
The Philippines is an archipelago that comprises 7,641 islands with a total land area of 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi). It is the world's fifth largest island country. The eleven largest islands contain 95% of the total land area. The largest of these islands is Luzon at about 105,000 square kilometers (40,541 sq mi). The next largest island is Mindanao at about 95,000 square kilometers (36,680 sq mi). The archipelago is around 800 kilometers (500 mi) from the Asian mainland and is located between Taiwan and Borneo.

Manila Bay is a natural harbor that serves the Port of Manila, in the Philippines. Strategically located around the capital city of the Philippines, Manila Bay facilitated commerce and trade between the Philippines and its neighboring countries, becoming the gateway for socio-economic development even prior to Spanish occupation. With an area of 1,994 km2 (769.9 sq mi), and a coastline of 190 km (118.1 mi), Manila Bay is situated in the western part of Luzon and is bounded by Cavite and Metro Manila on the east, Bulacan and Pampanga on the north, and Bataan on the west and northwest. Manila Bay drains approximately 17,000 km2 (6,563.7 sq mi) of watershed area, with the Pampanga River contributing about 49% of the freshwater influx. With an average depth of 17 m (55.8 ft), it is estimated to have a total volume of 28.9 billion cubic meters. Entrance to the bay is 19 km (11.8 mi) wide and expands to a width of 48 km (29.8 mi). However, width of the bay varies from 22 km (13.7 mi) at its mouth and expanding to 60 km (37.3 mi) at its widest point.

The Philippine Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean east of the Philippine archipelago, the largest in the world, occupying an estimated surface area of 5 million square kilometers. The Philippine Sea Plate forms the floor of the sea. Its western border is the first island chain to the west, comprising the Ryukyu Islands in the northwest and Taiwan in the west. Its southwestern border comprises the Philippine islands of Luzon, Catanduanes, Samar, Leyte, and Mindanao. Its northern border comprises the Japanese islands of Honshu, Shikoku and Kyūshū. Its eastern border is the second island chain to the west, comprising the Bonin Islands and Iwo Jima in the northeast, the Mariana Islands in the due east, and Halmahera, Palau, Yap and Ulithi in the southeast. Its southern border is Indonesia's Morotai Island.

Macclesfield Bank is an elongated sunken atoll of underwater reefs and shoals in the South China Sea. It lies east of the Paracel Islands, southwest of Pratas Island and north of the Spratly Islands. It is about 130 km (81 mi) long from southwest to northeast, and about 70 km (43 mi) wide at its broadest part. With an ocean area of 6,448 km2 (2,490 sq mi) it is one of the largest atolls of the world. The Macclesfield Bank is part of what China calls the Zhongsha Islands, which includes a number of geographically separate submarine features, and also refers to a county-level administrative division.
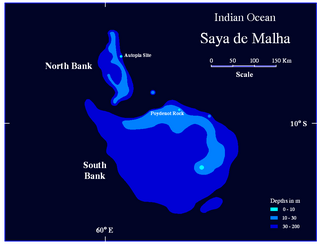
The Saya de Malha Bank is one of the largest submerged ocean banks in the world, a part of the vast undersea Mascarene Plateau.

Scarborough Shoal, also known as Bajo de Masinloc, Panatag Shoal, Huangyan Island, and Democracy Reef, are two rocks in a shoal located between Luzon and Macclesfield Bank within the Philippine EEZ in the South China Sea. It is 220 kilometres (119 nmi) away from the nearest landmass of Luzon, the largest island of the Philippines.

Southeast Asian coral reefs have the highest levels of biodiversity for the world's marine ecosystems. They serve many functions, such as forming the livelihood for subsistence fishermen and even function as jewelry and construction materials. Corals inhabit coastal waters off of every continent except Antarctica, with an abundance of reefs residing along Southeast Asian coastline in several countries including Indonesia, the Philippines, and Thailand. Coral reefs are developed by the carbonate-based skeletons of a variety of animals and algae. Slowly and overtime, the reefs build up to the surface in oceans. Coral reefs are found in shallow, warm salt water. The sunlight filters through clear water and allows microscopic organisms to live and reproduce. Coral reefs are actually composed of tiny, fragile animals known as coral polyps. Coral reefs are significantly important because of the biodiversity. Although the number of fish are decreasing, the remaining coral reefs contain more unique sea creatures. The variety of species living on a coral reef is greater than anywhere else in the world. An estimation of 70-90% of fish caught are dependent on coral reefs in Southeast Asia and reefs support over 25% of all known marine species. However, those sensitive coral reefs are facing detrimental effects on them due to variety of factors: overfishing, sedimentation and pollution, bleaching, and even tourist-related damage.

Blast fishing, fish bombing, or dynamite fishing is a destructive fishing practice using explosives to stun or kill schools of fish for easy collection. This often illegal practice is extremely destructive to the surrounding ecosystem, as the explosion often destroys the underlying habitat that supports the fish. The frequently improvised nature of the explosives used, and undetonated charges, means danger for fishermen and divers as well, with accidents and injuries.

Pulley Ridge is a mesophotic coral reef system off the shores of the continental United States. The reef rests on sunken barrier islands and lies 100 miles west of the Tortugas Ecological Reserve and stretches north about 60 miles at depths ranging from 60 to 80 meters. Pulley Ridge was originally discovered in 1950 during a dredging operation conducted by an academic group from Texas. While well known to fishermen, this remarkable habitat remained undiscovered by scientists until 1999 when the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) and graduate students from the University of South Florida happened upon it. This reef system, like other mesophotic ecosystems, is inhabited by photosynthesizing corals and algae that are adapted to low-light environments. It is habitat for numerous species of bottom fish including Epinephelus morio spawning area.
Today,environmental problems in the Philippines include pollution, illegal mining and logging, deforestation, threats to environmental activists, dynamite fishing, landslides, coastal erosion, biodiversity loss, extinction, global warming and climate change. Due to the paucity of extant documents, a complete history of land use in the archipelago remains unwritten. However, relevant data shows destructive land use increased significantly in the eighteenth century when Spanish colonialism enhanced its extraction of the archipelago's resources for the early modern global market. The Philippines is projected to be one of the most vulnerable countries to the impacts of climate change. Meanwhile, the country is projected to be one of the most vulnerable countries to the impacts of climate change, which would exacerbate these weather extremes. As The Philippines lies on the Pacific Ring of Fire, it is prone to natural disasters, like earthquakes, typhoons, and volcanic eruptions. In 2021, the Philippines ranked the fourth most affected country from "weather-related loss events", partly due to the close proximity of major infrastructure and residential areas to the coast and unreliable government support. One of the most devastating typhoons to hit the archipelago was Typhoon Haiyan, known locally as Yolanda, in 2013 that killed 6,300 people and left 28,689 injured. Philippine politicians have demonstrated awareness of environmental crises with the passing of policies like The Clean Air Act of 1999, the Philippine Clean Water Act of 2004, the Climate Change Act of 2009, and participation in the Paris Agreement. However, research has found that outside of cities, the general public doesn't feel equally informed. Environmental activists and land defenders, consisting mostly of Indigenous communities who have been attempting to bring attention to the environmental issues in the country have been met with violence or murder. As a result, the Philippines has been ranked one of the most dangerous places in the world for environmental activists.

The Philippines' Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources, is an agency of the Philippine government under the Department of Agriculture responsible for the development, improvement, law enforcement, management and conservation of the Philippines' fisheries and aquatic resources.
Oceana, inc. is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit ocean conservation organization focused on influencing specific policy decisions on the national level to preserve and restore the world's oceans. It is headquartered in Washington D.C. with offices in Juneau, Alaska, Monterey, California, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, New York City, New York, Portland, Oregon, Toronto, Ontario, Mexico City, Madrid, Brussels, Copenhagen, Geneva, London, Manila, Belmopan, Brasilia, Santiago, and Lima, and it is the largest international advocacy group dedicated entirely to ocean conservation.

The habitat of deep-water corals, also known as cold-water corals, extends to deeper, darker parts of the oceans than tropical corals, ranging from near the surface to the abyss, beyond 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) where water temperatures may be as cold as 4 °C (39 °F). Deep-water corals belong to the Phylum Cnidaria and are most often stony corals, but also include black and thorny corals and soft corals including the Gorgonians. Like tropical corals, they provide habitat to other species, but deep-water corals do not require zooxanthellae to survive.

The Coral Triangle (CT) is a roughly triangular area in the tropical waters around Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, the Solomon Islands and Timor-Leste. This area contains at least 500 species of reef-building corals in each ecoregion. The Coral Triangle is located between the Pacific and Indian oceans and encompasses portions of two biogeographic regions: the Indonesian-Philippines Region, and the Far Southwestern Pacific Region. As one of eight major coral reef zones in the world, the Coral Triangle is recognized as a global centre of marine biodiversity and a global priority for conservation. Its biological resources make it a global hotspot of marine biodiversity. Known as the "Amazon of the seas", it covers 5.7 million square kilometres (2,200,000 sq mi) of ocean waters. It contains more than 76% of the world's shallow-water reef-building coral species, 37% of its reef fish species, 50% of its razor clam species, six out of seven of the world's sea turtle species, and the world’s largest mangrove forest. In 2014, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) reported that the gross domestic product of the marine ecosystem in the Coral Triangle is roughly $1.2 trillion per year and provides food to over 120 million people. According to the Coral Triangle Knowledge Network, the region annually brings in about $3 billion in foreign exchange income from fisheries exports, and another $3 billion from coastal tourism revenues.
The Benham Rise, officially known as Philippine Rise, is an extinct volcanic ridge located in the Philippine Sea approximately 250 kilometers (160 mi) east of the northern coastline of Dinapigue, Isabela. The rise has been known to the people of Catanduanes as Kalipung-awan as early as the precolonial era of the Philippines, which literally means "loneliness from an isolated place".

Relations between People's Republic of China and the Philippines have suffered due to the worsening West Philippine Sea dispute. The current policy of the president of the Philippines aims for distancing relations between the Philippines and China to the benefit of the country's relationship with the United States, while the current policy of the president of China aims for greater influence over the Philippines, and the region in general, while combating American influence.

Angel Chua Alcala,, is a Filipino biologist who was named a National Scientist of the Philippines in 2014. Alcala is known for his fieldwork to build sanctuaries and to promote biodiversity in the aquatic ecosystems of the Philippines. He is currently Chairman of the Board of Advisers at the Angelo King Center for Research and Environmental Management located in Silliman University. Responsible for publishing more than 200 peer-reviewed articles and books, his biological contributions to the environment and ecosystems have made him a renowned hero for natural sciences in the Philippines.

Oxypora glabra is a species of large polyp stony coral in the family Lobophylliidae. It is a colonial coral with thin encrusting laminae. It is native to the central Indo-Pacific.

Climate change in the Philippines is having serious impacts such as increased frequency and severity of natural disasters, sea level rise, extreme rainfall, resource shortages, and environmental degradation. All of these impacts together have greatly affected the Philippines' agriculture, water, infrastructure, human health, and coastal ecosystems and they are projected to continue having devastating damages to the economy and society of the Philippines.
Josefa Slipways, Inc. is a medium-category shipbuilding company based in Navotas, Philippines. It was established in 2005 to provide shipbuilding and ship repair services to shipping companies and maritime government agencies in the Philippines. The company has two slipways in Navotas for docking and launching vessels as well as another facility in Sual, Pangasinan.



















