
The Philippines is an archipelago that comprises 7,641 islands, and with a total land area of 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi), it is the world's fifth largest island country. The eleven largest islands contain 95% of the total land area. The largest of these islands is Luzon at about 105,000 square kilometers (40,541 sq mi). The next largest island is Mindanao at about 95,000 square kilometers (36,680 sq mi). The archipelago is around 800 kilometers (500 mi) from the Asian mainland and is located between Taiwan and Borneo.

Zambales, officially the Province of Zambales, is a province in the Philippines located in the Central Luzon region. Its capital is Iba, which is located in the middle of the province. Olongapo is the largest city of the province wherein it is geographically located but politically independent.

Misamis Occidental, officially the Province of Misamis Occidental, is a province located in the region of Northern Mindanao in the Philippines. Its capital is the city of Oroquieta. The province borders Zamboanga del Norte and Zamboanga del Sur to the west and is separated from Lanao del Norte by Panguil Bay to the south and Iligan Bay to the east. The province of Misamis was originally inhabited by Subanens who were an easy target by the sea pirates from Lanao.

Lanao del Norte, officially the Province of Lanao del Norte, is a province in the Philippines located in the Northern Mindanao region. Its capital is Tubod.

Oriental Mindoro, officially the Province of Oriental Mindoro, is a province in the Philippines located on the island of Mindoro under Mimaropa region in Luzon, about 140 kilometres (87 mi) southwest of Manila. The province is bordered by the Verde Island Passage and the rest of Batangas to the north, by Marinduque, Maestre de Campo Island, Tablas Strait and the rest of Romblon to the east, by Semirara and the rest of Caluya Islands, Antique to the south, and by Occidental Mindoro to the west. Calapan, the only city in the island, is the provincial capital and Mimaropa's regional center.

Occidental Mindoro, officially the Province of Occidental Mindoro, is a province in the Philippines located in the Mimaropa region. The province occupies the western half of the island of Mindoro. Its capital is Mamburao, but the most populous municipality is San Jose. Sablayan is its largest municipality in terms of area, occupying almost half of the entire province. As of 2020, Occidental Mindoro has 525,354 inhabitants.

Lanao del Sur, officially the Province of Lanao del Sur, is a province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM). The capital is the city of Marawi, and it borders Lanao del Norte to the north, Bukidnon to the east, and Maguindanao del Norte and Cotabato to the south. To the southwest lies Illana Bay, an arm of the Moro Gulf.

Taal Lake, formerly known as Bombón Lake, is a fresh water caldera lake in the province of Batangas, on the island of Luzon in the Philippines. The lake fills Taal Volcano, a large volcanic caldera formed by very large eruptions between 500,000 and 100,000 years ago.

Mamburao, officially the Municipality of Mamburao, is a 2nd class municipality and capital of the province of Occidental Mindoro, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 47,705 people.

Sablayan, officially the Municipality of Sablayan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Occidental Mindoro, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 92,598 people.
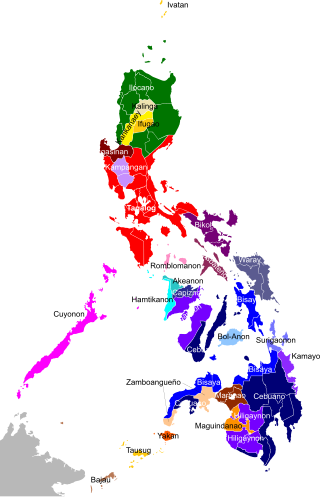
The Philippines is inhabited by more than 182 ethnolinguistic groups, many of which are classified as "Indigenous Peoples" under the country's Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act of 1997. Traditionally-Muslim peoples from the southernmost island group of Mindanao are usually categorized together as Moro peoples, whether they are classified as Indigenous peoples or not. About 142 are classified as non-Muslim Indigenous people groups, and about 19 ethnolinguistic groups are classified as neither Indigenous nor Moro. Various migrant groups have also had a significant presence throughout the country's history.
The Interim Batasang Pambansa was the legislature of the Republic of the Philippines from its inauguration on June 12, 1978, to June 5, 1984. It served as a transitional legislative body mandated by the 1973 Constitution as the Philippines shifted from a presidential to a semi-presidential form of government.

Apo Reef is a coral reef system in the Philippines situated in the western waters of Occidental Mindoro province in the Mindoro Strait. Encompassing 34 square kilometres (13 sq mi), it is considered the world's second-largest contiguous coral reef system, and is the largest in the country. The reef and its surrounding waters are protected areas administered as the Apo Reef Natural Park (ARNP). It is one of the best known and most popular diving regions in the country, and is in the tentative list for UNESCO World Heritage Sites.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Philippines:

Polytechnic University of the Philippines, Sablayan Campus or PUP Sablayan is the 21st PUP campus located in Sitio Macambang, Brgy. Buenavista, municipality of Sablayan, Occidental Mindoro, Philippines. It is an LGU-funded campus.

Eduardo Baltazar Gadiano is a Filipino politician who has served as Governor of Occidental Mindoro since 2019. He is a member of the Partido Federal ng Pilipinas. He previously served as mayor of Sablayan from 2010 to 2019.





















