
Rio de Janeiro, or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of Rio de Janeiro. It is the second-most-populous city in Brazil and the sixth-most-populous city in the Americas.

Rio de Janeiro/Galeão–Antonio Carlos Jobim International Airport, popularly known by its original name Galeão International Airport, is the main international airport serving Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
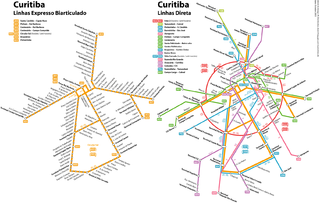
Rede Integrada de Transporte is a bus rapid transit (BRT) system in Curitiba, Brazil, implemented in 1974. It was one of the first BRT systems in the world and a component of one of the first and most successful examples of transit-oriented development.

Downtown Paterson is the main commercial district of Paterson, Passaic County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. The area is the oldest part of the city, along the banks of the Passaic River and its Great Falls. It is roughly bounded by Interstate 80, Garret Mountain Reservation, Route 19, Oliver Street, and Spruce Street on the south; the Passaic River, West Broadway, Cliff Street, North 3rd Street, Haledon Avenue, and the borough of Prospect Park on the west; and the Passaic River also to the north.

54th Street is a two-mile-long, one-way street traveling west to east across Midtown Manhattan in New York City.

Glória is a middle-class neighborhood of the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It is located between the neighbourhoods of Centro and Flamengo, Rio de Janeiro.

The São Mateus–Jabaquara metropolitan corridor (Portuguese: Corredor Metropolitano São Mateus-Jabaquara), also called ABD Corridor (Corredor ABD) is a bus rapid transit line in Brazil, linking the city of São Paulo to three neighboring cities, Diadema, São Bernardo do Campo and Santo André, as well as (indirectly) Mauá. Operations started in 1988. Its other name references one letter per city (A for Santo André, B for São Bernardo do Campo, and D for Diadema), the same way the ABC region in Greater São Paulo is named.

Vicente de Carvalho Station is an integrated Rio de Janeiro Metro subway and BRT bus station that services the neighbourhood of Vicente de Carvalho in the North Zone of Rio de Janeiro.

Terminal Alvorada is a bus station in Barra da Tijuca in the West Zone of Rio de Janeiro. The terminal was renovated in 2013.
Georgia Coates is a British swimmer who won five medals at the 2015 European Games. She has been selected to compete for Great Britain at the 2016 Summer Olympics in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.

The Atlantic Greyhound Bus Terminal, at 109 Martin Luther King, Jr. Blvd. in Savannah, Georgia was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2016.
BRT ABC is a future bus rapid transit (BRT) system for the southwest Greater São Paulo as a successor of the São Paulo Metro Line 18-Bronze monorail project, cancelled in 2019 by governor João Doria.










