme with systematic name hydrogen-sulfide:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalises the following chemical reaction

The enzyme 3-dehydroquinate synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a NAD+ glycohydrolase (EC 3.2.2.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a cystathionine gamma-synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of cystathionine from cysteine and an activated derivative of homoserine, e.g.:
Phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase (CDS) is the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of CDP-diacylglycerol from cytidine triphosphate and phosphatidate.

Aldo-keto reductase family 1, member B1 (AKR1B1), also known as aldose reductase, is an enzyme that is encoded by the AKR1B1 gene in humans. It is a reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-dependent enzyme catalyzing the reduction of various aldehydes and ketones to the corresponding alcohol. The involvement of AKR1B1 in oxidative stress diseases, cell signal transduction, and cell proliferation process endows AKR1B1 with potential as a therapeutic target.
5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase is an enzyme produced by plants and microorganisms. EPSPS catalyzes the chemical reaction:

3-Deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonic acid 7-phosphate (DAHP) is a 7-carbon ulonic acid. This compound is found in the shikimic acid biosynthesis pathway and is an intermediate in the production of aromatic amino acids.
Edith Wilson Miles is a biochemist known for her work on the structure and function of enzymes, especially her work on tryptophan synthase.

Bettie Sue Siler Masters is an adjunct professor at Duke University known for her work on nitric oxide synthase and cytochrome P450 reductase. She was the 1992 recipient of the FASEB Excellence in Science Award, and has been elected to the National Academy of Medicine and the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
















