Related Research Articles

The Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively known as the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS), regulate international relations with respect to Antarctica, Earth's only continent without a native human population. It was the first arms control agreement established during the Cold War, designating the continent as a scientific preserve, establishing freedom of scientific investigation, and banning military activity; for the purposes of the treaty system, Antarctica is defined as all the land and ice shelves south of 60°S latitude. Since September 2004, the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat, which implements the treaty system, is headquartered in Buenos Aires, Argentina.

The Ross Dependency is a region of Antarctica defined by a sector originating at the South Pole, passing along longitudes 160° east to 150° west, and terminating at latitude 60° south. It is claimed by New Zealand, a claim accepted by the other six countries with territorial claims in Antarctica. Under the 1961 Antarctic Treaty, of which all territorial claimants are signatories, including New Zealand, all claims are held in abeyance. Article IV states: "No acts or activities taking place while the present Treaty is in force shall constitute a basis for asserting, supporting or denying a claim to territorial sovereignty in Antarctica or create any rights of sovereignty in Antarctica".

The legality of cannabis for medical and recreational use varies by country, in terms of its possession, distribution, and cultivation, and how it can be consumed and what medical conditions it can be used for. These policies in most countries are regulated by three United Nations treaties: the 1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, the 1971 Convention on Psychotropic Substances, and the 1988 Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances. Since its descheduling in 2020, cannabis is classified as a Schedule I drug under the Single Convention treaty, meaning that signatories can allow medical use but that it is considered to be an addictive drug with a serious risk of abuse.

The British Antarctic Territory (BAT) is a sector of Antarctica claimed by the United Kingdom as one of its 14 British Overseas Territories, of which it is by far the largest by area. It comprises the region south of 60°S latitude and between longitudes 20°W and 80°W, forming a wedge shape that extends to the South Pole, overlapped by the Antarctic claims of Argentina and Chile. The claim to the region has been suspended since the Antarctic Treaty came into force in 1961.

This is a timeline of the history of New Zealand's involvement with Antarctica.

The United States Antarctic Program is an organization of the United States government which has a presence in the Antarctica continent. Founded in 1959, the USAP manages all U.S. scientific research and related logistics in Antarctica as well as aboard ships in the Southern Ocean.

The Misuse of Drugs Act 1975 is a New Zealand drug control law that classifies drugs into three classes, or schedules, purportedly based on their projected risk of serious harm. However, in reality, classification of drugs outside of passing laws, where the restriction has no legal power, is performed by the governor-general in conjunction with the Minister of Health, neither of whom is actually bound by law to obey this restriction.

Drug liberalization is a drug policy process of decriminalizing or legalizing the use or sale of prohibited drugs. Variations of drug liberalization include drug legalization, drug relegalization, and drug decriminalization. Proponents of drug liberalization may favor a regulatory regime for the production, marketing, and distribution of some or all currently illegal drugs in a manner analogous to that for alcohol, caffeine and tobacco.
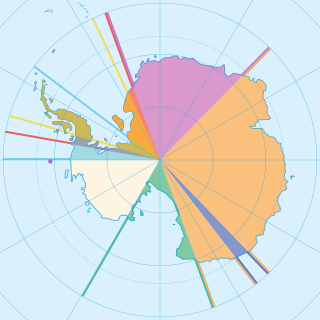
Seven sovereign states – Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the United Kingdom – have made eight territorial claims in Antarctica. These countries have tended to place their Antarctic scientific observation and study facilities within their respective claimed territories; however, a number of such facilities are located outside of the area claimed by their respective countries of operation, and countries without claims such as China, India, Italy, Japan, Pakistan, Russia, South Africa (SANAE), Poland, and the United States have constructed research facilities within the areas claimed by other countries. There are overlaps among the territories claimed by Argentina, Chile, and the United Kingdom.

Tourism started in Antarctica by the sea in the 1960s. Air overflights started in the 1970s with sightseeing flights by airliners from Australia and New Zealand, and were resumed in the 1990s. The (summer) tour season lasts from November to March. Most of the estimated 14,762 visitors to Antarctica from 1999–2000 were on sea cruises. During the 2009 to 2010 tourist season, over 37,000 people visited Antarctica.
In the early 21st century, advocacy for drug legalization has increased in Latin America. Spearheading the movement, the Uruguayan government announced in 2012 plans to legalize state-controlled sales of marijuana in order to fight drug-related crimes.

Cannabis is legal in Uruguay, and is one of the most widely used drugs in the nation.

"Weed the People", officially "Weed the People: A Cannabis Legalization Celebration", was an event held in Portland on July 3, 2015, two days after recreational marijuana became legal in the U.S. state of Oregon. Sponsored by the Portland Mercury and two cannabis companies, the event was attended by an estimated 1,500–2,000 people, who were provided up to seven grams of marijuana for immediate consumption or to take home. Organizers complied with restrictions on recreational sales by distributing free cannabis and required attendees to pay an entry fee. More than 1,300 tickets were sold, but the building's 500-person capacity meant long wait times to enter. Media outlets reported on the historic nature of the event, which was described as a "stoner's paradise" and a celebration of freedom.

Cannabis in India has been known to be used at least as early as 2000 BCE. In Indian society, common terms for cannabis preparations include charas (resin), ganja (flower), and bhang, with Indian drinks such as bhang lassi and bhang thandai made from bhang being one of the most common legal uses.

Minors and the legality of cannabis is one of the issues around the legalisation of cannabis, with most jurisdictions placing strict age limits in a similar way as is done with the drinking age for alcohol.

−

The possession, use, and distribution of cannabis without a license in the State of Israel are violations under the Dangerous Drugs Ordinance. A decade ago, despite these regulations, enforcement was relatively lax, partially influenced by a political movement advocating tolerance. Over the years, the enforcement approach has progressively become more lenient. As of 2021, cannabis use has been fully decriminalized, with it being treated as an administrative infraction primarily when used in highly visible public places. There is a possibility that cannabis may be legalized for recreational use by adults aged 21 and older in the future, with regulations akin to those for alcohol. Public and cross-party political support for the complete decriminalization of cannabis increased in the 2010s with increasing usage for both medical and recreational purposes, and the establishment of a political party primarily devoted to this cause; on July 19, 2018, the Knesset approved a bill for decriminalization, although the supporters of recreational cannabis use insisted that this did not represent complete decriminalization. The law came into effect on April 1, 2019. On June 25, 2020, further legislation designed to decriminalize possession of up to 50 grams of cannabis began its passage through the Knesset.

The Cannabis Act is a law which legalized recreational cannabis use in Canada in combination with its companion legislation Bill C-46, An Act to Amend the Criminal Code. The law is a milestone in the legal history of cannabis in Canada, alongside the 1923 prohibition.
Whilst crime in Antarctica is relatively rare, isolation and boredom affect certain people there negatively and may lead to crime. Alcoholism is a known problem on the continent and has led to fights and indecent exposure. Other types of crime that have occurred in Antarctica include illicit drug use, torturing and killing wildlife, racing motorbikes through environmentally sensitive areas, assault with a deadly weapon, attempted murder and arson. Sexual harassment also has been reported.
References
Sources
- Ali Wunderman (July 6, 2018), "Can you smoke weed in Antarctica?", High Times
- Robert Reinhold (November 30, 1981). "Drugs are an issue at the south pole". The New York Times.
- David Downs (April 25, 2011). "U.S. Marshals: No Dope Growing in Antarctica!". East Bay Express . Oakland, California.
- David Hillier (April 17, 2019), "These are the Countries Most Likely to Legalize Weed Next", Vice ,
Antarctica has no government and no laws, so technically, as long as no one squabbles over their gear, you can toke away should you find yourself cruising the research stations of the icy province. However, scientists there are governed by the laws of their own land. So in principle, Canadians and Uruguayans can already toke on the South Pole, while Mexicans willing to deal with temperatures of -50°C should be able to roll up in front of the penguins before the end of the year.
- David Fisher (March 14, 2009), "Death on the ice", The New Zealand Herald , Auckland