A hedge fund is a pooled investment fund that trades in relatively liquid assets and is able to make extensive use of more complex trading, portfolio-construction and risk management techniques in an attempt to improve performance, such as short selling, leverage, and derivatives. Financial regulators generally restrict hedge fund marketing to institutional investors, high net worth individuals and others who are considered sufficiently sophisticated.
In finance, a put or put option is a financial market derivative instrument that gives the holder the right to sell an asset, at a specified price, by a specified date to the writer of the put. The purchase of a put option is interpreted as a negative sentiment about the future value of the underlying stock. The term "put" comes from the fact that the owner has the right to "put up for sale" the stock or index.

In finance, a warrant is a security that entitles the holder to buy the underlying stock of the issuing company at a fixed price called exercise price until the expiration date.

A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses or gains that may be incurred by a companion investment. A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, gambles, many types of over-the-counter and derivative products, and futures contracts.
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund and exchange-traded product, i.e. they are traded on stock exchanges. ETFs are similar in many ways to mutual funds, except that ETFs are bought and sold from other owners throughout the day on stock exchanges whereas mutual funds are bought and sold from the issuer based on their price at day's end. An ETF holds assets such as stocks, bonds, currencies, futures contracts, and/or commodities such as gold bars, and generally operates with an arbitrage mechanism designed to keep it trading close to its net asset value, although deviations can occasionally occur. Most ETFs are index funds: that is, they hold the same securities in the same proportions as a certain stock market index or bond market index. The most popular ETFs in the U.S. replicate the S&P 500 Index, the total market index, the NASDAQ-100 index, the price of gold, the "growth" stocks in the Russell 1000 Index, or the index of the largest technology companies. With the exception of non-transparent actively managed ETFs, in most cases, the list of stocks that each ETF owns, as well as their weightings, is posted daily on the website of the issuer. The largest ETFs have annual fees of 0.03% of the amount invested, or even lower, although specialty ETFs can have annual fees well in excess of 1% of the amount invested. These fees are paid to the ETF issuer out of dividends received from the underlying holdings or from selling assets.
In finance, the beta is a measure of how an individual asset moves when the overall stock market increases or decreases. Thus, beta is a useful measure of the contribution of an individual asset to the risk of the market portfolio when it is added in small quantity. Thus, beta is referred to as an asset's non-diversifiable risk, its systematic risk, market risk, or hedge ratio. Beta is not a measure of idiosyncratic risk.

The Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), located at 433 West Van Buren Street in Chicago, is the largest U.S. options exchange with annual trading volume that hovered around 1.27 billion contracts at the end of 2014. CBOE offers options on over 2,200 companies, 22 stock indices, and 140 exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
Long/short equity is an investment strategy generally associated with hedge funds. It involves buying equities that are expected to increase in value and selling short equities that are expected to decrease in value. This is different from the risk reversal strategies where investors will simultaneously buy a call option and sell a put option to simulate being long in a stock.
Active management is an approach to investing. In an actively managed portfolio of investments, the investor selects the investments that make up the portfolio. Active management is often compared to passive management or index investing.

Asset allocation is the implementation of an investment strategy that attempts to balance risk versus reward by adjusting the percentage of each asset in an investment portfolio according to the investor's risk tolerance, goals and investment time frame. The focus is on the characteristics of the overall portfolio. Such a strategy contrasts with an approach that focuses on individual assets.
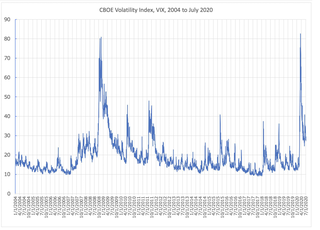
VIX is the ticker symbol and the popular name for the Chicago Board Options Exchange's CBOE Volatility Index, a popular measure of the stock market's expectation of volatility based on S&P 500 index options. It is calculated and disseminated on a real-time basis by the CBOE, and is often referred to as the fear index or fear gauge.
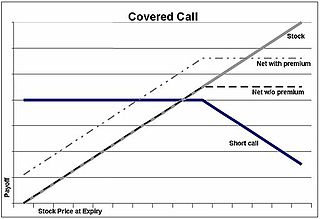
A covered call is a financial market transaction in which the seller of call options owns the corresponding amount of the underlying instrument, such as shares of a stock or other securities. If a trader buys the underlying instrument at the same time the trader sells the call, the strategy is often called a "buy-write" strategy. In equilibrium, the strategy has the same payoffs as buying a put option.
The CBOE S&P 500 BuyWrite Index is a benchmark index designed to show the hypothetical performance of a portfolio that engages in a buy-write strategy using S&P 500 index call options.

In finance, an option is a contract which conveys to its owner, the holder, the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset or instrument at a specified strike price on or before a specified date, depending on the style of the option. Options are typically acquired by purchase, as a form of compensation, or as part of a complex financial transaction. Thus, they are also a form of asset and have a valuation that may depend on a complex relationship between underlying asset value, time until expiration, market volatility, and other factors. Options may be traded between private parties in over-the-counter (OTC) transactions, or they may be exchange-traded in live, orderly markets in the form of standardized contracts.
Alternative beta is the concept of managing volatile "alternative investments", often through the use of hedge funds. Alternative beta is often also referred to as "alternative risk premia".
The CBOE S&P DJIA BuyWrite Index is a benchmark index designed to show the hypothetical performance of a portfolio that engages in a buy-write strategy on the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA).
A 130–30 fund or a ratio up to 150/50 is a type of collective investment vehicle, often a type of specialty mutual fund, but which allows the fund manager simultaneously to hold both long and short positions on different equities in the fund. Traditionally, mutual funds were long-only investments. 130–30 funds are a fast-growing segment of the financial industry; they should be available both as traditional mutual funds, and as exchange-traded funds (ETFs). While this type of investment has existed for a while in the hedge fund industry, its availability for retail investors is relatively new.
The CBOE S&P 500 PutWrite Index is a benchmark index that measures the performance of a hypothetical portfolio that sells S&P 500 Index (SPX) put options against collateralized cash reserves held in a money market account.
In finance, model risk is the risk of loss resulting from using insufficiently accurate models to make decisions, originally and frequently in the context of valuing financial securities. However, model risk is more and more prevalent in activities other than financial securities valuation, such as assigning consumer credit scores, real-time probability prediction of fraudulent credit card transactions, and computing the probability of air flight passenger being a terrorist. Rebonato in 2002 defines model risk as "the risk of occurrence of a significant difference between the mark-to-model value of a complex and/or illiquid instrument, and the price at which the same instrument is revealed to have traded in the market".

The Islamic banking and finance movement that developed in the late 20th century as part of the revival of Islamic identity sought to create an alternative to conventional banking that complied with sharia (Islamic) law. Following sharia it banned from its practices riba (usury) – which it defined as any interest paid on all loans of money – and involvement in haram (forbidden) goods or services such as pork or alcohol. It also forbids gambling (maisir) and excessive risk.







