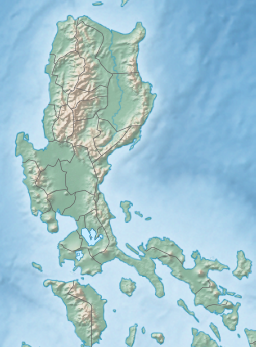
Ilocos Norte, officially the Province of Ilocos Norte, is a province of the Philippines located in the Ilocos Region. It is located in the northwest corner of Luzon Island, bordering Cagayan and Apayao to the east, and Abra to the southeast, and Ilocos Sur to the southwest. Ilocos Norte faces the South China Sea to the west and the Luzon Strait to the north. Its capital is Laoag City, which is the most populous in the province.

Davao del Norte, officially the Province of Davao del Norte, is a province in the Philippines located in the Davao Region in Mindanao. Its capital and largest city is Tagum. The province also includes Samal Island to the south in Davao Gulf.

Laoag, officially the City of Laoag, is a 3rd class component city and capital of the province of Ilocos Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 111,651 people.

Pagudpud, officially the Municipality of Pagudpud, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Ilocos Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 25,098 people.

Currimao, officially the Municipality of Currimao, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Ilocos Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 12,215 people.

Dingras, officially the Municipality of Dingras, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Ilocos Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 40,127 people distributed over 31 barangays.

Paoay, officially the Municipality of Paoay, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Ilocos Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 25,001 people.

Piddig, officially the Municipality of Piddig is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Ilocos Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 22,475 people.

Pinili, officially the Municipality of Pinili, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Ilocos Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 17,626 people.

San Nicolas, officially the Municipality of San Nicolas, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Ilocos Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 38,895 people.

Sarrat, officially the Municipality of Sarrat, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Ilocos Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 25,186 people.

Vintar, officially the Municipality of Vintar, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Ilocos Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 33,339 people.
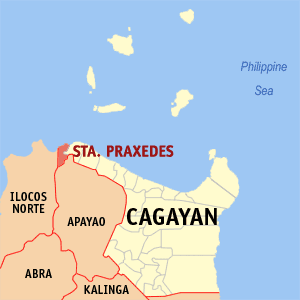
Santa Praxedes, officially the Municipality of Santa Praxedes, is a 5th class municipality in the province of Cagayan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 4,434 people, making it the least populated municipality in the province.

Calanasan, officially the Municipality of Calanasan, (Isnag: Ili naya Calanasan; Ilocano: Ili ti Calanasan; Tagalog: Bayan ng Calanasan), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Apayao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 12,550 people, making it the least populated municipality in the province.

Batac, officially the City of Batac, is a 5th class component city in the province of Ilocos Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 55,484 people.

Mariano Marcos State University is a higher education institution with campuses and facilities throughout Ilocos Norte province in the Philippines. Its main campus is in Batac.

The MacArthur Highway, officially the Manila North Road, is a 684.855-kilometer (425.549 mi), two-to-six lane, national primary highway and tertiary highway in Luzon, Philippines, connecting Caloocan in Metro Manila to Aparri in Cagayan at the north. It is the second longest road in the Philippines, after Pan-Philippine Highway. It is primarily known as MacArthur Highway in segments from Caloocan to Urdaneta, Pangasinan, although it is also applied up to Ilocos Sur, and likewise called as Manila North Road for the entire length.

The Saint Augustine Parish Church, commonly known as the Paoay Church, is a Roman Catholic church in the municipality of Paoay, Ilocos Norte in the Philippines. It is under the jurisdiction of the Diocese of Laoag. Completed in 1710, the church is famous for its distinct architecture highlighted by the enormous buttresses on the sides and back of the building. It is declared as a National Cultural Treasure by the Philippine government in 1973 and a UNESCO World Heritage Site under the collective group of Baroque Churches of the Philippines in 1993.

Saint Andrew the Apostle Parish, commonly known as Bacarra Church, is a Roman Catholic church located in the municipality of Bacarra, Ilocos Norte, Philippines under the jurisdiction of the Diocese of Laoag.

The Malacañang of the North is a presidential museum in Paoay, Ilocos Norte, Philippines. It was the residence of the family of Ferdinand Marcos when he was the President of the Philippines.