
Lychee is a monotypic taxon and the sole member in the genus Litchi in the soapberry family, Sapindaceae.

The Urticaceae are a family, the nettle family, of flowering plants. The family name comes from the genus Urtica. The Urticaceae include a number of well-known and useful plants, including nettles in the genus Urtica, ramie, māmaki, and ajlai.

Urtica is a genus of flowering plants in the family Urticaceae. Many species have stinging hairs and may be called nettles or stinging nettles. The generic name Urtica derives from the Latin for 'sting'.

Laurel forest, also called laurisilva or laurissilva, is a type of subtropical forest found in areas with high humidity and relatively stable, mild temperatures. The forest is characterized by broadleaf tree species with evergreen, glossy and elongated leaves, known as "laurophyll" or "lauroid". Plants from the laurel family (Lauraceae) may or may not be present, depending on the location.

Boehmeria is a genus of 47 species of flowering plants in the nettle family Urticaceae. Of the species, 33 are indigenous to the Old World and 14 to the New World; no species is indigenous to both the Old and New Worlds. The species include herbaceous perennials, shrubs and small trees. Although related to the similar-looking species of the stinging nettles of genus Urtica, species of Boehmeria do not have stinging hairs. Because of the similarity in appearance, some species are commonly called "false nettles".

The Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve is a biosphere reserve in the Nilgiri Mountains of the Western Ghats in South India. It is the largest protected forest area in India, spreading across Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Kerala. It includes the protected areas Mudumalai National Park, Mukurthi National Park, Sathyamangalam Wildlife Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu; Nagarhole National Park, Bandipur National Park, both in Karnataka; Silent Valley National Park, Aralam Wildlife Sanctuary, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, and Karimpuzha Wildlife Sanctuary in Kerala.

Osmanthus is a genus of about 30 species of flowering plants in the family Oleaceae. Most of the species are native to eastern Asia with a few species from the Caucasus, New Caledonia, and Sumatra. Osmanthus has been known in China since ancient times with the earliest writings coming from the Warring States period; the book Sea and Mountain. South Mountain states: "Zhaoyao Mountain had a lot of Osmanthus".

Symplocos is a genus of flowering plants in the order Ericales. It contains about 300 species distributed in Asia and the Americas. Many species grow in humid tropical regions. This is sometimes considered to be the only genus in family Symplocaceae. Plants in this family are shrubs and trees with white or yellow flowers. The oldest fossils of the genus date to the lower Eocene of Europe and North America, with the genus being present in Europe as late as the Pliocene. Fossil seeds of †Symplocos granulosa are frequent in sediment rock layers of the Late Oligocene to the Late Miocene of Denmark, Germany, Austria and Poland. The fossil seeds are very similar to the seeds of the extan southern Chinese species Symplocos glandulifera and Symplocos sulcata. Fossil seeds of †Symplocos paucicostata are known from the Middle Pliocene sediment rock layers in Reuver, the Netherlands and from the Late Pliocene sediment rock layers in northern Italy. The fossil seeds are very similar to the seeds of the extant East Asian species Symplocos paniculata
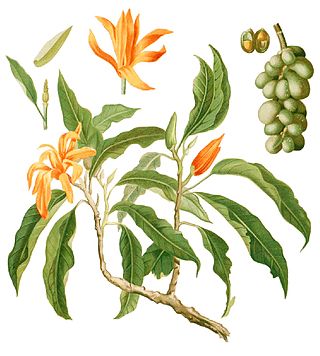
Magnolia champaca, known in English as champak, is a large evergreen tree in the family Magnoliaceae. It was previously classified as Michelia champaca. It is known for its fragrant flowers, and its timber used in woodworking.

Taxus sumatrana, or the Sumatran yew, is a large evergreen shrub and one of the eight species of yew. Its taxonomic namesake is indicative of the species being found in Indonesia ; however, T. sumatrana is also found in a number of South and Southeast Asian countries, including parts of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Indochina, Nepal, Pakistan, the Philippines, Taiwan, and Tibet. Given this broad geographical range, it is also known as the Taiwan yew, the Chinese yew, as well as the East Himalayan yew. Plants of the World Online recognizes T. sumatrana as a synonym of Taxus wallichiana.

Beilschmiedia is a genus of trees and shrubs in family Lauraceae. Most of its species grow in tropical climates, but a few of them are native to temperate regions, and they are widespread in tropical Asia, Africa, Madagascar, Australia, New Zealand, North America, Central America, the Caribbean, and South America. The best-known species to gardeners in temperate areas are B. berteroana and B. miersii because of their frost tolerance. Seeds of B. bancroftii were used as a source of food by Australian Aborigines. Timbers of some species are very valuable.

Rubus ellipticus, commonly known as ainselu, golden evergreen raspberry, golden Himalayan raspberry, or yellow Himalayan raspberry, is an Asian species of thorny fruiting shrub in the rose family. It's native range stretches from the Indian subcontinent to southern China and Indochina and the Philippines.

Tropical evergreen forests of India are found in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the Western Ghats, which fringe the Arabian Sea, the coastline of peninsular India, and the greater Assam region in the north-east. Small remnants of evergreen forest are found in Odisha state. Semi-evergreen forest is more extensive than the evergreen formation partly because evergreen forests tend to degrade to semi-evergreen with human interference. There are substantial differences between the three major evergreen forest regions.The average annual rainfall is 65-75 inches.

Pouzolzia is a genus of flowering plants in the nettle family. There are about 35 species distributed throughout the tropical world. Most are shrubs, and some are herbs. The genus was named for French botanist and plant collector Pierre Marie Casimir de Pouzolz (1785–1858).

Dendrocnide sinuata is a poisonous plant called pulutus', pulus, stinging tree, fever nettle, or elephant nettle, growing in subtropical wet evergreen forests throughout Asia. Some of its uses in herbal medicine have been scientifically validated.

Elatostema is a genus of flowering plants containing approximately 350 known species in the nettle family Urticaceae, native to tropical forest clearings throughout Australasia, Asia and Africa. There may be as many as 1,000 species of this little-known genus, which is susceptible to deforestation and other forms of human exploitation. Some species, for instance the recently discovered E. fengshanense, show unusual adaptations to growing in deep shade in caves. DNA analysis suggests that the three genera Elastostema, Pellionia, and Pilea be grouped together as one.

Boehmeria cylindrica, with common names false nettle and bog hemp, is an herb in the family Urticaceae. It is widespread in eastern North America and the Great Plains from New Brunswick to Florida to Texas to Nebraska, with scattered reports of isolated populations in New Mexico, Arizona, and Utah, as well as in Bermuda, Mexico, Central America, the West Indies, and South America.

Boehmeria virgata subsp. macrophylla is a subspecies of Boehmeria virgata, a flowering plant in the nettle family Urticaceae. This herbaceous plant perennial is native to tropical Africa and the western Indian Ocean. Some sources say that it is also native to China.

Boehmeria japonica is a species of flowering plant in the nettle family (Urticaceae). It native to eastern Asia, where it is found in China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan.
Memecylon caeruleum is a shrub or tree species in the Melastomataceae family. It is found from New Guinea, west through Southeast Asia to Tibet, Zhōngguó/China. It has become an invasive weed in the Seychelles. It has some local use for wood and food.



















