
Amaryllis is the only genus in the subtribe Amaryllidinae. It is a small genus of flowering bulbs, with two species. The better known of the two, Amaryllis belladonna, is a native of the Western Cape region of South Africa, particularly the rocky southwest area between the Olifants River Valley and Knysna.

A pollinator is an animal that moves pollen from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma of a flower. This helps to bring about fertilization of the ovules in the flower by the male gametes from the pollen grains.

Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, for example beetles or butterflies; birds, and bats; water; wind; and even plants themselves. Pollinating animals travel from plant to plant carrying pollen on their bodies in a vital interaction that allows the transfer of genetic material critical to the reproductive system of most flowering plants. When self-pollination occurs within a closed flower. Pollination often occurs within a species. When pollination occurs between species, it can produce hybrid offspring in nature and in plant breeding work.

Darlingtonia californica —also called the California pitcher plant, the Oregon pitcher plant, cobra lily or cobra plant—is a species of carnivorous plant in the new world pitcher plant family, Sarraceniaceae. It is the sole species within its monotypic genus, Darlingtonia. The cobra lily is native to Northern California and Oregon, in the western United States, where the climate—while typically thought of as cool and humid—may be quite arid for many months of the year, more so than many carnivorous or pitcher plant genera could feasibly survive. However, the cobra lily has evolved into life along the West Coast and in the lower Pacific Northwest through its carnivorous adaptions, where it may be found near bogs, vernal pools, on forested rocky slopes, creeks, or near seeps with cold running water, usually on serpentine soils. It has even been observed growing in drainage ditches or on the sides of roads. Despite being fairly commonly cultivated, Darlingtonia is designated as uncommon due to its rarity in the field.

The Limnanthaceae are a small family of annual herbs occurring throughout temperate North America. There are eight species and nineteen taxa currently recognized. Members of this family are prominent in vernal pool communities of California. Some taxa have been domesticated for use as an oil seed crop. Some members are listed as threatened or endangered and have been the focus of disputes over development plans

Howellia aquatilis, the water howellia, is a small plant in the family Campanulaceae that was considered a federally threatened species between 1994 and 2021 under the Endangered Species Act of 1973. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Howellia. Thomas Jefferson Howell and Joseph Howell discovered the species in 1878.

Stylidium is a genus of dicotyledonous plants that belong to the family Stylidiaceae. The genus name Stylidium is derived from the Greek στύλος or stylos, which refers to the distinctive reproductive structure that its flowers possess. Pollination is achieved through the use of the sensitive "trigger", which comprises the male and female reproductive organs fused into a floral column that snaps forward quickly in response to touch, harmlessly covering the insect in pollen. Most of the approximately 300 species are only found in Australia, making it the fifth largest genus in that country. Triggerplants are considered to be protocarnivorous or carnivorous because the glandular trichomes that cover the scape and flower can trap, kill, and digest small insects with protease enzymes produced by the plant. Recent research has raised questions as to the status of protocarnivory within Stylidium.

Ophrys insectifera, the fly orchid, is a species of orchid and the type species of the genus Ophrys. It is remarkable as an example of the use of sexually deceptive pollination and floral mimicry, as well as a highly selective and highly evolved plant–pollinator relationship.

Lindera is a genus of about 80–100 species of flowering plants in the family Lauraceae, mostly native to eastern Asia but with three species in eastern North America. The species are shrubs and small trees; common names include spicewood, spicebush, and Benjamin bush.

Prasophyllum, commonly known as leek orchids, is a genus of about 140 species of flowering plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae and is found in Australia and New Zealand. The Australian species are found in all states but have not been recorded in the Northern Territory. The common name arises from their having a hollow, leek- or onion-like leaf. Some species only flower after summer fires and have flowers similar to those of Xanthorrhoea which flower at the same time, suggesting that they employ the same pollinating insects. Leek orchids are similar to those in the genus Genoplesium except that the free part of the leaf is cylindrical and the labellum has a solid connection to the column. They range in size from the little laughing leek orchid at about 15 cm (6 in) to the king leek orchid which grows up to 2 m (80 in) tall.

Clianthus puniceus, common name kaka beak, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Clianthus of the legume family Fabaceae, native to New Zealand's North Island.

Saxifraga paniculata is an alpine species of flowering plant in the saxifrage family, with native distribution in the temperate northern hemisphere. Common names include alpine saxifrage, encrusted saxifrage, lifelong saxifrage, lime-encrusted saxifrage, livelong saxifrage, white mountain saxifrage, and silver saxifrage.

Asarum caudatum is a plant native to rich moist forests of western North America. It has heart-shaped leaves and a three-lobed purplish flower.

Orobanche uniflora, commonly known as one-flowered broomrape, one-flowered cancer root, ghost pipe or naked broomrape, is an annual parasitic herbaceous plant. It is native to much of North America, where it is a parasitic plant, tapping nutrients from many other species of plants, including those in the families Asteraceae and Saxifragaceae and in the genus Sedum. The name "orobanche" can be translated to "vetch-strangler" and "uniflora" can be translated to "single-flower".

Lithophragma is a genus of flowering plants in the saxifrage family containing about nine species native to western North America. These plants are known generally as woodland stars. The petals of the flowers are usually bright white with deep, long lobes or teeth. Each petal may look like three to five petals, when at closer inspection the lobes fuse into a single petal at its base. Most species reproduce via bulblets instead of seeds. L. maximum is a federally listed endangered species. Lithophragma specifically coevolved with moths of the genus Greya, who pollinate and only lay eggs on Lithophragma plants.

Callitriche stagnalis is a perennial aquatic vascular plant species. Also known as pond water-starwort, C. stagnalis, may thrive in a variety of aquatic and subaquatic habitats, specially those exhibiting slowly moving to non-moving water. Although C. stagnalis does not pose a threat to humans, its reproductive rate may pose a threat to native vegetation in areas where it has been introduced, as the resulting dense vegetative mats frequently out-compete native species.

Restrepia guttulata, commonly called the small-spotted restrepia, is a species of orchid occurring from Venezuela to Ecuador.

Astragalus osterhoutii, or the Osterhout milkvetch or Kremmling milkvetch, is an endangered species of milkvetch, discovered and collected in 1905 at Sulfur Spring in Grand County Colorado by Colorado botanist George Everett Osterhout for which the plant was named. It is found in the U.S. state of Colorado, in a 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) radius near the town of Kremmling.

Eucephalus vialis is a rare North American species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known by the common name wayside aster. It is native to southwestern Oregon and northwestern California in the United States.
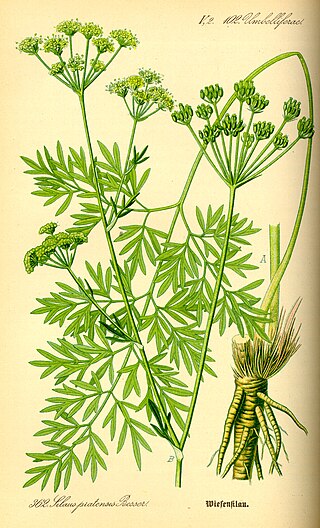
Silaum silaus, commonly known as pepper-saxifrage, is a perennial plant in the family Apiaceae (Umbelliferae) found across south-eastern, central, and western Europe, including the British Isles. It grows in damp grasslands on neutral soils.




















