
Cagayan Valley, designated as Region II, is an administrative region in the Philippines. Located in the northeastern section of Luzon, it is composed of five Philippine provinces: Batanes, Cagayan, Isabela, Nueva Vizcaya, and Quirino. The region hosts four chartered cities: Cauayan, Ilagan, Santiago, and Tuguegarao.

Northern Mindanao is an administrative region in the Philippines, designated as Region X. It comprises five provinces: Bukidnon, Camiguin, Misamis Occidental, Misamis Oriental, and Lanao del Norte, and two cities classified as highly urbanized, all occupying the north-central part of Mindanao island, and the island-province of Camiguin. The regional center and largest city is Cagayan de Oro. Lanao del Norte was transferred to Northern Mindanao from Region XII by virtue of Executive Order No. 36 in September 2001.

Cagayan, officially the Province of Cagayan, is a province in the Philippines located in the Cagayan Valley region, covering the northeastern tip of Luzon. Its capital is Tuguegarao, the largest city of that province as well as the regional center of Cagayan Valley. It is about 431 kilometres (268 mi) northwest of Manila, and includes the Babuyan Islands to the north. The province borders Ilocos Norte and Apayao to the west, and Kalinga and Isabela to the south.

Isabela, officially the Province of Isabela, is the second largest province in the Philippines in land area located in the Cagayan Valley. Its capital and the largest local government unit is the city of Ilagan. It is bordered by the provinces of Cagayan to the north, Kalinga to the northwest, Mountain Province to the central-west, Ifugao and Nueva Vizcaya to the southwest, Quirino, Aurora and the independent city of Santiago to the south, and the Philippine Sea to the east.

Nueva Vizcaya, officially the Province of Nueva Vizcaya, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Cagayan Valley region in Luzon. Its capital and largest town is Bayombong. It is bordered by Benguet to the west, Ifugao to the north, Isabela to the northeast, Quirino to the east, Aurora to the southeast, Nueva Ecija to the south, and Pangasinan to the southwest. Quirino province was created from Nueva Vizcaya in 1966.

Quirino, officially the Province of Quirino, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Cagayan Valley region in Luzon. Its capital is Cabarroguis while Diffun is the most populous in the province. It is named after Elpidio Quirino, the sixth President of the Philippines.

The Ilocos Region, designated as Region I, is an administrative region of the Philippines. Located in the northwestern section of Luzon, it is bordered by the Cordillera Administrative Region to the east, the Cagayan Valley to the northeast and southeast, Central Luzon to the south, and the South China Sea to the west.
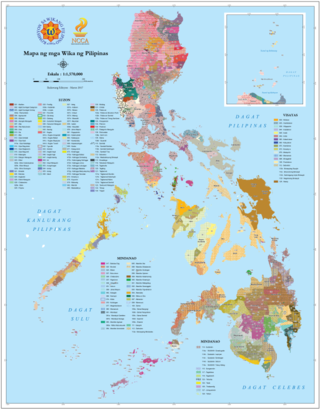
There are some 130 to 195 languages spoken in the Philippines, depending on the method of classification. Almost all are Malayo-Polynesian languages native to the archipelago. A number of Spanish-influenced creole varieties generally called Chavacano along with some local varieties of Chinese are also spoken in certain communities. The 1987 constitution designates Filipino, a standardized version of Tagalog, as the national language and an official language along with English. Filipino is regulated by Commission on the Filipino Language and serves as a lingua franca used by Filipinos of various ethnolinguistic backgrounds.

The indigenous peoples of the Cordillera in northern Luzon, Philippines, often referred to by the exonym Igorot people, or more recently, as the Cordilleran peoples, are an ethnic group composed of nine main ethnolinguistic groups whose domains are in the Cordillera Mountain Range, altogether numbering about 1.8 million people in the early 21st century.

Palanan, officially the Municipality of Palanan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Isabela, Philippines. It also served as the final capital of the First Philippine Republic from 1900 until the capture of President Emilio Aguinaldo by the Americans during the Philippine-American War in 1901. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 17,684 people.

Camalaniugan, officially the Municipality of Camalaniugan, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Cagayan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 25,236 people.

Cabagan, officially the Municipality of Cabagan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Isabela, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 53,897 people.

San Mariano, officially the Municipality of San Mariano; Ilocano: Ili ti San Mariano; Tagalog: Bayan ng San Mariano), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Isabela, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 60,124 people.
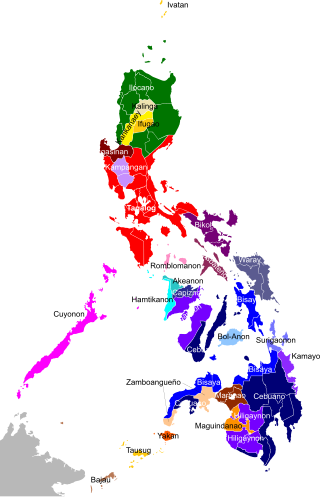
The Philippines is inhabited by more than 182 ethnolinguistic groups, many of which are classified as "Indigenous Peoples" under the country's Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act of 1997. Traditionally-Muslim peoples from the southernmost island group of Mindanao are usually categorized together as Moro peoples, whether they are classified as Indigenous peoples or not. About 142 are classified as non-Muslim Indigenous people groups, and about 19 ethnolinguistic groups are classified as neither Indigenous nor Moro. Various migrant groups have also had a significant presence throughout the country's history.
The Pangasinan people, also known as Pangasinense, are an ethnolinguistic group native to the Philippines. Numbering 1,823,865 in 2010, they are the tenth largest ethnolinguistic group in the country. In the 2020 census Pangasinan speaking households made up roughly 1.3% of Phillipine households. They live mainly in their native province of Pangasinan and the adjacent provinces of La Union and Tarlac, as well as Benguet, Nueva Ecija, Zambales, and Nueva Vizcaya. Smaller groups are found elsewhere in the Philippines and worldwide in the Filipino diaspora.
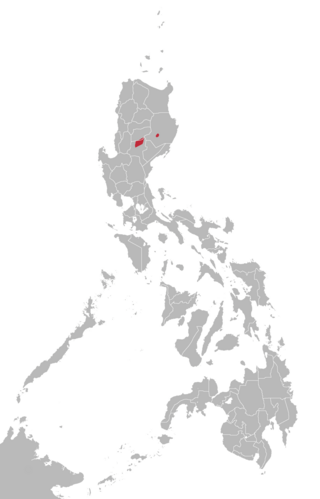
The Gaddang language is spoken by up to 30,000 speakers in the Philippines, particularly along the Magat and upper Cagayan rivers in the Region II provinces of Nueva Vizcaya and Isabela and by overseas migrants to countries in Asia, Australia, Canada, Europe, in the Middle East, United Kingdom and the United States. Most Gaddang speakers also speak Ilocano, the lingua franca of Northern Luzon, as well as Tagalog and English. Gaddang is associated with the "Christianized Gaddang" people, and is closely related to the highland tongues of Ga'dang with 6,000 speakers, Yogad, Cagayan Agta with less than 1,000 and Atta with 2,000, and more distantly to Ibanag, Itawis, Isneg and Malaweg.

Itawis is a Northern Philippine language spoken by the Itawis people, closely related to the Gaddang speech found in Isabela and Nueva Vizcaya. It also has many similarities to the neighboring Ibanag tongue, while remaining quite different from the prevalent Ilocano spoken in the region and the Tagalog-based Filipino national language.

The Gaddang are an indigenous peoples and a linguistically identified ethnic group resident in the watershed of the Cagayan River in Northern Luzon, Philippines. Gaddang speakers were recently reported to number as many as 30,000, a number that may not include another 6,000 related Ga'dang speakers or other small linguistic-groups whose vocabularies are more than 75% identical.

The Ibanag language is an Austronesian language spoken by up to 500,000 speakers, most particularly by the Ibanag people, in the Philippines, in the northeastern provinces of Isabela and Cagayan, especially in Tuguegarao, Solana, Abulug, Camalaniugan, Lal-lo, Cabagan, Tumauini, San Pablo, Sto. Tomas, Sta. Maria, and Ilagan and other neighboring towns and villages around the Cagayan River and with overseas immigrants in countries located in the Middle East, United Kingdom, and the United States. Most of the speakers can also speak Ilocano, the lingua franca of northern Luzon island. The name Ibanag comes from the prefix I which means 'people of', and bannag, meaning 'river'. It is closely related to Gaddang, Itawis, Agta, Atta, Yogad, Isneg, and Malaweg.


















