
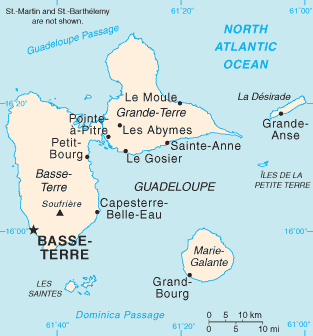
Basse-Terre is a commune in the French overseas department of Guadeloupe, in the Lesser Antilles. It is also the prefecture of Guadeloupe. The city of Basse-Terre is located on Basse-Terre Island, the western half of Guadeloupe.

Baie-Mahault is a commune in the overseas department and region of Guadeloupe, France. It is the second most populated commune of Guadeloupe, after Les Abymes. The extensive industrial zone of Jarry in Baie-Mahault is by far the most industrialized commune in the islands and the largest industrial park in the Lesser Antilles. It is part of the urban area of Pointe-à-Pitre, the largest metropolitan area in Guadeloupe, located in the northwest.

Bouillante is a commune in the French overseas region and department of Guadeloupe, in the Lesser Antilles.

Capesterre-Belle-Eau is a commune in the French overseas region and department of Guadeloupe, in the Lesser Antilles. It is located in the south-east of Basse-Terre Island. Capesterre-Belle-Eau covers an area of 103.3 km2. The 1999 population was 19,568. The population density is 189 persons per km2. The inhabitants are called Capesterriens.

Pointe-à-Pitre is the second most populous commune of Guadeloupe. Guadeloupe is an overseas region and department of France located in the Lesser Antilles, of which it is a sous-préfecture, being the seat of the Arrondissement of Pointe-à-Pitre.

The arrondissement of Basse-Terre is an arrondissement of France in the Guadeloupe department in the Guadeloupe region. It has 18 communes. Its population is 189,210 (2016), and its area is 854.3 km2 (329.8 sq mi).

Petit-Bourg is the seventh-largest commune in the French overseas department of Guadeloupe. It is located on the east side of the island of Basse-Terre, and is part of the metropolitan area of Pointe-à-Pitre, the largest metropolitan area in Guadeloupe.

Gourbeyre is a commune in the French overseas region and department of Guadeloupe, in the Lesser Antilles. It is a suburb of the city of Basse-Terre.
The Guadeloupe Division of Honour(French: Guadeloupe Division d'Honneur) is the top football league in Guadeloupe. It was created in 1952 and is headed by the Guadeloupean League of Football. 18 teams participate. The last 3 placed teams are relegated to the Honorary Promotion Championship.

Vieux-Habitants is a commune on Guadeloupe, a French overseas department in the Caribbean. It is located on the southwest coast of the island of Basse-Terre.

Saint-Claude is a commune in the French overseas department of Guadeloupe. It lies in the interior of southern Basse-Terre Island, just northeast of the capital city of Basse-Terre.

Morne-à-l'Eau is a commune located in the department of Guadeloupe.

Sainte-Rose is a commune in the department of Guadeloupe. It is the second largest commune of Guadeloupe, in terms of area, after Petit-Bourg. Sainte-Rose lies on the coast of the island of Basse-Terre.

Terre-de-Haut is a commune in the French overseas department of Guadeloupe, including Terre-de-Haut Island and a few other small uninhabited islands of the archipelago. It is the most populous island of the archipelago of Les Saintes. The Fort Napoléon is located in this commune.

Trois-Rivières is a commune in the overseas department of Guadeloupe, and the chef-lieu of the Canton of Trois-Rivières. It is on the south coast of the island of Basse-Terre. It is surrounded with the towns of Capesterre-Belle-Eau, Vieux-Fort and Gourbeyre.

Vieux-Fort is a commune in the French overseas department of Guadeloupe. It is located on Basse-Terre Island.

The Canton of Vieux-Habitants is a canton in the Arrondissement of Basse-Terre on the island of Guadeloupe.

Articles related to the French overseas department of Guadeloupe include:
The Invasion of Guadeloupe was the last conflict between French and British forces during the Napoleonic Wars and took place after Napoleon's defeat at Waterloo.
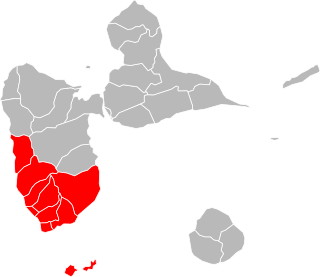
Communauté d'agglomération Grand Sud Caraïbe is a communauté d'agglomération, an intercommunal structure in the Guadeloupe overseas department and region of France. Created in 2011, its seat is in Basse-Terre. Its area is 343.5 km2. Its population was 77,186 in 2019.






















