
Ammonoids are extinct spiral shelled cephalopods comprising the subclass Ammonoidea. They are more closely related to living coleoids than they are to shelled nautiloids. The earliest ammonoids appeared during the Devonian, with the last species vanishing during or soon after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. They are often called ammonites, which is most frequently used for members of the order Ammonitida, the only living group of ammonoids from the Jurassic up until their extinction.

Amphisbaenia is a group of typically legless lizards, comprising over 200 extant species. Amphisbaenians are characterized by their long bodies, the reduction or loss of the limbs, and rudimentary eyes. As many species have a pink body and scales arranged in rings, they have a superficial resemblance to earthworms. While the genus Bipes retains forelimbs, all other genera are limbless. Phylogenetic studies suggest that they are nested within Lacertoidea, closely related to the lizard family Lacertidae. Amphisbaenians are widely distributed, occurring in North America, Europe, Africa, South America, Western Asia and the Caribbean. Most species are less than 6 inches (15 cm) long.

Anguidae refers to a large and diverse family of lizards native to the Northern Hemisphere. Common characteristics of this group include a reduced supratemporal arch, striations on the medial faces of tooth crowns, osteoderms, and a lateral fold in the skin of most taxa. The group is divided into two living subfamilies, the legless Anguinae, which contains slow worms and glass lizards, among others, found across the Northern Hemisphere, and Gerrhonotinae, which contains the alligator lizards, native to North and Central America. The family Diploglossidae was also formerly included. The family contains about 87 species in 8 genera.

Heloderma is a genus of toxicoferan lizards that contains five species, all of which are venomous. It is the only extant genus of the family Helodermatidae.

Mosasaurs are an extinct group of large aquatic reptiles within the family Mosasauridae that lived during the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains were discovered in a limestone quarry at Maastricht on the Meuse in 1764. They belong to the order Squamata, which includes lizards and snakes.

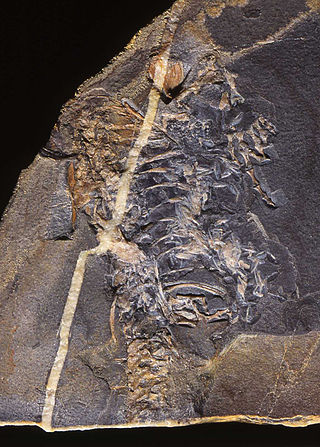
Snakeflies are a group of predatory insects comprising the order Raphidioptera with two extant families: Raphidiidae and Inocelliidae, consisting of roughly 260 species. In the past, the group had a much wider distribution than it does now; snakeflies are found in temperate regions worldwide but are absent from the tropics and the Southern Hemisphere. Recognisable representatives of the group first appeared during the Early Jurassic. They are a relict group, having reached their apex of diversity during the Cretaceous before undergoing substantial decline.

Stupendemys is an extinct genus of freshwater side-necked turtle, belonging to the family Podocnemididae. It is the largest freshwater turtle known to have existed, with a carapace over 2 meters long. Its fossils have been found in northern South America, in rocks dating from the Middle Miocene to the very start of the Pliocene, about 13 to 5 million years ago. Male specimens are known to have possessed bony horns growing from the front edges of the shell and the discovery of the fossil of a young adult shows that the carapace of these turtles flattens with age. A fossil skull described in 2021 indicates that Stupendemys was a generalist feeder.
Platecarpus is an extinct genus of aquatic lizards belonging to the mosasaur family, living around 84–81 million years ago during the middle Santonian to early Campanian, of the Late Cretaceous period. Fossils have been found in the United States and possible specimens in Belgium and Africa. A well-preserved specimen of Platecarpus shows that it fed on moderate-sized fish, and it has been hypothesized to have fed on squid, and ammonites as well. Like other mosasaurs, it was initially thought to have swum in an eel-like fashion, although another study suggests that it swam more like modern sharks. An exceptionally well-preserved specimen of P. tympaniticus known as LACM 128319 shows skin impressions, pigments around the nostrils, bronchial tubes, and the presence of a high-profile tail fluke, showing that it and other mosasaurs did not necessarily have an eel-like swimming method, but were more powerful, fast swimmers. It is held in the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. Isotopic analysis on teeth specimens has suggested that this genus and Clidastes may have entered freshwater occasionally, just like modern sea snakes.

Protostega is an extinct genus of sea turtle containing a single species, Protostega gigas. Its fossil remains have been found in the Smoky Hill Chalk formation of western Kansas, time-equivalent beds of the Mooreville Chalk Formation of Alabama and Campanian beds of the Rybushka Formation. Fossil specimens of this species were first collected in 1871, and named by Edward Drinker Cope in 1872. With a total length of 3.9 metres (13 ft), it is the second-largest sea turtle that ever lived, second only to the giant Archelon, and one of the three largest turtle of all time along Archelon and Gigantatypus.

The Scolecophidia, commonly known as blind snakes or thread snakes, are an infraorder of snakes. They range in length from 10 to 100 centimetres. All are fossorial. Five families and 39 genera are recognized. The Scolecophidia infraorder is most likely paraphyletic.

Gargantuavis is an extinct genus of large, primitive bird containing the single species Gargantuavis philoinos. It is the only member of the monotypic family Gargantuaviidae. Its fossils were discovered in several formations dating to 73.5 and 71.5 million years ago in what is now northern Spain, southern France, and Romania. Gargantuavis is the largest known bird of the Mesozoic, a size ranging between the cassowary and the ostrich, and a mass of 141 kg (311 lb) like modern ostriches, exemplifying the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs was not a necessary condition for the emergence of giant terrestrial birds. It was once thought to be closely related to modern birds, but the 2019 discovery of a pelvis from what was Hateg Island shows several primitive features.

Gobiconodon is an extinct genus of carnivorous mammals belonging to the family Gobiconodontidae. Undisputed records of Gobiconodon are restricted to the Early Cretaceous of Asia and North America, but isolated teeth attributed to the genus have also been described from formations in England and Morocco dating as far back as the Middle Jurassic. Species of Gobiconodon varied considerably in size, with G. ostromi, one of the larger species, being around the size of a modern Virginia opossum. Like other gobiconodontids, it possessed several speciations towards carnivory, such as shearing molariform teeth, large canine-like incisors and powerful jaw and forelimb musculature, indicating that it probably fed on vertebrate prey. Unusually among predatory mammals and other eutriconodonts, the lower canines were vestigial, with the first lower incisor pair having become massive and canine-like. Like the larger Repenomamus there might be some evidence of scavenging.

Titanoboa is an extinct genus of giant boid snake that lived during the middle and late Paleocene. Titanoboa was first discovered in the early 2000s by the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute who, along with students from the University of Florida, recovered 186 fossils of Titanoboa from La Guajira in northeastern Colombia. It was named and described in 2009 as Titanoboa cerrejonensis, the largest snake ever found at that time. It was originally known only from thoracic vertebrae and ribs, but later expeditions collected parts of the skull and teeth. Titanoboa is in the subfamily Boinae, being most closely related to other extant boines from Madagascar and the Pacific.

Balaur is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the late Cretaceous period, in what is now Romania. It is the type species of the monotypic genus Balaur, after the balaur, a dragon of Romanian folklore. The specific name bondoc means "stocky", so Balaur bondoc means "stocky dragon" in Romanian. This name refers to the greater musculature that Balaur had compared to its relatives. The genus, which was first described by scientists in August 2010, is known from two partial skeletons.
Reptiles arose about 320 million years ago during the Carboniferous period. Reptiles, in the traditional sense of the term, are defined as animals that have scales or scutes, lay land-based hard-shelled eggs, and possess ectothermic metabolisms. So defined, the group is paraphyletic, excluding endothermic animals like birds that are descended from early traditionally-defined reptiles. A definition in accordance with phylogenetic nomenclature, which rejects paraphyletic groups, includes birds while excluding mammals and their synapsid ancestors. So defined, Reptilia is identical to Sauropsida.

Oxalaia is a genus of spinosaurid dinosaur that lived in what is now the Northeast Region of Brazil during the Cenomanian stage of the Late Cretaceous period, sometime between 100.5 and 93.9 million years ago. Its only known fossils were found in 1999 on Cajual Island in the rocks of the Alcântara Formation, which is known for its abundance of fragmentary, isolated fossil specimens. The remains of Oxalaia were described in 2011 by Brazilian palaeontologist Alexander Kellner and colleagues, who assigned the specimens to a new genus containing one species, Oxalaia quilombensis. The species name refers to the Brazilian quilombo settlements. Oxalaia quilombensis is the eighth officially named theropod species from Brazil and the largest carnivorous dinosaur discovered there. It is closely related to the African genus Spinosaurus, and/or may be a junior synonym of this taxon.

Coxoplectoptera or "chimera wings" is an extinct order of stem-group mayflies containing one family, Mickoleitiidae. Together with mayflies (Ephemeroptera), Coxoplectoptera are assigned to the clade Heptabranchia.

Telmasaurus is an extinct genus of varanoid lizard from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. Fossils have been found from the Djadokha and Barun Goyot Formations that date between the early and middle Campanian stage from approximately 80 to 75 million years ago. The type species Telmasaurus grangeri was named in 1943.

Maip is a genus of large megaraptorid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Chorrillo Formation of Santa Cruz, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, M. macrothorax, known from an incomplete, disarticulated skeleton. Maip may represent the largest megaraptorid known from South America, and possibly the world.
Titanochampsa is a genus of large mesoeucrocodylian from the Maastrichtian Marilia Formation of Brazil. Although only known from a single skull roof, the material shows that Titanochampsa was not a member of Notosuchia, which were previously believed to have been the only crocodyliforms present in the strata of the Bauru Group. Body size estimates vary greatly and range between 2.98–5.88 m due to the incomplete nature of the holotype fossil. The overall anatomy of the skull roof, alongside its size and possible affinities with Neosuchians, may suggest that it was a semi-aquatic ambush hunter similar to modern crocodilians.


















