Related Research Articles

The Mojave River is an intermittent river in the eastern San Bernardino Mountains and the Mojave Desert in San Bernardino County, California, United States. Most of its flow is underground, while its surface channels remain dry most of the time, with the exception of the headwaters and several bedrock gorges in the lower reaches.

Fort Irwin National Training Center is a major training area for the United States military and is a census-designated place located in the Mojave Desert in northern San Bernardino County, California. Fort Irwin is at an average elevation of 2,454 feet (748 m). It is located 37 miles (60 km) northeast of Barstow, in the Calico Mountains.
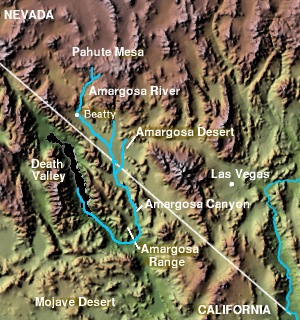
The Amargosa Valley is the valley through which the Amargosa River flows south, in Nye County, southwestern Nevada and Inyo County in the state of California. The south end is alternately called the "Amargosa River Valley'" or the "Tecopa Valley." Its northernmost point is around Beatty, Nevada and southernmost is Tecopa, California, where the Amargosa River enters into the Amargosa Canyon.

The Muddy River, formerly known as the Moapa River, is a short river located in Clark County, in southern Nevada, United States. It is in the Mojave Desert, approximately 60 miles (97 km) north of Las Vegas.

The Old Spanish Trail is a historical trade route that connected the northern New Mexico settlements of Santa Fe, New Mexico with those of Los Angeles, California and southern California. Approximately 700 mi (1,100 km) long, the trail ran through areas of high mountains, arid deserts, and deep canyons. It is considered one of the most arduous of all trade routes ever established in the United States. Explored, in part, by Spanish explorers as early as the late 16th century, the trail saw extensive use by pack trains from about 1830 until the mid-1850s.

The Mojave Road, also known as Old Government Road, is a historic route and present day dirt road across what is now the Mojave National Preserve in the Mojave Desert in the United States. This rough road stretched 147 miles (237 km) from Beale's Crossing, to Fork of the Road location along the north bank of the Mojave River where the old Mojave Road split off from the route of the Old Spanish Trail/Mormon Road.

Alvord Mountain is a mountain range in San Bernardino County, California. The mountain was named for Charles Alvord, who prospected in the area of the mountain between 1860 and 1862. It is located 17.5 miles northeast of Yermo, California.

The Salt Spring Hills are a low mountain range in the Mojave Desert, in northern San Bernardino County, California. They are just outside the southeastern corner of Death Valley National Park, southeast of the Saddle Peak Hills. The road south from Shoshone to Baker passes through the hills.

Southern Emigrant Trail, also known as the Gila Trail, the Kearny Trail, Southern Trail and the Butterfield Stage Trail, was a major land route for immigration into California from the eastern United States that followed the Santa Fe Trail to New Mexico during the California Gold Rush. Unlike the more northern routes, pioneer wagons could travel year round, mountain passes not being blocked by snows, however it had the disadvantage of summer heat and lack of water in the desert regions through which it passed in New Mexico Territory and the Colorado Desert of California. Subsequently, it was a route of travel and commerce between the eastern United States and California. Many herds of cattle and sheep were driven along this route and it was followed by the San Antonio-San Diego Mail Line in 1857-1858 and then the Butterfield Overland Mail from 1858 - 1861.

James Henry Carleton was an officer in the U.S. Army and a Union general during the American Civil War. Carleton is best known as an Indian fighter in the southwestern United States.

Glen Helen Regional Park is a county park located in San Bernardino, California, United States adjacent to the Cajon Pass. It was the site of both US Festivals of the early 1980s. It is also home to the Glen Helen Amphitheater, the largest outdoor amphitheater in the United States. The park also hosts several off-road races since 1985.
The Bitter Spring Expedition of 1860 was a U. S. Army expedition from Fort Tejon, by Company K, First Regiment of Dragoons, led by Major James Henry Carleton, to punish suspected Southern Paiute raiders that had attacked travelers at Bitter Spring along the Los Angeles - Salt Lake Road, the winter trade route and wagon road between Utah and California.

Camp Cady was a U.S. Army Camp, on the Mojave Road near the Mojave River in the Mojave Desert, located about 20 miles east of modern-day Barstow, California in San Bernardino County, at an elevation of 1690 feet. Camp Cady was named after Major Albemarle Cady, 6th Infantry Regiment, who was a friend of Carleton and commander at Fort Yuma in 1860.
Impassable Pass is a gap in Alvord Mountain, in San Bernardino County, California. It is located just south and outside of the boundary fence of Fort Irwin National Training Center.
Red Pass is a gap in the Avawatz Mountains, in San Bernardino County, California. Red Pass, lies between the Silurian Valley and the valley drained by an as yet unnamed tributary of Salt Creek, which drains much of the area of Fort Irwin National Training Center, through Red Pass into the Silurian Valley and into the Amargosa River in Death Valley.
Spanish Canyon, is a canyon that has its head near the middle of the southwest slope of Alvord Mountain below Impassable Pass at 35°07′10″N116°35′37″W and trends south to its mouth, 1.6 miles east northeast of Alvord Well at an elevation of 2, 188 feet / 667 meters. The canyon is named for the Old Spanish Trail which passed through the canyon.
Fork of the Road was the locale along the Mojave River where the junction of the Mojave Trail / Mojave Road and the Old Spanish Trail / Mormon Road was located in San Bernardino County, California. The location of Fork of the Road was on the north side of the Mojave River, 18.75 miles southwest of Bitter Spring, about 14.5 miles east of Grapevine, and 10.9 miles west of Camp Cady. The location was an oasis where the Mojave River came to the surface. There travelers could get water, camp, rest and graze their animals before or after crossing the desert.

The Mohave Trail was a Native American trade route between Mohave Indian villages on the Colorado River and settlements in coastal Southern California.
Mormon Road, also known to the 49ers as the Southern Route, of the California Trail, was a seasonal wagon road first pioneered by a Mormon party from Salt Lake City, Utah led by Jefferson Hunt, that followed the route of Spanish explorers and the Old Spanish Trail across southwestern Utah, northwestern Arizona, southern Nevada and the Mojave Desert of California to Los Angeles in 1847. From 1855, it became a military and commercial wagon route between California and Utah, called the Los Angeles - Salt Lake Road. In later decades this route was variously called the "Old Mormon Road", the "Old Southern Road", or the "Immigrant Road" in California. In Utah, Arizona and Nevada it was known as the "California Road".

The Mojave Road Los Angeles was designated a California Historic Landmark on March 19, 1985. It runs from Drum Barracks in Los Angeles County to the Colorado River in San Bernardino County, California
References
- ↑ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Bitter Spring
- ↑ Edward Leo Lyman, Overland Journey from Utah to California: Wagon Travel from the City of Saints to the City of Angels, University of Nevada Press, 2008.
- ↑ Los Angeles Star, Number 38, 28 January 1860, p.2, col.2 Murder on the Mojave
- ↑ Los Angeles Star, Number 47, 31 March 1860, p.2, col.2, The Indian Murders.
- ↑ William Gorenfeld and John Gorenfeld, Bvt. Major James Carleton at Bitter Spring 1860, Originally published in Wild West, June 19, 2001. From Saturday, January 15, 2005 musketoon.blogspot.com accessed October 3, 2015