
The South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) is a 2004 agreement that created a free-trade area of 1.6 billion people in Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka with the vision of increasing economic cooperation and integration.

Bilateral relations exist between Australia and Japan.

New Zealand is party to 14 free trade agreements (FTAs) worldwide. Together they accounted for over 70% of New Zealand's trade in 2023.

According to a 2010 Gallup poll, 40% of Singaporeans approve of India's leadership, with 23% disapproving and 37% uncertain.

Foreign diplomatic relations between Australia and India are well-established, with both nations sharing a "Comprehensive Strategic Partnership" since both were part of the British Empire. Both are members of the Commonwealth of Nations, and share political, economic, security, lingual and sporting ties. Besides strong trading & migration, culture, arts, music, commercial & international sports like cricket, tennis, badminton have emerged as a strong cultural connection between the two nations. Military cooperation between Australia and India includes the regular joint naval exercise AUSINDEX.

The Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) is a free trade agreement between India and South Korea. The agreement was signed on August 7, 2009. The signing ceremony took place in Seoul and the agreement was signed by the Indian Commerce Minister, Anand Sharma and South Korean Commerce Minister, Kim Jong-Hoon. The negotiations took three-and-a-half years, with the first session being held in February 2006. The agreement was passed in the South Korean parliament on 6 November 2009. It was passed in the Indian parliament the next week. Once passed, the agreement came into effect sixty days later, on January 1, 2010. It is equivalent to a free trade agreement. The agreement will provide better access for the Indian service industry in South Korea. Services include Information technology, engineering, finance, and the legal field. South Korean car manufactures will see large tariffs cuts to below 1%. All the while, Korean corporations have flooded India with cheaper imports of raw metal, steel and finished products.
The Comprehensive Economic Partnership for East Asia (CEPEA) is a Japanese led proposal for trade co-operation, free trade agreement, among the 16 present member countries of the East Asia Summit. All those movements and efforts were taken over by the following Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership.
The ASEAN–India Free Trade Area (AIFTA) is a free trade area among the ten member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and the Republic of India. The initial framework agreement was signed on 8 October 2003 in Bali, Indonesia. and the final agreement was on 13 August 2009. The free trade area came into effect on 1 January 2010. India hosted the latest ASEAN-India Commemorative Summit in New Delhi on 26 January 2018. In the financial year 2017–18, Indo-ASEAN bilateral trade grew by almost 14% to reach US$81.3 billion. India's imports from ASEAN were valued at US$47.13 billion while its exports to ASEAN stood at US$34.2 billion.

Relations between the European Union and the Republic of India are currently defined by the 1994 EU–India Cooperation Agreement. The EU is a significant trade partner for India and the two sides have been attempting to negotiate a free trade deal since 2007. Indo-EU bilateral trade stood at US$104.3 billion in the financial year 2018–19.

The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership is a free trade agreement among the Asia-Pacific countries of Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam. The 15 member countries account for about 30% of the world's population and 30% of global GDP, making it the largest trade bloc in history. Signed in November 2020, RCEP is the first free trade agreement among the largest economies in Asia, including China, Indonesia, Japan, and South Korea.

The Korea–Australia Free Trade Agreement (KAFTA) is a bilateral free trade agreement designed to diminish barriers to trade and investment between Australia and South Korea, effective from the 12th December 2014. The agreement confers substantially improved market access for Australian exporters of goods and services, as well as for investors seeking opportunities within the South Korean market. KAFTA builds upon several decades of bilateral relations, rooted in diplomatic, trade, and security cooperation, which have evolved since 1962. During that year, President Park Chung-Hee introduced a series of five-year economic plans aimed at fostering South Korea's industrial development and accelerating its integration into the global economy in the aftermath of the Korean War.
The Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) is a free trade agreement between Singapore and India to strengthen bilateral trade. It was signed on 29 June 2005.
The negotiations for the Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement were held between 12 countries between 2008 and 2015. The negotiations were aimed at obtaining an agreement between the Trans-Pacific Strategic Economic Partnership Agreement parties Brunei, Chile, Singapore and New Zealand, as well as the Australia and the United States.
The Timor-Leste–Indonesia–Australia Growth Triangle (TIA-GT) is a combined initiative of the regions of Eastern Indonesia, Northern Australia, and the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste. This initiative aims to promote and foster economic growth through integrated economic development in the region that these nations reside in. The growth triangle was created in 2012, after a meeting was held by Indonesian president Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono with Prime Minister of Australia Julia Gillard and Timor-Leste Prime Minister Xanana Gusmao. The initiative aims to support economic, social, and cultural development primarily by attracting investment, developing manufacturing industries, enhancing human capital, and overall building a stronger cooperative relationship between the three countries involved. The initiative also aimed to accelerate the accession of Timor-Leste into the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) and to fulfill goals set by Timor-Leste's Strategic Development Plan, such as increasing the nation's economic prosperity and stability. The growth triangle is often misinterpreted as a free-trade zone; however, while there are elements of free trade agreements between Indonesia and Australia specifically, the terms of the growth triangle initiative are not directly linked to these free trade agreements, and the goals of the growth triangle do not specifically encompass free trade between the three nations.

The Indonesia–Australia Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement is a bilateral agreement signed between Australia and Indonesia in March 2019, ratified by Australia in November 2019 and Indonesia in February 2020. The agreement contains a free trade agreement removing tariffs from nearly all products traded between both countries, in addition to loosening investment regulations in Indonesia for Australian firms and increasing the quota for Indonesians seeking vocational training in Australia.
India is party to free trade agreements (FTAs) and other trade agreements with many countries and trade blocs, and is negotiating with many others. As of 2022, India has preferential access, economic cooperation and FTA with more than 50 individual countries.
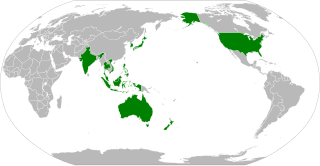
The Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) is an economic initiative launched by U.S. President Joe Biden on May 23, 2022. The framework launched with fourteen participating founding member nations in the Indo-Pacific region with an open invitation for other countries to join.
"Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement" is the first trade agreement between India and Australia. Piyush Goyal Union Minister of Commerce and Industry, Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution and Textiles said while addressing a press conference on the ECTA. Australia has approved the trade pact between these two countries in its Parliament.

Australia is party to 18 free trade agreements (FTAs) worldwide covering 30 economies.












