Related Research Articles

Hashish, or hash, is a drug made from the resin of the cannabis plant. It is consumed by inhaling from a small piece, typically in a pipe, bong, vaporizer or joint, or via oral ingestion. As pure hashish will not burn if rolled alone in a joint, it is typically mixed with herbal cannabis, tobacco or another type of herb for this method of consumption. Depending on region or country, multiple synonyms and alternative names exist.

While recreational use, possession and trade of non-medicinal drugs described by the Opium Law are all technically illegal under Dutch law, official policy since the late 20th century has been to openly tolerate all recreational use while tolerating the other two under certain circumstances. This pragmatic approach was motivated by the idea that a drug-free Dutch society is unrealistic and unattainable, and efforts would be better spent trying to minimize harm caused by recreational drug use. As a result of this gedoogbeleid, the Netherlands is typically seen as much more tolerant of drugs than most other countries.

The legality of cannabis for medical and recreational use varies by country, in terms of its possession, distribution, and cultivation, and how it can be consumed and what medical conditions it can be used for. These policies in most countries are regulated by the United Nations Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs that was ratified in 1961, along with the 1971 Convention on Psychotropic Substances and the 1988 Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances.

Medical cannabis, or medical marijuana (MMJ), is cannabis and cannabinoids that are prescribed by physicians for their patients. The use of cannabis as medicine has not been rigorously tested due to production and governmental restrictions, resulting in limited clinical research to define the safety and efficacy of using cannabis to treat diseases. Preliminary evidence suggests that cannabis can reduce nausea and vomiting during chemotherapy, improve appetite in people with HIV/AIDS, reduces chronic pain and muscle spasms and treats severe forms of epilepsy.

The Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of 1961 is an international treaty to prohibit production and supply of specific drugs and of drugs with similar effects except under licence for specific purposes, such as medical treatment and research. As noted below, its major effects included updating the Paris Convention of 13 July 1931 to include the vast number of synthetic opioids invented in the intervening thirty years and a mechanism for more easily including new ones. From 1931 to 1961, most of the families of synthetic opioids had been developed, including drugs related to methadone, pethidine (meperidine/Demerol), morphinans and dextromoramide. Research on fentanyls and piritramide was also nearing fruition at that point.

Cannabis, also known as marijuana among other names, is a psychoactive drug from the Cannabis plant used primarily for medical or recreational purposes. The main psychoactive component of cannabis is tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is one of the 483 known compounds in the plant, including at least 65 other cannabinoids. Cannabis can be used by smoking, vaporizing, within food, or as an extract.
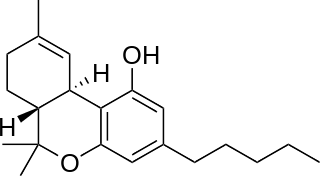
Nabiximols is a specific Cannabis extract that was approved in 2010 as a botanical drug in the United Kingdom despite a lack of convincing evidence of effectiveness for spasticity reduction. Nabiximols is sold as a mouth spray intended to alleviate neuropathic pain, spasticity, overactive bladder, and other symptoms of multiple sclerosis; it was developed by the UK company GW Pharmaceuticals. Nabiximols is a combination drug standardized in composition, formulation, and dose. Its principal active cannabinoid components are the cannabinoids: tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Each spray delivers a dose of 2.7 mg THC and 2.5 mg CBD.

This is a list of the annual prevalence of cannabis use by country as a percentage of the population aged 15–64. The indicator is an "annual prevalence" rate which is the percentage of the youth and adult population who have consumed cannabis at least once in the past survey year.
Adult lifetime cannabis use by country is the lifetime prevalence of cannabis use among all adults in surveys among the general population. Lifetime prevalence means any use of cannabis during a person’s life. Unless another reference is indicated all the data comes from the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addictions statistical bulletin from 2007.
Cannabis in Nigeria is illegal, yet the country is a major source of West African-grown cannabis, and ranked the world's eighth highest consumer of cannabis. Cannabis is widely grown across the States of Nigeria, including Ondo State, Edo State, Delta State, Osun State, Oyo State and Ogun State.
Cannabis in Namibia is illegal for recreational and medical uses, but cannabis and mandrax (methaqualone) are the most popular illicit drugs in the country. Per the 2011 UNODC report, the incidence of annual cannabis usage in Namibia was 3.9% in 2000.
Cannabis in Luxembourg is decriminalized for recreational use and legalized for medical use. Prosecution depends on the amount of cannabis one possesses. Since 2001, prison penalty has been substituted by a monetary fine ranging from 250 to 2,500 euros.

Cannabis in Albania is illegal, but the drug is widely cultivated.
Cannabis in Sierra Leone is illegal, but is widely cultivated and consumed in the country, and exported to neighboring countries and to Europe. Cannabis is known locally as diamba.
Cannabis in Gibraltar is illegal, but due to its proximity to North Africa and to mainland Europe, the area around Gibraltar in Spain is frequently used for cannabis trafficking. Gibraltar itself is not a usual destination for drug smuggling from Morocco as it only has a small population and customs controls with Spain make it difficult to move the merchandise further on into Europe. Gibraltarian authorities take a hard line on drug smuggling and prohibited the use of fast speed boats in its waters in 1995, a measure introduced by Spain in 2018.
Cannabis in Mauritania is illegal, but the country serves as a major transit point for Moroccan cannabis en route to Europe.
Cannabis in Mozambique is illegal; the drug is locally referred to as suruma.
Cannabis in Liechtenstein is illegal with severe penalties for the production, sale, and possession of marijuana for medicinal or recreational purposes.
Cannabis in Monaco is illegal with the production, sale, and possession of marijuana for medicinal or recreational purposes being a criminal offense with a penalty of up to one year in jail in addition to a fine of up to €1680. Despite the strong laws, the police and courts are often lenient, letting offenders off with a warning.
Cannabis in Haiti is illegal with severe punishments for the production, sale, and possession of marijuana for medicinal or recreational purposes.
References
- ↑ William R. Brownfield (May 2011). International Narcotics Control Strategy Report: Volume I: Drug and Chemical Control. DIANE Publishing. pp. 447–. ISBN 978-1-4379-8272-5.
- ↑ Europe's outdoor cannabis capital - BBC News