
Ethanethiol, commonly known as ethyl mercaptan, is an organosulfur compound with the formula CH3CH2SH. is a colorless liquid with a distinct odor. Abbreviated EtSH, it consists of an ethyl group (Et), CH3CH2, attached to a thiol group, SH. Its structure parallels that of ethanol, but with sulfur in place of oxygen. The odor of EtSH is infamous. Ethanethiol is more volatile than ethanol due to a diminished ability to engage in hydrogen bonding. Ethanethiol is toxic in high concentrations. It occurs naturally as a minor component of petroleum, and may be added to otherwise odorless gaseous products such as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) to help warn of gas leaks. At these concentrations, ethanethiol is not harmful.

Allyl chloride is the organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCH2Cl. This colorless liquid is insoluble in water but soluble in common organic solvents. It is mainly converted to epichlorohydrin, used in the production of plastics. It is a chlorinated derivative of propylene. It is an alkylating agent, which makes it both useful and hazardous to handle.
Morpholine is an organic chemical compound having the chemical formula O(CH2CH2)2NH. This heterocycle features both amine and ether functional groups. Because of the amine, morpholine is a base; its conjugate acid is called morpholinium. For example, treating morpholine with hydrochloric acid makes the salt morpholinium chloride. It is a colorless liquid with a weak, ammonia- or fish-like odor. The naming of morpholine is attributed to Ludwig Knorr, who incorrectly believed it to be part of the structure of morphine.

Phosphorus trichloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PCl3. A colorless liquid when pure, it is an important industrial chemical, being used for the manufacture of phosphites and other organophosphorus compounds. It is toxic and reacts readily with water to release hydrogen chloride.
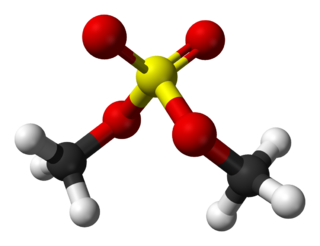
Dimethyl sulfate (DMS) is a chemical compound with formula (CH3O)2SO2. As the diester of methanol and sulfuric acid, its formula is often written as (CH3)2SO4 or Me2SO4, where CH3 or Me is methyl. Me2SO4 is mainly used as a methylating agent in organic synthesis.

Allyl alcohol is an organic compound with the structural formula CH2=CHCH2OH. Like many alcohols, it is a water-soluble, colourless liquid. It is more toxic than typical small alcohols. Allyl alcohol is used as a raw material for the production of glycerol, but is also used as a precursor to many specialized compounds such as flame-resistant materials, drying oils, and plasticizers. Allyl alcohol is the smallest representative of the allylic alcohols.
Benzyl chloride, or α-chlorotoluene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2Cl. This colorless liquid is a reactive organochlorine compound that is a widely used chemical building block.

Disulfur dichloride is the inorganic compound of sulfur and chlorine with the formula S2Cl2. It is an amber oily liquid.

Dimethoxymethane, also called methylal, is a colorless flammable liquid with a low boiling point, low viscosity and excellent dissolving power. It has a chloroform-like odor and a pungent taste. It is the dimethyl acetal of formaldehyde. Dimethoxymethane is soluble in three parts water and miscible with most common organic solvents.

Crotonaldehyde is a chemical compound with the formula CH3CH=CHCHO. The compound is usually sold as a mixture of the E- and Z-isomers, which differ with respect to the relative position of the methyl and formyl groups. The E-isomer is more common (data given in Table is for the E-isomer). This lachrymatory liquid is moderately soluble in water and miscible in organic solvents. As an unsaturated aldehyde, crotonaldehyde is a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis. It occurs in a variety of foodstuffs, e.g. soybean oils.
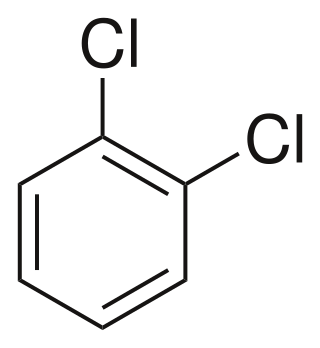
1,2-Dichlorobenzene, or orthodichlorobenzene (ODCB), is an organic compound with the formula C6H4Cl2. This colourless liquid is poorly soluble in water but miscible with most organic solvents. It is a derivative of benzene, consisting of two adjacent chlorine atoms.
Perchloryl fluoride is a reactive gas with the chemical formula ClO
3F. It has a characteristic sweet odor that resembles gasoline and kerosene. It is toxic and is a powerful oxidizing and fluorinating agent. It is the acid fluoride of perchloric acid.
Chloroalkyl ethers are a class of organic compounds with the general structure R-O-(CH2)n-Cl, characterized as an ether connected to a chloromethyl group via an alkane chain.

Dibenzo-18-crown-6 is the organic compound with the formula [OC6H4OCH2CH2OCH2CH2]2. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. As one of the most popular crown ethers, it facilitates the dissolution of many salts in organic solvents. It is related to the non-benzannulated 18-crown-6.
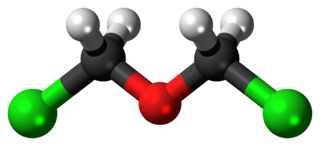
Bis(chloromethyl) ether is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH2Cl)2O. It is a colourless liquid with an unpleasant suffocating odour and it is one of the chloroalkyl ethers. Bis(chloromethyl) ether was once produced on a large scale, but was found to be highly carcinogenic and thus such production has ceased.

Chloroacetaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula ClCH2CHO. Like some related compounds, it is highly electrophilic reagent and a potentially dangerous alkylating agent. The compound is not normally encountered in the anhydrous form, but rather as the hemiacetal (ClCH2CH(OH))2O.

Diethylethanolamine (DEAE) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H15NO. It is used as a precursor in the production of a variety of chemical commodities such as the local anesthetic procaine. It can be reacted with 4-aminobenzoic acid to make procaine. DEAE can be used as a precursor for DEAE-cellulose resin, which is commonly used in ion exchange chromatography. DEAE can also be conveniently obtained from renewable sources. It is chemically stable and able to absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from its surroundings. In solution, it can decrease the surface tension of water when the temperature is increased.
Diglycidyl ethers are chemical compounds used as a reactive diluents for epoxy resin. Other uses include treating textiles and stabilizing chlorinated organic compounds. Diglycidyl ether itself is extremely toxic, and can prove fatal or cause permanent damage if inhaled or consumed orally. As a class of compounds, there are a number of them available commercially with much lower toxicity profiles. One such example is epoxy resin itself Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether
2-Chloroethyl ethyl sulfide is the organosulfur compound with the formula C2H5SC2H4Cl. It is a colorless liquid. The compound is part of the family of vesicant compounds known as half mustards, has been heavily investigated because of its structural similarity to the sulfur mustard S(C2H4Cl)2. The LD50s of the half and full mustard are 252 and 2.4 mg/kg (oral, rats).
Bis(2-chloroethyl)sulfide is the organosulfur compound with the formula (ClCH2CH2)2S. It is a prominent member of a family of cytotoxic and blister agents known as mustard agents. Sometimes referred to as mustard gas, the term is technically incorrect: bis(2-chloroethyl)sulfide is a liquid at room temperature. In warfare it was dispersed in the form of a fine mist of liquid droplets.


















