
Long Valley Caldera is a depression in eastern California that is adjacent to Mammoth Mountain. The valley is one of the Earth's largest calderas, measuring about 20 mi (32 km) long (east-west), 11 mi (18 km) wide (north-south), and up to 3,000 ft (910 m) deep.

A fumarole is a vent in the surface of the Earth or another rocky planet from which hot volcanic gases and vapors are emitted, without any accompanying liquids or solids. Fumaroles are characteristic of the late stages of volcanic activity, but fumarole activity can also precede a volcanic eruption and has been used for eruption prediction. Most fumaroles die down within a few days or weeks of the end of an eruption, but a few are persistent, lasting for decades or longer. An area containing fumaroles is known as a fumarole field.

The geothermal areas of Yellowstone include several geyser basins in Yellowstone National Park as well as other geothermal features such as hot springs, mud pots, and fumaroles. The number of thermal features in Yellowstone is estimated at 10,000. A study that was completed in 2011 found that a total of 1,283 geysers have erupted in Yellowstone, 465 of which are active during an average year. These are distributed among nine geyser basins, with a few geysers found in smaller thermal areas throughout the Park. The number of geysers in each geyser basin are as follows: Upper Geyser Basin (410), Midway Geyser Basin (59), Lower Geyser Basin (283), Norris Geyser Basin (193), West Thumb Geyser Basin (84), Gibbon Geyser Basin (24), Lone Star Geyser Basin (21), Shoshone Geyser Basin (107), Heart Lake Geyser Basin (69), other areas (33). Although famous large geysers like Old Faithful are part of the total, most of Yellowstone's geysers are small, erupting to only a foot or two. The hydrothermal system that supplies the geysers with hot water sits within an ancient active caldera. Many of the thermal features in Yellowstone build up sinter, geyserite, or travertine deposits around and within them.

Mammoth Mountain is a lava dome complex partially located within the town of Mammoth Lakes, California, in the Inyo National Forest of Madera and Mono Counties. It is home to a large ski area primarily on the Mono County side.
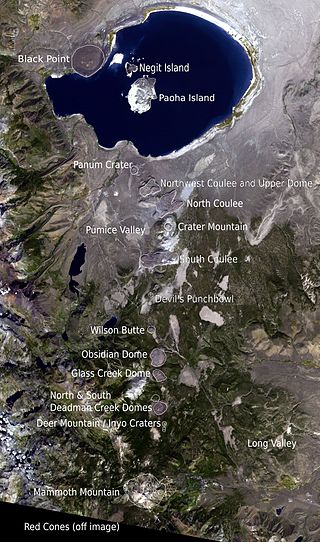
The Mono–Inyo Craters are a volcanic chain of craters, domes and lava flows in Mono County, Eastern California. The chain stretches 25 miles (40 km) from the northwest shore of Mono Lake to the south of Mammoth Mountain. The Mono Lake Volcanic Field forms the northernmost part of the chain and consists of two volcanic islands in the lake and one cinder cone volcano on its northwest shore. Most of the Mono Craters, which make up the bulk of the northern part of the Mono–Inyo chain, are phreatic volcanoes that have since been either plugged or over-topped by rhyolite domes and lava flows. The Inyo volcanic chain form much of the southern part of the chain and consist of phreatic explosion pits, and rhyolitic lava flows and domes. The southernmost part of the chain consists of fumaroles and explosion pits on Mammoth Mountain and a set of cinder cones south of the mountain; the latter are called the Red Cones.

The Lassen volcanic area presents a geological record of sedimentation and volcanic activity in and around Lassen Volcanic National Park in Northern California, U.S. The park is located in the southernmost part of the Cascade Mountain Range in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. Pacific Oceanic tectonic plates have plunged below the North American Plate in this part of North America for hundreds of millions of years. Heat and molten rock from these subducting plates has fed scores of volcanoes in California, Oregon, Washington and British Columbia over at least the past 30 million years, including these in the Lassen volcanic areas.

Lassen Peak, commonly referred to as Mount Lassen, is a lava dome volcano and the southernmost active volcano in the Cascade Range of the Western United States. Located in the Shasta Cascade region of Northern California, it is part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, which stretches from southwestern British Columbia to northern California. Lassen Peak reaches an elevation of 10,457 ft (3,187 m), standing above the northern Sacramento Valley. It supports many flora and fauna among its diverse habitats, which are subject to frequent snowfall and reach high elevations.

Solfatara is a shallow volcanic crater at Pozzuoli, near Naples, part of the Phlegraean Fields volcanic area. It is a dormant volcano, which still emits jets of steam with sulfurous fumes. The name comes from the Latin, Sulpha terra, "land of sulfur", or "sulfur earth". It was formed around 4000 years ago and last erupted in 1198 with what was probably a phreatic eruption – an explosive steam-driven eruption caused when groundwater interacts with magma. The crater floor was a popular tourist attraction until 2017, as it has many fumaroles and mud pools. The area is well known for its bradyseism. The vapours had been used for medical purposes since Roman times.

The Coso Volcanic Field is located in Inyo County, California, at the western edge of the Basin and Range geologic province and northern region of the Mojave Desert. The Fossil Falls are part of the Coso Field, created by the prehistoric Owens River. They are within the Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake and northeast of Little Lake and U.S. Route 395.
Volcán Santo Tomás is a stratovolcano in southern Guatemala. Its highest point lies at an altitude of 3,542 m above sea level.

Ollagüe or Ullawi is a massive andesite stratovolcano in the Andes on the border between Bolivia and Chile, within the Antofagasta Region of Chile and the Potosi Department of Bolivia. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, its highest summit is 5,868 metres (19,252 ft) above sea level and features a summit crater that opens to the south. The western rim of the summit crater is formed by a compound of lava domes, the youngest of which features a vigorous fumarole that is visible from afar.
Mount Leonard Kniaseff, or simply Leonard Kniaseff, is a stratovolcano between the municipalities of Mabini and Maco in the province of Davao de Oro, island of Mindanao, Philippines.

Mount Binuluan is a remote volcano in the Kalinga province of the Cordillera Administrative Region of the Philippines. The 2,329-metre-high (7,641 ft) mountain is part of the Cordillera Central mountain range on Luzon island, the largest island in the country. Binuluan exhibits active volcanism through numerous fumarole fields, solfataras and hot springs on its slope. There were reports of possible eruptions in 1952 and 1986, but they are unverified.

Mount Malinao is a potentially active stratovolcano located in the Bicol Region of the Philippines. The volcano displays strong fumarolic activity which is harnessed for generating electricity. Located on its slope is Tiwi Geothermal Power Plant, one of the first geothermal energy plant commissioned in the country.

Puyehue and Cordón Caulle are two coalesced volcanic edifices that form a major mountain massif in Puyehue National Park in the Andes of Ranco Province, in the South of Chile. In volcanology this group is known as the Puyehue-Cordón Caulle Volcanic Complex (PCCVC). Four volcanoes constitute the volcanic group or complex, the Cordillera Nevada caldera, the Pliocene Mencheca volcano, Cordón Caulle fissure vents and the Puyehue stratovolcano.

Lastarria is a 5,697 metres (18,691 ft) high stratovolcano that lies on the border between Chile and Argentina. It is remote, and the surroundings are uninhabited but can be reached through an unpaved road. The volcano is part of the Central Volcanic Zone, one of the four segments of the volcanic arc of the Andes. Over a thousand volcanoes—of which about 50 are active—lie in this over 1,500 kilometres (930 mi) long chain of volcanoes, which is generated by subduction of the Nazca Plate beneath the South American Plate.

Apacheta-Aguilucho volcanic complex is a volcanic complex in Chile. It consists of two volcanoes Cerro Apacheta and Cerro Aguilucho, which are constructed mainly by lava flows and surrounded by outcrops of lava. A sector collapse and its landslide deposit are located on Apacheta's eastern flank. Two lava domes are associated with the volcanic complex, Chac-Inca and Pabellón.

Tutupaca is a volcano in the region of Tacna in Peru. It is part of the Peruvian segment of the Central Volcanic Zone, one of several volcanic belts in the Andes. Tutupaca consists of three overlapping volcanoes formed by lava flows and lava domes made out of andesite and dacite, which grew on top of older volcanic rocks. The highest of these is usually reported to be 5,815 metres (19,078 ft) tall and was glaciated in the past.
Soborom is a group of hot springs with accompanying fumaroles and mud volcanoes in the Tibesti Mountains of Chad. Three dispersed groups of vents are active there, some of which are used as spas by the local population.

Hveravellir is a geothermal field of the Oddnýjarhnjúkur-Langjökull subglacial volcanic system in the north of Langjökull glacier.

















