
Telopea speciosissima, commonly known as the New South Wales waratah or simply waratah, is a large shrub in the plant family Proteaceae. It is endemic to New South Wales in Australia and is the floral emblem of that state. No subspecies are recognised, but the closely related Telopea aspera was only recently classified as a separate species.

Acacia cultriformis, known as the knife-leaf wattle, dogtooth wattle, half-moon wattle or golden-glow wattle, is a perennial tree or shrub of the genus Acacia native to Australia. It is widely cultivated, and has been found to have naturalised in Asia, Africa, North America, New Zealand and South America. A. cultriformis grows to a height of about 4 m (13 ft) and has triangle-shaped phyllodes. The yellow flowers appear from August to November in its natural range. Its attractive foliage and bright flowers make it a popular garden plant.

Xerochrysum bracteatum, commonly known as the golden everlasting or strawflower, is a flowering plant in the family Asteraceae native to Australia. Described by Étienne Pierre Ventenat in 1803, it was known as Helichrysum bracteatum for many years before being transferred to a new genus Xerochrysum in 1990. It is an annual up to 1 m (3.3 ft) tall with green or grey leafy foliage. Golden yellow or white flower heads are produced from spring to autumn; their distinctive feature is the papery bracts that resemble petals. The species is widespread, growing in a variety of habitats across the country, from rainforest margins to deserts and subalpine areas. The golden everlasting serves as food for various larvae of lepidopterans, and adult butterflies, hoverflies, native bees, small beetles, and grasshoppers visit the flower heads.

Banksia spinulosa, the hairpin banksia, is a species of woody shrub, of the genus Banksia in the family Proteaceae, native to eastern Australia. Widely distributed, it is found as an understorey plant in open dry forest or heathland from Victoria to northern Queensland, generally on sandstone though sometimes also clay soils. It generally grows as a small shrub to 2 metres (7 ft) in height, though can be a straggly tree to 6 metres (20 ft). It has long narrow leaves with inflorescences which can vary considerably in coloration; while the spikes are gold or less commonly yellowish, the emergent styles may be a wide range of colours – from black, purple, red, orange or yellow.

Drosera binata, commonly known as the forked sundew or fork-leaved sundew, is a large, perennial sundew native to Australia and New Zealand. The specific epithet is Latin for "having pairs" - a reference to the leaves, which are dichotomously divided or forked.

Isopogon anethifolius, commonly known as narrow-leaf drumsticks or narrow-leafed drumsticks, is a shrub in the family Proteaceae. The species is found only in coastal areas near Sydney in New South Wales, and to the immediate west. It occurs naturally in woodland, open forest and heathland on sandstone soils. An upright shrub, it can reach to 3 m (9.8 ft) in height, with terete leaves that are divided and narrow. The yellow flowers appear in the Spring, from September to December, and are prominently displayed. They are followed by round grey cones, which give the plant its common name of drumsticks. The small hairy seeds are found in the old flower parts.

Brachyscome is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. Most are endemic to Australia, and a few occur in New Zealand and New Guinea.

Santolina chamaecyparissus, known as cotton lavender or lavender-cotton, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae, native to the western and central Mediterranean.

Dianella caerulea, commonly known as the blue flax-lily, blueberry lily, or paroo lily, is a perennial herb of the family Asphodelaceae, subfamily Hemerocallidoideae, found across the eastern states of Australia and Tasmania. It is a herbaceous strappy perennial plant to a metre high, with dark green blade-like leaves to 70 cm long. Blue flowers in spring and summer are followed by indigo-coloured berries. It adapts readily to cultivation and is commonly seen in Australian gardens and amenities plantings.

Goodenia ovata, commonly called the hop goodenia, is a species of flowering plant and is endemic to south-eastern Australia. It is a shrub with sticky, often varnished foliage, toothed egg-shaped to elliptic leaves and racemes or thyrses of yellow flowers.

Gazania rigens, sometimes called treasure flower, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae, native to coastal areas of southern Africa. It is naturalised elsewhere and is widely cultivated as an ornamental plant.

Brachyscome chrysoglossa, the yellow-tongue daisy, is a perennial herb from Australia in the family Asteraceae. The species is endemic to Australia.

Telopea oreades, commonly known as the Gippsland-, mountain- or Victorian waratah, is a large shrub or small tree in the family Proteaceae. Native to southeastern Australia, it is found in wet sclerophyll forest and rainforest on rich acidic soils high in organic matter. No subspecies are recognised, though a northern isolated population hybridises extensively with the Braidwood waratah (T. mongaensis). Reaching a height of up to 19 metres, T. oreades grows with a single trunk and erect habit. It has dark green leaves with prominent veins that are 11–28 centimetres (4.3–11 in) long and 1.5–6 cm (0.6–2.4 in) wide. The red flower heads, known as inflorescences, appear in late spring. Each is composed of up to 60 individual flowers.

Grevillea johnsonii, commonly known as Johnson's grevillea or Johnson's spider flower, is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to New South Wales. It is a shrub with divided, needle-like leaves and red to orange flowers, and grows in rocky places.
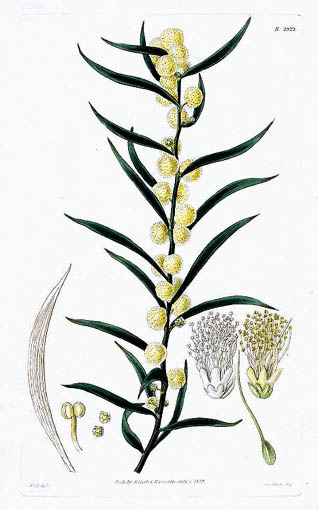
Acacia lanigera, commonly known as woolly wattle or hairy wattle, is a tree species that is endemic south eastern Australia.

Pulsatilla nuttalliana, known as American pasqueflower, prairie pasqueflower, prairie crocus, cutleaf anemone, or simply pasqueflower, is a flowering plant native to much of North America, from the western side of Lake Michigan, to northern Canada in the Northwest Territories, south to New Mexico in the southwestern United States. Pasqueflower is the provincial flower of Manitoba and the state flower of South Dakota.

Brachyscome scapigera, commonly known as tufted daisy, is a perennial herb in the family Asteraceae. The species is endemic to south-eastern Australia.

Brachyscome segmentosa, commonly known as the Lord Howe Island daisy or mountain daisy, is a herb in the family Asteraceae. The specific epithet comes from the Latin segmentum ("segment") with the suffix -osa, alluding to the many deep divisions of the leaf.

Brachyscome ascendens, the border ranges daisy, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae and is endemic to Australia. It has mostly mauve daisy-like flowers and a yellow centre.

Brachyscome dentata, commonly known as lobe-seed daisy, is a tufted perennial herb in the family Asteraceae and is endemic to Australia. It has mostly white or mauve daisy-like flowers, a yellow centre and pale green leaves. It is endemic to Australia.





















