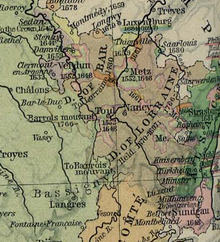
The Duchy of Lorraine, originally Upper Lorraine, was a duchy now included in the larger present-day region of Lorraine in northeastern France. Its capital was Nancy.

A prince-bishop is a bishop who is also the civil ruler of some secular principality and sovereignty. Thus the principality or prince-bishopric ruled politically by a prince-bishop could wholly or largely overlap with his diocesan jurisdiction, but some parts of his diocese, even the city of his residence, could be exempt from his civil rule, obtaining the status of free imperial city. If the episcopal see is an archbishop, the correct term is prince-archbishop; the equivalent in the regular (monastic) clergy is prince-abbot. A prince-bishop is usually considered an elected monarch.

The Imperial Territory of Alsace-Lorraine was a territory created by the German Empire in 1871 after it annexed most of Alsace and the Moselle department of Lorraine following its victory in the Franco-Prussian War. The Alsatian part lay in the Rhine Valley on the west bank of the Rhine River and east of the Vosges Mountains. The Lorraine section was in the upper Moselle valley to the north of the Vosges.

The Archbishopric of Magdeburg was a Roman Catholic archdiocese (969–1552) and Prince-Archbishopric (1180–1680) of the Holy Roman Empire centered on the city of Magdeburg on the Elbe River.

The Three Bishoprics constituted a government of the Kingdom of France consisting of the dioceses of Metz, Verdun, and Toul within the Lorraine region. The three dioceses had been Prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire until they were seized by King Henry II of France between April and June 1552. At the end of the Thirty Years' War, they were officially ceded to France by the 1648 Peace of Westphalia.

German mediatisation was the major territorial restructuring that took place between 1802 and 1814 in Germany and the surrounding region by means of the mass mediatisation and secularisation of a large number of Imperial Estates. Most ecclesiastical principalities, free imperial cities, secular principalities, and other minor self-ruling entities of the Holy Roman Empire lost their independent status and were absorbed into the remaining states. By the end of the mediatisation process, the number of German states had been reduced from almost 300 to just 39.
The Prince-Bishopric of Liège or Principality of Liège was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire situated for the most part in present-day Belgium. As a prince, the bishop of Liège was an Imperial Estate and had seat and vote at the Imperial Diet. The Prince-Bishopric of Liège should not be confused with the Diocese of Liège, which was larger and over which the prince-bishop exercised only the usual responsibilities of a bishop.

Nicolas of Lorraine, Duke of Mercœur was the second son of Antoine, Duke of Lorraine and Renée de Bourbon.

The Italian War of 1551–1559, sometimes known as the Habsburg–Valois War and the Last Italian War, began when Henry II of France declared war against Holy Roman Emperor Charles V with the intent of recapturing Italy and ensuring French, rather than Habsburg, domination of European affairs. Historians have emphasized the importance of gunpowder technology, new styles of fortification to resist cannon fire, and the increased professionalization of the soldiers.

The Prince-Bishopric of Trent, was an ecclesiastical principality roughly corresponding to the present-day Northern Italian autonomous province of Trentino. It was created in 1027 and existed until 1802, when it was secularised and absorbed into the County of Tyrol held by the House of Habsburg. Trent was a Hochstift, an Imperial State under the authority of a prince-bishop at Trento.

The Roman Catholic Diocese of Metz is a diocese of the Latin Rite of the Roman Catholic Church in France. In the Middle Ages it was a prince-bishopric of the Holy Roman Empire, a de facto independent state ruled by the prince-bishop who had the ex officio title of count. It was annexed to France by King Henry II in 1552; this was recognized by the Holy Roman Empire in the Peace of Westphalia of 1648. It formed part of the province of the Three Bishoprics. Since 1801 the Metz diocese has been a public-law corporation of cult.

The Bishopric of Verdun was a state of the Holy Roman Empire. It was located at the western edge of the Empire and was bordered by France, the Duchy of Luxembourg, and the Duchy of Bar.

The Diocese of Toul was a Roman Catholic diocese seated at Toul in present-day France. It existed from 365 until 1824. From 1048 until 1552, it was also a state of the Holy Roman Empire.

The Treaty of Chambord was an agreement signed on 15 January 1552 at the Château de Chambord between the Catholic King Henry II of France and three Protestant princes of the Holy Roman Empire led by Elector Maurice of Saxony. Based on the terms of the treaty, Maurice ceded the vicariate over the Three Bishoprics of Toul, Verdun, and Metz to France. In return, he was promised military and economic aid from Henry II in order to fight against the forces of Emperor Charles V of Habsburg.

The Prince-Bishopric of Osnabrück) was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1225 until 1803. It should not be confused with the Diocese of Osnabrück, which was larger and over which the prince-bishop exercised only the spiritual authority of an ordinary bishop. It was named after its capital, Osnabrück.

The Prince-Bishopric of Bamberg was an ecclesiastical State of the Holy Roman Empire. It goes back to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Bamberg established at the 1007 synod in Frankfurt, at the behest of King Henry II to further expand the spread of Christianity in the Franconian lands. The bishops obtained the status of Imperial immediacy about 1245 and ruled their estates as Prince-bishops until they were subsumed to the Electorate of Bavaria in the course of the German Mediatisation in 1802.

The Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck, was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire until 1803. Originally ruled by Roman-Catholic bishops, after 1586 it was ruled by lay administrators and bishops who were members of the Protestant Holstein-Gottorp line of the House of Oldenburg. The prince-bishops had seat and vote on the Ecclesiastical Bench of the College of Ruling Princes of the Imperial Diet.
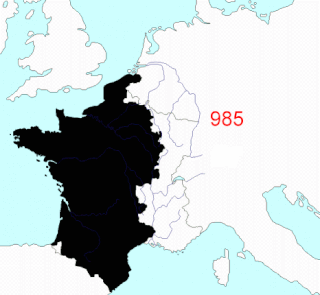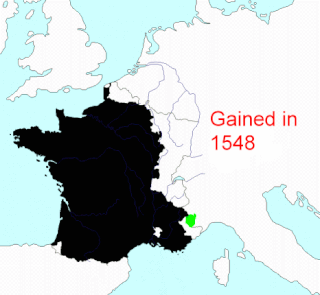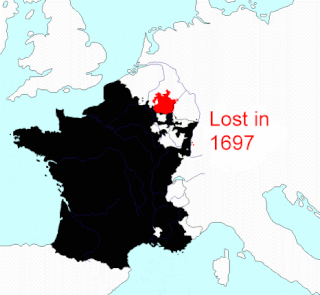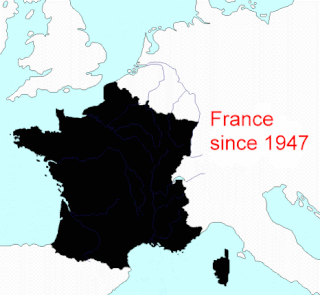
This article describes the process by which the territorial extent of metropolitan France came to be as it is since 1947. The territory of the French State is spread throughout the world. Metropolitan France is that part which is in Europe.
Metz, the capital and the prefecture of both the Lorraine region and the Moselle department in France, has a recorded history dating back over 3,000 years. During this time, it was successively a Celtic oppidum, an important Gallo-Roman city, the Merovingian capital of the Austrasia kingdom, the birthplace of the Carolingian dynasty, a cradle of Gregorian chant, and one of the oldest republics of the common era in Europe. As an important city in the heart of Europe and the crossroads of different cultures, Metz has variously experienced an integration into the Roman Empire, the period of christianization, the barbarian depredations, religious wars, the French Revolution, the Industrial Revolution, an annexation into the German Empire, and World War II.

The County of Saarwerden was a county located in Lorraine, within the Holy Roman Empire. Its capital was in Bockenheim and later in New Saarwerden or Ville Neuve de Sarrewerden, both in the present city of Sarre-Union. Today, the area of the county belongs to Bas-Rhin, Alsace.