
Astragalus is a large genus of over 3,000 species of herbs and small shrubs, belonging to the legume family Fabaceae and the subfamily Faboideae. It is the largest genus of plants in terms of described species. The genus is native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Common names include milkvetch, locoweed and goat's-thorn. Some pale-flowered vetches are similar in appearance, but they are more vine-like than Astragalus.

A calcareous glade is a type of ecological community that is found in the central Eastern United States. Calcareous glades occur where bedrock such as limestone occurs near or at the surface, and have very shallow and little soil development. Due to the shallow soil and the extreme conditions created by it, trees are often unable to grow in the glades. This creates a habitat that is usually sunny, dry, and hot. Calcareous glade vegetation is more similar to that of a desert habitat than a grassland, being dominated by small spring annuals with occasional geophytic or succulent perennials.

Echinacea tennesseensis, also known as the Tennessee coneflower or Tennessee purple coneflower, is a flowering plant in the family Asteraceae, endemic to the cedar glades of the central portion of the U.S. state of Tennessee.

Astragalus lentiginosus Astragalus lentiginosus is a species of legume native to western North America where it grows in a range of habitats. Common names include spotted locoweed and freckled milkvetch. There are a great number of wild varieties. The flower and the fruit of an individual plant are generally needed to identify the specific variety.
Astragalus anxius is a rare species of milkvetch known by the common names troubled milkvetch and Ash Valley milkvetch. It is endemic to northern Lassen County, California, where it is critically imperiled. It was formally described in 1992.

Astragalus ertterae is a rare species of milkvetch known by the common name Walker Pass milkvetch. It is endemic to California, where it is known from only three occurrences near Walker Pass in the Sierra Nevada. It is endangered by trampling, trail use, and also grazing.

Astragalus kentrophyta is a species of milkvetch known by the common name spiny milkvetch. It is native to western North America from central to west Canada, to California, to New Mexico. It grows in rocky mountainous areas, such as the Sierra Nevada, and on plateaus.
Astragalus lentiginosus var. pseudiodanthus, synonym Astragalus pseudiodanthus, is a variety of the species Astragalus lentiginosus, a milkvetch. It is known by the common name Tonopah milkvetch. It is native to the Great Basin deserts of Nevada and eastern California, such as the Tonopah area, where it grows in sandy habitat.

Dalea foliosa, commonly called leafy prairie clover, is a species of flowering plant in the legume family (Fabaceae). It is an endangered species in the United States, where it occurs in three states: Illinois, Tennessee, and Alabama.

Astragalus limnocharis var. montii, synonym Astragalus montii, is a rare variety of flowering plant in the legume family. It is known by the common name Monti's milkvetch. It is endemic to Utah in the United States, where there are only three known populations. Under the synonym A. montii, it is a federally listed threatened species of the United States.

Astragalus barrii is a species of flowering plant in the legume family known by the common name Barr's milkvetch. It is native to the United States, where it is a "regional endemic", occurring in parts of southwestern South Dakota, northeastern Wyoming, southeastern Montana, and Nebraska.

Astragalus microcymbus is a species of flowering plant in the legume family known by the common name skiff milkvetch. It is endemic to Colorado in the United States, where it is known from Gunnison County and the edge of Saguache County. It was discovered in 1945 by Rupert Barneby, a British botanist. Currently, skiff milkvetch is experiencing population declines and is listed as a Tier 1 species in the Rare Plant Addendum to the Colorado State Wildlife Action Plan.

Astragalus tennesseensis is a species of flowering plant in the legume family known by the common name Tennessee milkvetch. It is native to the United States, where it is known from Illinois, Indiana, Tennessee and Alabama. Most of the occurrences are in Tennessee.
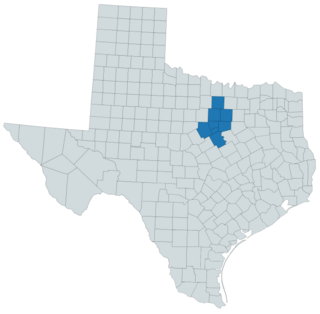
Dalea reverchonii is a species of flowering plant in the legume family known by the common name Comanche Peak prairie-clover. It is endemic to Texas in the United States, where it is known from Bosque, Erath, Hood, Johnson, Parker, Somervell, Tarrant, and Wise counties. This species was first collected by Julien Reverchon at the top of Comanche Peak. As of 2015 the species still grows there.

Astragalus molybdenus is a species of flowering plant in the legume family known by the common names Leadville milkvetch and molybdenum milkvetch. It is endemic to Colorado in the United States. If the separate species Astragalus shultziorum and Astragalus lackschewitzii are included in A. molybdenum the range expands into Wyoming and Montana.

Astragalus lentiginosus var. iodanthus, synonym Astragalus iodanthus, is a variety of Astragalus lentiginosus, a flowering plant in the legume family, Fabaceae. It is known by the common names Humboldt River milkvetch and violet milkvetch. It is native to the western United States, where its range includes California, Idaho, Nevada, Oregon, and Utah. It grows on hills and in valleys in barren sandy and volcanic soils in habitat such as sagebrush.

Leavenworthia crassa is a species of flowering plant in the mustard family, Brassicaceae, known commonly as the fleshy-fruit gladecress. It is endemic to Alabama in the United States, where it occurs in only two counties. It is "likely one of the most imperiled plant species in the Southeast," and the United States Fish and Wildlife Service issued a final rule listing it as an endangered species in 2014.

Astragalus crassicarpus, known as ground plum or buffalo plum, is a perennial species of flowering plant in the legume family, Fabaceae, native to North America. It was described in 1813. The fruit is edible and was used by Native Americans as food and horse medicine. It is a host of afranius duskywing larvae. It is also known as groundplum milkvetch and pomme de prairie.

Astragalus aquilonius, the Lemhi milkvetch, is a species of milkvetch in the family Fabaceae. It is native to Idaho.

Astragalus harbisonii is a species of short-lived perennial plant in the family Fabaceae commonly known as the Punta Baja milkvetch. It is endemic to the Punta Baja peninsula in the Mexican state of Baja California and the immediate surrounding coastline. It is named after Charles F. Harbison, curator of entomology at the San Diego Natural History Museum from 1942 to 1969. This species is characterized by connate stipules and sessile bladdery pods, traits that it shares with Astragalus anemophilus, but the two species can be distinguished by their indumentum and distinct flowers.





















