
A debit card, also known as a check card or bank card, is a payment card that can be used in place of cash to make purchases. The card usually consists of the bank's name, a card number, the cardholder's name, and an expiration date, on either the front or the back. Many new cards now have a chip on them, which allows people to use their card by touch (contactless), or by inserting the card and keying in a PIN as with swiping the magnetic stripe. Debit cards are similar to a credit card, but the money for the purchase must be in the cardholder's bank account at the time of the purchase and is immediately transferred directly from that account to the merchant's account to pay for the purchase.

Electronic Funds Transfer at Point Of Sale, abbreviated as EFTPOS, is the technical term referring to a type of payment transaction where electronic funds transfers (EFT) are processed at a point of sale (POS) system or payment terminal usually via payment methods such as payment cards. EFTPOS technology was developed during the 1980s.
Electronic cash was, until 2007, the debit card system of the German Banking Industry Committee, the association that represents the top German financial interest groups. Usually paired with a transaction account or current account, cards with an Electronic Cash logo were only handed out by proper credit institutions. An electronic card payment was generally made by the card owner entering their PIN at a so-called EFT-POS-terminal (Electronic-Funds-Transfer-Terminal). The name "EC" originally comes from the unified European checking system Eurocheque. Comparable debit card systems are Maestro and Visa Electron. Banks and credit institutions who issued these cards often paired EC debit cards with Maestro functionality. These combined cards, recognizable by an additional Maestro logo, were referred to as "EC/Maestro cards".
A personal identification number is a numeric passcode used in the process of authenticating a user accessing a system.
Bank fraud is the use of potentially illegal means to obtain money, assets, or other property owned or held by a financial institution, or to obtain money from depositors by fraudulently posing as a bank or other financial institution. In many instances, bank fraud is a criminal offence.

Interac is a Canadian interbank network that links financial institutions and other enterprises for the purpose of exchanging electronic financial transactions. Interac serves as the Canadian debit card system and the predominant funds transfer network via its e-Transfer service. There are over 59,000 automated teller machines that can be accessed through the Interac network in Canada, and over 450,000 merchant locations accepting Interac debit payments.

President's Choice Financial, commonly shortened to PC Financial, is the financial service brand of the Canadian supermarket chain Loblaw Companies.

A traveller's cheque is a medium of exchange that can be used in place of hard currency. They can be denominated in one of a number of major world currencies and are preprinted, fixed-amount cheques designed to allow the person signing it to make an unconditional payment to someone else as a result of having paid the issuer for that privilege.

A cheque is a document that orders a bank, building society to pay a specific amount of money from a person's account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued. The person writing the cheque, known as the drawer, has a transaction banking account where the money is held. The drawer writes various details including the monetary amount, date, and a payee on the cheque, and signs it, ordering their bank, known as the drawee, to pay the amount of money stated to the payee.

Visa Debit is a brand of debit card issued by Visa in many countries. Numerous banks and financial institutions issue Visa Debit cards to their customers for access to their bank accounts. In many countries the Visa Debit functionality is often incorporated on the same plastic card that allows access to ATM and any domestic networks like EFTPOS or Interac.
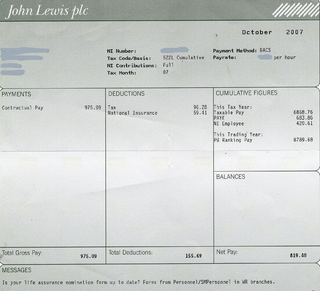
A paycheck, also spelled paycheque, pay check or pay cheque, is traditionally a paper document issued by an employer to pay an employee for services rendered. In recent times, the physical paycheck has been increasingly replaced by electronic direct deposits to the employee's designated bank account or loaded onto a payroll card. Employees may still receive a pay slip to detail the calculations of the final payment amount.
A payment is the tender of something of value, such as money or its equivalent, by one party to another in exchange for goods or services provided by them, or to fulfill a legal obligation or philanthropy desire. The party making the payment is commonly called the payer, while the payee is the party receiving the payment. Whilst payments are often made voluntarily, some payments are compulsory, such as payment of a fine.

Payment cards are part of a payment system issued by financial institutions, such as a bank, to a customer that enables its owner to access the funds in the customer's designated bank accounts, or through a credit account and make payments by electronic transfer with a payment terminal and access automated teller machines (ATMs). Such cards are known by a variety of names, including bank cards, ATM cards, client cards, key cards or cash cards.

An ATM card is a dedicated payment card card issued by a financial institution which enables a customer to access their financial accounts via its and others' automated teller machines (ATMs) and, in some countries, to make approved point of purchase retail transactions. ATM cards are not credit cards or debit cards, however most credit and debit cards can also act as ATM cards and that is the most common way that banks issue cards since the 2010s.

The Eurocheque was a type of cheque used in Europe that was accepted across national borders and which could be written in a variety of currencies.

A cheque guarantee card was an abbreviated portable letter of credit granted by a bank to a qualified depositor in the form of a plastic card that was used in conjunction with a cheque.

Credit card fraud is an inclusive term for fraud committed using a payment card, such as a credit card or debit card. The purpose may be to obtain goods or services or to make payment to another account, which is controlled by a criminal. The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard is the data security standard created to help financial institutions process card payments securely and reduce card fraud.

A credit card is a payment card, usually issued by a bank, allowing its users to purchase goods or services, or withdraw cash, on credit. Using the card thus accrues debt that has to be repaid later. Credit cards are one of the most widely used forms of payment across the world.

girocard is an interbank network and debit card service connecting virtually all automated teller machines (ATMs) and banks. It is based on standards and agreements developed by the German Banking Industry Committee.
The term digital card can refer to a physical item, such as a memory card on a camera, or, increasingly since 2017, to the digital content hosted as a virtual card or cloud card, as a digital virtual representation of a physical card. They share a common purpose: identity management, credit card, debit card or driver's license. A non-physical digital card, unlike a magnetic stripe card, can emulate (imitate) any kind of card.
















