
Trilobites are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian stage of the Early Cambrian period and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian, all trilobite orders except the Proetida died out. The last trilobites disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian about 251.9 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 22,000 species having been described.

Nevadia is an extinct genus of redlichiid trilobites, with species of average size. It lived during the Atdabanian stage, which lasted from 530 to 524 million years ago, in what are today Western Canada, the Western United States, and Mexico.

Naraoia is a genus of small to average size marine arthropods within the family Naraoiidae, that lived from the early Cambrian to the late Silurian period. The species are characterized by a large alimentary system and sideways oriented antennas.
Penarosa is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the Middle Cambrian, approximately 505 to 500 million years ago.
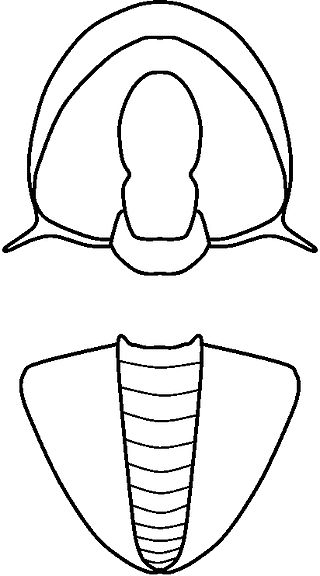
Acidiscus is a genus of eodiscinid trilobite belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida Salter (1864). It lived during the Botomian stage = late Lower Cambrian Stage 4 ; the upper Botomian boundary corresponds to base of the Middle Cambrian, Miaolingian Series and Wuliuan stage.

Acimetopus is a genus of eodiscinid trilobite belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi (1943), Order Agnostida Salter (1864). It lived during the Botomian stage. = late Lower Cambrian Stage 4 ; the upper Botomian boundary corresponds to base of the Middle Cambrian, Miaolingian Series and Wuliuan stage.

Analox is a genus of eodiscinid trilobites belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida It lived during the Botomian stage. It can easily be distinguished from other trilobites by the two furrows that extend forwards and sidewards from the front of the glabella.

Bolboparia is an extinct genus of eodiscinid agnostid trilobites. It lived during the late Lower Cambrian in what today Canada and the United States.
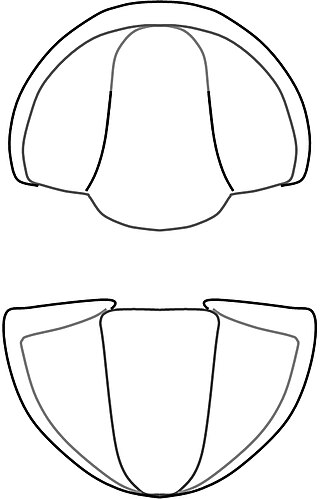
Cobboldites is a genus of eodiscinid trilobite belonging to the family Weymouthiidae, order Agnostida. It lived during the Botomian stage, which lasted from approximately 524 to 518.5 million years ago. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period.
Eoagnostus is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the terminal Lower Cambrian (Toyonian), until the earliest Middle Cambrian.
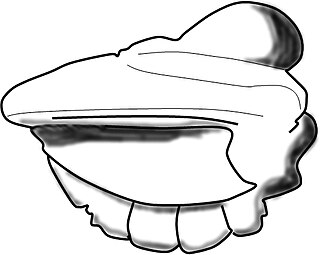
Chelediscus is a genus of Eodiscinid trilobite belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida Salter (1864). The Treatise assigns this genus to the Calodiscidae; Cotton and Fortey (2005) however move it to the Weymouthiidae. Chelediscus lived during the later part of the Botomian stage.

Wanneria is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the later part of the Botomian stage, which lasted from approximately 524 to 518.5 million years ago. This faunal stage was part of the Cambrian Period. W. walcottana and W. cranbrookense are the only known species in this genus.
Cirquella is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the Atdabanian stage, in the former continent Laurentia.

Nevadella is an extinct genus of trilobites, fossil marine arthropods, with species of average size. It lived during the late Atdabanian stage, which lasted from 530 to 524 million years ago during the early part of the Cambrian Period.

Yunnanocephalus is a genus of ptychopariid trilobite. It lived during the late Atdabanian and Botomian stages, in what are currently Antarctica, Australia and China. It was a "moderately common" member of the Chengjiang Fauna. Yunnanocephalus is the only genus currently assigned to the Yunnanocephalidae family.
Acrocephalella is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived from 501 to 497 million years ago during the Guzhangian of the late Cambrian Period.
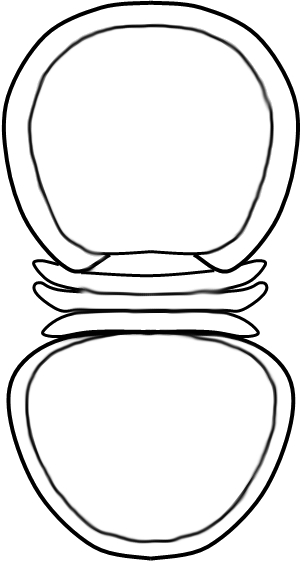
Weymouthia is an extinct genus of eodiscinid agnostid trilobites which lived at the end of the Lower Cambrian. Its fossils are found in Lower Cambrian marine strata from what are now the eastern United States, England, Siberia and China.
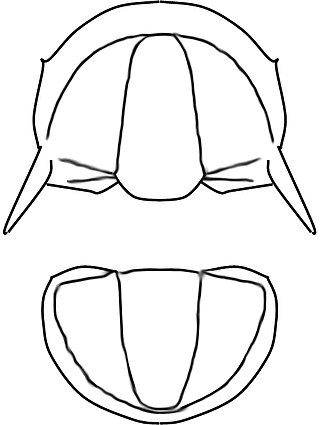
Litometopus is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the Botomian stage.
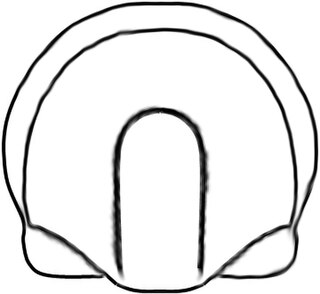
Mallagnostus Howell, 1935, is a trilobite genus belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida Salter (1864) according to Whittington et al. 1997. It lived during the late Lower Cambrian, with remains found in USA, Canada (Newfoundland), Spain, England, Russia, Mongolia, and the early Middle Cambrian as reported from China and Russia (Yakutia).

Serrodiscus Richter and Richter 1941. is a genus of eodiscinid trilobite belonging to the family Weymouthiidae Kobayashi T. (1943), Order Agnostida. It lived during the late Lower Cambrian, with remains found in Canada, China (Gansu), The United Kingdom (England), Germany (Silesia), Poland, the Russian Federation, and the United States. It is named for the spines on the ventral side of the pygidium, which give it a serrated impression.
















