
Nueva Ecija, officially the Province of Nueva Ecija, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Central Luzon region. Its capital is the city of Palayan, while Cabanatuan, its former capital, is the largest local government unit (LGU). Nueva Ecija borders, from the south clockwise, Bulacan, Pampanga, Tarlac, Pangasinan, Nueva Vizcaya and Aurora. The province is nationally known as the Rice Granary of the Philippines, producing the largest rice yield in the country.

Aurora, officially the Province of Aurora, is a province in the Philippines located in the eastern part of Central Luzon region, facing the Philippine Sea. Its capital is Baler and borders, clockwise from the south, the provinces of Quezon, Bulacan, Nueva Ecija, Nueva Vizcaya, Quirino, and Isabela.

Nueva Vizcaya, officially the Province of Nueva Vizcaya, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Cagayan Valley region in Luzon. Its capital is Bayombong. It is bordered by Benguet to the west, Ifugao to the north, Isabela to the northeast, Quirino to the east, Aurora to the southeast, Nueva Ecija to the south, and Pangasinan to the southwest. Quirino province was created from Nueva Vizcaya in 1966.

Quirino, officially the Province of Quirino, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Cagayan Valley region in Luzon. Its capital is Cabarroguis. It is named after Elpidio Quirino, the sixth President of the Philippines.

Central Luzon, designated as Region III, is an administrative region in the Philippines. The region comprises seven provinces: Aurora, Bataan, Bulacan, Nueva Ecija, Pampanga, Tarlac, and Zambales; and two highly urbanized cities, Angeles and Olongapo. The region contains the largest plain in the country and produces most of the country's rice supply, earning itself the nickname "Rice Granary of the Philippines". It is also the region to have the most number of provinces.

Baler, officially the Municipality of Baler, is a 3rd class municipality and capital of the province of Aurora, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 43,785 people.

Bambang, officially the Municipality of Bambang, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Nueva Vizcaya, Philippines. According to the 2020 censusus, it has a population of 55,789 people.

The indigenous peoples of the Cordillera in northern Luzon, Philippines, often referred to by the exonym Igorot people, or more recently, as the Cordilleran peoples, are an ethnic group composed of nine main ethnolinguistic groups whose domains are in the Cordillera Mountain Range, altogether numbering about 1.8 million people in the early 21st century.

Dupax del Sur, officially the Municipality of Dupax del Sur, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Nueva Vizcaya, Philippines. At the 2020 census, it had a population of 21,224 people.

Cabarroguis, officially the Municipality of Cabarroguis, is a 3rd class municipality and capital of the province of Quirino, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 33,533 people.

Maddela, officially the Municipality of Maddela, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Quirino, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 40,943 people.

Casiguran, officially the Municipality of Casiguran, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Aurora, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 26,564 people.

Maria Aurora, officially the Municipality of Maria Aurora, is the only landlocked and 2nd class municipality in the province of Aurora, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 44,958 people.

Pantabangan, officially the Municipality of Pantabangan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Nueva Ecija, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 31,763 people.
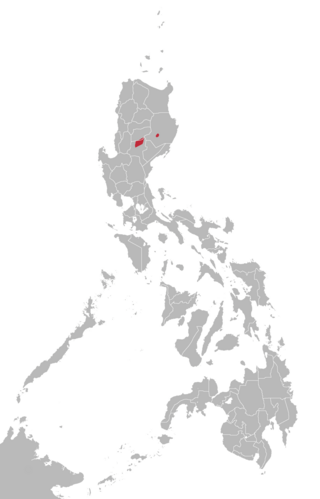
The Gaddang language is spoken by up to 30,000 speakers in the Philippines, particularly along the Magat and upper Cagayan rivers in the Region II provinces of Nueva Vizcaya and Isabela and by overseas migrants to countries in Asia, Australia, Canada, Europe, in the Middle East, United Kingdom and the United States. Most Gaddang speakers also speak Ilocano, the lingua franca of Northern Luzon, as well as Tagalog and English. Gaddang is associated with the "Christianized Gaddang" people, and is closely related to the highland tongues of Ga'dang with 6,000 speakers, Yogad, Cagayan Agta with less than 1,000 and Atta with 2,000, and more distantly to Ibanag, Itawis, Isneg and Malaweg.
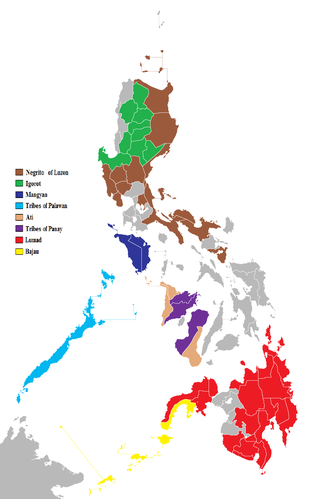
The indigenous peoples of the Philippines are ethnolinguistic groups or subgroups that maintain partial isolation or independence throughout the colonial era, and have retained much of their traditional pre-colonial culture and practices.

Bugkalot is a language of the indigenous Bugkalot people of northern Luzon, Philippines.

Isinai is a Northern Luzon language primarily spoken in Nueva Vizcaya province in the northern Philippines. By linguistic classification, it is more divergent from other Central Cordilleran languages, such as Kalinga, Itneg or Ifugao and Kankanaey.

The Casecnan Protected Landscape is a protected area in the Casecnan River watershed of eastern Luzon in the Philippines. It has a total area of 88,846.80 hectares straddling the provinces of Nueva Vizcaya, Quirino and Aurora. The 57,930-hectare (143,100-acre) Casecnan River Watershed Forest Reserve was established in August 1987 by virtue of Executive Order No. 136 issued by President Corazon Aquino. In April 2000, the forest reserve was enlarged to 88,846.80 hectares and was reclassified as a protected landscape area through Proclamation No. 289. It is considered one of the last remaining substantial water sources for the region of Central Luzon.
The Kalanguya are an Austronesian ethnic group most closely associated with the Philippines' Cordillera Administrative Region, but whose core population can be found across an area which also includes the provinces of Nueva Vizcaya, Nueva Ecija, and Pangasinan. While this area spans Region I, the Cordillera Administrative Region, and Region II, it represents a largely geographically contiguous area. Initially thought by some researchers as a subgroup of the Ifugao people, extensive studies have now shown that the Kalanguya are distinct from the Ifugao.





























