
Cortaderia is a genus of plants in the Poaceae or grass family of plants.

The Australian wood duck, maned duck or maned goose is a dabbling duck found throughout much of Australia. It is the only living species in the genus Chenonetta. Traditionally placed in the subfamily Anatinae, it might belong to the subfamily Tadorninae (shelducks); the ringed teal may be its closest living relative.

The dark dagger is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775. It is distributed throughout Europe, Turkey, the Near East, the European part of Russia, southern Siberia, the Ural, the Russian Far East, the Korean Peninsula, China and Japan (Hokkaido).

Caragana is a genus of about 80–100 species of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae, native to Asia and eastern Europe.

Gynerium is a monotypic genus of Neotropical plants in the grass family, native to Mexico and Colombia, Central America, South America, and the West Indies. It is classified in its own tribe Gynerieae.

Caragana arborescens, the Siberian peashrub, Siberian pea-tree, or caragana, is a species of legume native to Siberia and parts of China and neighboring Mongolia and Kazakhstan. It was taken to the United States by Eurasian immigrants, who used it as a food source while travelling west. In some areas of the United States it is considered an invasive species. Introduced on the Canadian prairies in the 1880's, the hardy caragana provided shelter-belts, wildlife habitat, nitrogen fixation, and windbreaks to prevent soil erosion and snow drifting.

Pfaffia is a genus of plants in the family Amaranthaceae.

Pfaffia jubata is a plant native to cerrado vegetation in Brazil.

Gennady Pavlovich Yakovlev was a Russian botanist, pharmacognosist, phytochemist. He was a director of Saint-Petersburg State Chemical-Pharmaceutical Academy (1992–2004), and an expert in Fabaceae taxonomy. Yakovlev died on 12 January 2024, at the age of 85.

Caragana halodendron is a species of flowering plant in the pea family (Fabaceae). It is known by several common names, including common salt tree and Russian salt tree. It is native to Russia and southern Asia, but it can be found on other continents where it is an introduced species, and one that is often a noxious weed. This is a deciduous spiny shrub sprawling to a few meters in maximum width and up to three meters tall. Stems branch from the base and bear clusters of about four leaflets on sharp spurs. The ends of branches narrow to spines. Flowers also appear at the ends of spurs in clusters of two to four pink pealike blossoms each one to two centimeters wide. The fruit is a black woody inflated pod about 2 centimeters long containing legume seeds. The plant has a deep and wide root system, with the lateral roots sending up new shoots. In this manner the plant forms extensive thickets. When introduced to an area of suitable climate, such as California where it is a known weed, it can invade cultivated land and spread relatively quickly. It is tolerant of saline soils.

The Western Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion of Nepal, India, and Tibet, which lies between the tree line and snow line in the western portion of the Himalaya Range.

Cortaderia jubata is a species of grass known by several common names, including purple pampas grass and Andean pampas grass. It is similar to its more widespread relative, the pampas grass C. selloana, but it can get quite a bit taller, approaching seven meters in height at maximum.

Calophaca is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It includes nine species, which range from Ukraine through southern Russia and Central Asia to Xinjiang and Pakistan. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae and is closely related to the genus Caragana. Nine species are accepted:

α-Viniferin is a stilbene trimer. It can be isolated from Caragana chamlagu and from Caragana sinica and from the stem bark of Dryobalanops aromatica. It is also present in relation to resistance to Botrytis cinerea and Plasmopara viticola in Vitis vinifera and Vitis riparia. It has been shown to inhibit acetylcholinesterase.
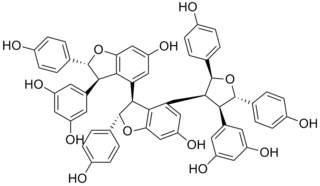
Kobophenol A is a stilbenoid. It is a tetramer of resveratrol. It can be isolated from Caragana chamlagu, from Caragana sinica and from Carex folliculata seeds.

A tetramer (tetra-, "four" + -mer, "parts") is an oligomer formed from four monomers or subunits. The associated property is called tetramery. An example from inorganic chemistry is titanium methoxide with the empirical formula Ti(OCH3)4, which is tetrameric in solid state and has the molecular formula Ti4(OCH3)16. An example from organic chemistry is kobophenol A, a substance that is formed by combining four molecules of resveratrol.
Coleophora kaszabi is a moth of the family Coleophoridae. It is found in Mongolia.
Miyabenol C is a stilbenoid. It is a resveratrol trimer. It is found in Vitis vinifera (grape), in Foeniculi fructus, in Caragana sinica.

Caragana frutex is a species of flowering plant belonging to the family Fabaceae.
Caragana korshinskii, also known as the Korshinsk pea shrub, is a shrub from the genus Caragana. The plant is native to sandy grass and desert areas of northern China and Mongolia. This plant is a minor host of Scolytus schevyrewi. Caragana korshinskii is utilized in Northern China for both the fixation of sand and soil/water conservation. This plant is found in desert regions of China and is adapted to suit that environment. This adaption is seen in its ability to survive under conditions prone to salty, cold, and dry conditions.
















