
Suzlon Energy is an Indian multinational wind turbine manufacturer headquartered in Pune.

Tarago is a town in the Southern Tablelands of New South Wales, Australia in Goulburn Mulwaree Council. Part of the defined locality, which includes a large area of grazing country, is on the eastern shore of Lake George in the area of the Queanbeyan–Palerang Regional Council. The town is situated 39 kilometres south of the city of Goulburn and 69 kilometres northeast of Canberra, the capital city of Australia. It is located on the Goulburn-Braidwood road. The town is notable for recent renewable energy projects in the surrounding districts.

Bungendore is a town in the Queanbeyan Region of New South Wales, Australia, in Queanbeyan-Palerang Regional Council. It is on the Kings Highway near Lake George, the Molonglo River Valley and the Australian Capital Territory border. It has become a major tourist centre in recent years, popular with visitors from Canberra and some of it has heritage protection. It has expanded rapidly in recent years as a dormitory town of Canberra.

AGL Energy Ltd is an Australian listed public company involved in both the generation and retailing of electricity and gas for residential and commercial use. AGL is Australia's largest electricity generator, and the nation's largest carbon emitter. In 2022, 83% of its energy came from burning coal. It produces more emissions as a single company than the nations of New Zealand, Portugal or Sweden, according to its largest shareholder, Mike Cannon-Brookes, who named it "one of the most toxic companies on the planet".

Wind power in Germany is a growing industry. The installed capacity was 55.6 gigawatts (GW) at the end of 2017, with 5.2 GW from offshore installations. In 2020, 23.3% of the country's total electricity was generated through wind power, up from 6.2% in 2010 and 1.6% in 2000.

Wind power became a significant energy source within South Australia over the first two decades of the 21st century. In 2015, there was an installed capacity of 1,475 MW, which accounted for 34% of electricity production in the state. This accounted for 35% of Australia's installed wind power capacity. In 2021, there was an installed capacity of 2052.95 MW, which accounted for 42.1% of the electricity production in the state in 2020.

The Hallett Wind Farm is the collective name for four wind farms near the town of Hallett, South Australia. They are owned and operated by AGL Energy.
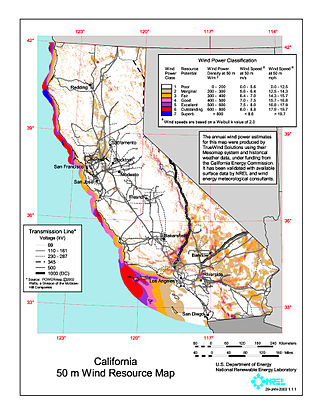
Wind power in California had initiative and early development during Governor Jerry Brown's first two terms in the late 1970s and early 1980s. The state's wind power capacity has grown by nearly 350% since 2001, when it was less than 1,700 MW. In 2016, wind energy supplied about 6.9% of California's total electricity needs, or enough to power more than 1.3 million households. Most of California's wind generation is found in the Tehachapi area of Kern County, California, with some large projects in Solano, Contra Costa and Riverside counties as well. California is among the states with the largest amount of installed wind power capacity. In recent years, California has lagged behind other states when it comes to the installation of wind power. It was ranked 4th overall for wind power electrical generation at the end of 2016 behind Texas, Iowa, and Oklahoma. As of 2019, California had 5,973 megawatts (MW) of wind power generating capacity installed.

China is the world leader in wind power generation, with the largest installed capacity of any nation and continued rapid growth in new wind facilities. With its large land mass and long coastline, China has exceptional wind power resources: Wind power remained China's third-largest source of electricity at the end of 2021, accounting for 7.5% of total power generation.

Wind power constitutes a small but growing proportion of New Zealand's electricity. As of December 2020, wind power accounts for 690 MW of installed capacity and over 5 percent of electricity generated in the country.
The Sydney Desalination Plant also known as the Kurnell Desalination Plant is a potable drinking water desalination plant that forms part of the water supply system of Greater Metropolitan Sydney. The plant is located in the Kurnell industrial estate, in Southern Sydney in the Australian state of New South Wales. The plant uses reverse osmosis filtration membranes to remove salt from seawater and is powered using renewable energy, supplied to the national power grid from the Infigen Energy–owned Capital Wind Farm located at Bungendore.
The Macarthur Wind Farm is a wind farm located in Macarthur, Victoria, Australia, near Hamilton, 260 km west of Melbourne. It is on a 5,500 ha site which has an installed capacity of 420 megawatts (MW). Based on a capacity factor of around 35%, it is estimated that the long-term average generation will be approximately 1,250 GWh per year. Its actual capacity factor is much lower, with a historical average of 26.29% since 2013.

Australia is the driest habitable continent on Earth and its installed desalination capacity has been increasing. Until a few decades ago, Australia met its demands for water by drawing freshwater from dams and water catchments. As a result of the water supply crisis during the severe 1997–2009 drought, state governments began building desalination plants that purify seawater using reverse osmosis technology. Approximately one percent of the world's drinkable water originates from desalination plants.

Energy in Jordan describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Jordan. Jordan is among the highest in the world in dependency on foreign energy sources, with 92.3% of the country's energy supply being imported.

Infigen Energy (Infigen), operating under this name since 29 April 2009, is a developer, owner and operator of renewable energy generation assets in Australia. Infigen's wind farm portfolio has an installed capacity of 557 MW. Most of Infigen's assets generate electricity from renewable sources and are eligible to sell Large-scale Generation Certificates (LGCs) under the mandatory Renewable Energy Target scheme, which operates in Australia under the Renewable Energy (Electricity) Act 2000. Since 2020, Infigen Energy has been a subsidiary of Iberdrola.
The Woodlawn Wind Farm is a wind farm located near Bungendore, New South Wales. It is part of the Capital Renewable Energy Precinct, along with nearby Capital Wind Farm and the Woodlawn Bioreactor.
Temporary Generation South and its larger sibling Temporary Generation North were gas turbine power stations in South Australia. They were bought by the Government of South Australia in 2017 as a response to the 2016 South Australian blackout and load-shedding in February 2017.

Bodangora Wind Farm is a 113.2 MW wind farm owned by Infigen Energy in the district of Bodangora near Wellington, New South Wales, Australia. It consists of 33 wind turbines. The towers are 85 metres tall, and the rotor diameter is 130 metres. The wind turbine blades were manufactured in Bergama, Turkey. The development of the project began in 2009. It received planning approval in August 2013. The wind farm was completed on 27 February 2019. Annually it is supposed to generate on average 361 GWh of energy at capacity factor of 36.4%.















