 Location of Vanuatu (red) | |
| Medicinal | Legal |
|---|---|
| Recreational | Illegal |
| Hemp | Legal |
| Part of a series on |
| Cannabis |
|---|
 |
Cannabis in Vanuatu is illegal for recreational purposes but is legal for medical and industrial purposes.
 Location of Vanuatu (red) | |
| Medicinal | Legal |
|---|---|
| Recreational | Illegal |
| Hemp | Legal |
| Part of a series on |
| Cannabis |
|---|
 |
Cannabis in Vanuatu is illegal for recreational purposes but is legal for medical and industrial purposes.
A 2017 news report noted recent increases in cannabis arrests as police attempted to clarify and enforce cannabis law on remote islands where "locals did not adapt." [1] A 2018 report recounted an incident on the Epi Island to Port Vila ferry where some 60 young people from Malekula were being transported under police escort for cannabis cultivation, distribution, and consumption. [2]
A September 2018 news report noted that Vanuatu's national health care system was considering clinical trials of a cannabis-based drug to treat diabetes. [3] On September 20, 2018, the government's Council of Ministers issued Decision 157/2018 allowing for the establishment of industries for the production of medical cannabis and industrial hemp. [4]

The legality of cannabis for medical and recreational use varies by country, in terms of its possession, distribution, and cultivation, and how it can be consumed and what medical conditions it can be used for. These policies in most countries are regulated by three United Nations treaties: the 1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, the 1971 Convention on Psychotropic Substances, and the 1988 Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances. Cannabis was reclassified in 2020 to a Schedule I-only drug under the Single Convention treaty, with the schedules from strictest to least being IV, I, II, and III. As a Schedule I drug under the treaty, countries can allow the medical use of cannabis but it is considered to be an addictive drug with a serious risk of abuse.

In the United States, increased restrictions and labeling of cannabis as a poison began in many states from 1906 onward, and outright prohibitions began in the 1920s. By the mid-1930s cannabis was regulated as a drug in every state, including 35 states that adopted the Uniform State Narcotic Drug Act. The first national regulation was the Marihuana Tax Act of 1937.

The use, sale, and possession of cannabis containing over 0.3% THC by dry weight in the United States, despite laws in many states permitting it under various circumstances, is illegal under federal law. As a Schedule I drug under the federal Controlled Substances Act (CSA) of 1970, cannabis containing over 0.3% THC by dry weight is considered to have "no accepted medical use" and a high potential for abuse and physical or psychological dependence. Cannabis use is illegal for any reason, with the exception of FDA-approved research programs. However, individual states have enacted legislation permitting exemptions for various uses, including medical, industrial, and recreational use.

Cannabis in the United Kingdom is illegal for recreational use and is classified as a Class B drug. In 2004, the United Kingdom made cannabis a Class C drug with less severe penalties, but it was moved back to Class B in 2009. Medical use of cannabis, when prescribed by a registered specialist doctor, was legalised in November 2018.

Cannabis in British Columbia (BC) relates to a number of legislative, legal, and cultural events surrounding the use and cultivation of cannabis in the Canadian province of British Columbia. As with the rest of Canada, cannabis became legalized on 17 October 2018, following the enactment of the Cannabis Act, or Bill C-45. Prior to that, though the drug was illegal in Canada, its recreational use was often tolerated and was more commonplace in the province of BC as compared to most of the rest of the country. The province's inexpensive hydroelectric power and abundance of water and sunshine—in addition to the many hills and forests —made it an ideal cannabis growing area. The British Columbia cannabis industry is worth an estimated CA$2 billion annually and produces 36.6 percent of all Canadian cannabis. The province is also the home of the cannabis activist and businessman Marc Emery.

In the United States, cannabis is legal in 38 of 50 states for medical use and 24 states for recreational use. At the federal level, cannabis is classified as a Schedule I drug under the Controlled Substances Act, determined to have a high potential for abuse and no accepted medical use, prohibiting its use for any purpose. Despite this prohibition, federal law is generally not enforced against the possession, cultivation, or intrastate distribution of cannabis in states where such activity has been legalized. On May 1, 2024, the Associated Press reported on plans by the Drug Enforcement Administration to move marijuana to the less-restrictive Schedule III.
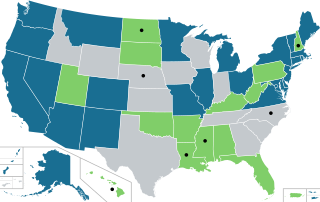
The legal history of cannabis in the United States began with state-level prohibition in the early 20th century, with the first major federal limitations occurring in 1937. Starting with Oregon in 1973, individual states began to liberalize cannabis laws through decriminalization. In 1996, California became the first state to legalize medical cannabis, sparking a trend that spread to a majority of states by 2016. In 2012, Washington and Colorado became the first states to legalize cannabis for recreational use.

Cannabis in India has been known to be used at least as early as 2000 BCE. In Indian society, common terms for cannabis preparations include charas (resin), ganja (flower), and bhang, with Indian drinks such as bhang lassi and bhang thandai made from bhang being one of the most common legal uses.
Cannabis in Texas is illegal for recreational use. Possession of up to two ounces is a class B misdemeanor, punishable by up to 180 days in prison and a fine of up to $2000. Several of the state's major municipalities have enacted reforms to apply lesser penalties or limit enforcement, however.

Cannabis in New York has been legal for medical purposes under New York law since 2016, and recreational purposes since 2021. As of 2022, recreational cannabis is for sale legally in the state, only through state-approved dispensaries.

Cannabis in Hawaii is illegal for recreational use, but decriminalized for possession of three grams or less. Medical use was legalized through legislation passed in 2000, making Hawaii the first state to legalize medical use through state legislature rather than through ballot initiative.

Cannabis in New Jersey is legal for both medical use and recreational use. An amendment to the state constitution legalizing cannabis became effective on January 1, 2021, and enabling legislation and related bills were signed into law by governor Phil Murphy on February 22, 2021.
Cannabis in Greece is illegal for recreational purposes. In 2017, the Greek government legalized the use of cannabis for medical purposes, and a year later, they lifted the ban on growing or producing it. This enables pharmaceutical companies to grow cannabis legally, and industrial hemp suppliers too.
Cannabis in Italy is currently legal for medical and industrial uses, although it is strictly regulated, while it is decriminalized for recreational uses. In particular, the possession of small amounts of marijuana for personal use is a civil infraction. The possible sanctions for possession vary from the issuing of a diffida to first offenders, that is an injunction not to use the drug again; to the temporary suspension of certain personal documents for repeat offenders. Conversely, the unauthorized sale of cannabis-related products is illegal and punishable with imprisonment, as is the unlicensed cultivation of cannabis, although recent court cases have effectively established the legality of cultivating small amounts of cannabis for exclusively personal use. The licensed cultivation of cannabis for medical and industrial purposes requires the use of certified seeds; however, there is no need for authorization to plant certified seeds with minimal levels of psychoactive compounds.

Cannabis has been cultivated in Japan since the Jōmon period of Japanese prehistory approximately six to ten thousand years ago. As one of the earliest cultivated plants in Japan, cannabis hemp was an important source of plant fiber used to produce clothing, cordage, and items for Shinto rituals, among numerous other uses. Hemp remained ubiquitous for its fabric and as a foodstuff for much of Japanese history, before cotton emerged as the country's primary fiber crop amid industrialization during the Meiji period. Following the conclusion of the Second World War and subsequent occupation of Japan, a prohibition on cannabis possession and production was enacted with the passing of the Cannabis Control Law.
The list includes and details significant events that occurred in the global history of national-level implementations of, or changes made to, laws surrounding the use, sale, or production of the psychoactive drug cannabis.

The Cannabis Act (C-45) of June, 2018 paved the way for the legalization of cannabis in Canada on 17 October 2018. Police and prosecution services in all Canadian jurisdictions are currently capable of pursuing criminal charges for cannabis marketing without a licence issued by Health Canada. The Supreme Court of Canada has held that the federal Parliament has the power to criminalize the possession of cannabis and that doing so does not infringe upon the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms. The Ontario Court of Appeal and the Superior Court of Ontario have, however, held that the absence of a statutory provision for medical marijuana is unconstitutional, and to that extent the federal law is of no force and/or effect if a prescription is obtained. The recreational use of cannabis has been legalized by the federal government, and took effect on 17 October 2018.

Cannabis in Ontario is legal for both medical and recreational purposes. Cannabis in Canada has been legal for medicinal purposes since 2001 under conditions outlined in the Access to Cannabis for Medical Purposes Regulations, issued by Health Canada, while seed, grain, and fibre production are permitted under licence. The federal Cannabis Act, legalizing cannabis for recreational use, came into effect on 17 October 2018.

Cannabis in Prince Edward Island became legal when the national Cannabis Act went into force on October 17, 2018.

Cannabis in Saskatchewan became legal when the national Cannabis Act went into force on 17 October 2018.