
Trillium is a genus of about fifty flowering plant species in the family Melanthiaceae. Trillium species are native to temperate regions of North America and Asia, with the greatest diversity of species found in the southern Appalachian Mountains in the southeastern United States.
Grayanotoxins are a group of closely related neurotoxins named after Leucothoe grayana, a plant native to Japan originally named for 19th century American botanist Asa Gray. Grayanotoxin I is also known as andromedotoxin, acetylandromedol, rhodotoxin and asebotoxin. Grayanotoxins are produced by Rhododendron species and other plants in the family Ericaceae. Honey made from the nectar and so containing pollen of these plants also contains grayanotoxins and is commonly referred to as mad honey. Consumption of the plant or any of its secondary products, including mad honey, can cause a rare poisonous reaction called grayanotoxin poisoning, mad honey disease, honey intoxication, or rhododendron poisoning. It is most frequently produced and consumed in regions of Nepal and Turkey as a recreational drug and traditional medicine.
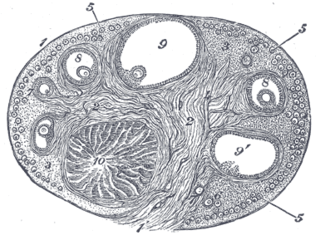
The corpus luteum is a temporary endocrine structure in female ovaries and is involved in the production of relatively high levels of progesterone and moderate levels of estradiol and inhibin A. It is the remains of the ovarian follicle that has released a mature ovum during a previous ovulation.

Trilliaceae was the botanical name of a family of flowering plants. The family has been recognised as distinct since 1846 when it was recognized; this table for a summarizes the placement of these taxa. The family has been recognized by taxonomists such as Takhtajan, Dahlgren, Thorne, and Watson & Dallwitz; other taxonomists have considered these plants to belong to the family Liliaceae. The APG IV system, of 2016, does not recognize such a family either and assigns the plants involved to family Melanthiaceae, tribe Parideae. One problem with this recognition is the lack of morphological synapomorphies for the family Melanthiaceae; this chart provides a summary of the characters in each of the major groups.

Gagea lutea, known as the yellow star-of-Bethlehem, is a Eurasian flowering plant species in the family Liliaceae. It is widespread in central Europe with scattered populations in Great Britain, Spain, and Norway to Siberia and Japan.

The buff ermine is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is sometimes placed in the genus Spilosoma. The species was first described by Johann Siegfried Hufnagel in 1766. It is found throughout the temperate belt of the Palearctic region south to northern Turkey, Georgia, Kazakhstan, southern Siberia, eastern Mongolia, Amur Region, China, Korea and Japan.

The endangered flower Delphinium luteum, the yellow larkspur, is a perennial of the buttercup family which is endemic to the rocky, foggy hillsides of coastal Sonoma County, California. As of 2005 there were about 200 individuals believed to be in existence. This rare plant is a small herb bearing bright yellow cornucopia-shaped flowers.

Rhododendron luteum, the yellow azalea or honeysuckle azalea, is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae, native to southeastern Europe and southwest Asia. In Europe, it occurs from southern Poland and Austria south through the Balkans and east to southern Russia; and in Asia, east to the Caucasus.

Trillium luteum, the yellow trillium or yellow wakerobin, is a species of flowering plant in the bunchflower family Melanthiaceae with native populations in the Great Smoky Mountains of the United States and surrounding areas.

Trillium sessile, known as toadshade, sessile trillium, sessile-flowered wake-robin, and toad trillium, is a perennial spring wildflower native to the central part of the eastern United States and the Ozarks. Toadshade can be distinguished from other Trillium species by its single, foul smelling, stalkless, flower nestled in the middle of its three bracts. The bracts are sometimes, but not always mottled with shades of light and dark green. The specific epithet comes from the Latin word sessilis which means low sitting, referring to its stalkless flower.

Chamaelirium is a genus of flowering plants containing the single species Chamaelirium luteum, commonly known as blazing-star, devil's bit, false unicorn, fairy wand, and helonias. It is a perennial herb native to the eastern United States. It can be found in a variety of habitats, including wet meadows and deciduous woodlands.

A corpus luteum cyst is a type of ovarian cyst which may rupture about the time of menstruation, and take up to three months to disappear entirely. A corpus luteum cyst rarely occurs in women over the age of 50, because eggs are no longer being released after menopause. Corpus luteum cysts may contain blood and other fluids. The physical shape of a corpus luteum cyst may appear as an enlargement of the ovary itself, rather than a distinct mass -like growth on the surface of the ovary.

Calostemma is a small genus of herbaceous, perennial and bulbous plants in the Amaryllis family, commonly known as Wilcannia Lily. It consists of three species endemic to Australia, where they are distributed in arid regions with summer precipitation.

Calostemma purpureum, the garland lily, is a long-lived perennial flowering plant that is native to South Australia, Victoria and New South Wales. Flowers may be cream, yellow, pink or purple. Related to the common daffodil, garland lilies were once common in large colonies in grassy areas, in particular the plain on which the city of Adelaide now stands. Due to urbanisation and grazing, the garland lily is now rare, only occurring in small pockets in parks on the outskirts of the city.

Solanum villosum, the hairy nightshade, red nightshade or woolly nightshade, is a sprawling annual weed in Europe, western Asia, northern Africa, North America, and is also naturalized in Australia.
Luteum or lutea may refer to:
Grapevine trunk diseases (GTD) are the most destructive diseases of vineyards worldwide. Fungicides with the potential to control GTD have been banned in Europe and there are no highly effective treatments available. Action to develop new strategies to fight these diseases are needed.
Peltophyllum is a genus of myco-heterotrophic plants in family Triuridaceae, native to southern South America. It contains the following species:

Rhabdadenia is a genus of plant in the family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1860. It is native to South America, Central America, southern Mexico, the West Indies, and Florida.
- Rhabdadenia barbata(Desv. ex Ham.) Miers = Pentalinon luteum(L.) B.F.Hansen & Wunderlin
- Rhabdadenia berteroi(A.DC.) Müll.Arg. = Angadenia berteroi(A.DC.) Miers
- Rhabdadenia campestris(Vell.) Miers = Mandevilla hirsuta(Rich.) K.Schum.
- Rhabdadenia corallicolaSmall = Angadenia berteroi(A.DC.) Miers
- Rhabdadenia cubensisMüll.Arg. = Angadenia berteroi(A.DC.) Miers
- Rhabdadenia laxifloraMiers = Pentalinon luteum(L.) B.F.Hansen & Wunderlin
- Rhabdadenia lindenianaMüll.Arg. = Angadenia lindeniana(Müll.Arg.) Miers
- Rhabdadenia lucidaMiers = Odontadenia nitida(Vahl) Müll.Arg.
- Rhabdadenia polyneuraUrb = Odontadenia polyneura(Urb.) Woodson
- Rhabdadenia sagrae(A.DC.) Müll.Arg. ex Griseb. = Angadenia berteroi(A.DC.) Miers
- Rhabdadenia wrightianaMüll.Arg. = Neobracea valenzuelana(A.Rich.) Urb.

Calostemmateae are a very small tribe of subfamily Amaryllidoideae. They are herbaceous monocot perennial flowering plants endemic to Australasia. The tribe consists of two genera, Proiphys and Calostemma.














