Related Research Articles

Obsidian is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock.

Long Valley Caldera is a depression in eastern California that is adjacent to Mammoth Mountain. The valley is one of the Earth's largest calderas, measuring about 20 mi (32 km) long (east-west), 11 mi (18 km) wide (north-south), and up to 3,000 ft (910 m) deep.

Mono County is a county located in the east central portion of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 13,195, making it the fourth-least populous county in California. The county seat is Bridgeport. The county is located east of the Sierra Nevada between Yosemite National Park and Nevada. The only incorporated town in the county is Mammoth Lakes, which is located at the foot of Mammoth Mountain. Other locations, such as June Lake, are also famous as skiing and fishing resorts. Located in the middle of the county is Mono Lake, a vital habitat for millions of migratory and nesting birds. The lake is located in a wild natural setting, with pinnacles of tufa arising out of the salty and alkaline lake. Also located in Mono County is Bodie, the official state gold rush ghost town, which is now a California State Historic Park.

Mammoth Lakes is a town in Mono County, California, and is the county's only incorporated community. It is located immediately to the east of Mammoth Mountain, at an elevation of 7,880 feet (2,400 m). As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 7,191, reflecting a 12.7% decrease from the 2010 Census.
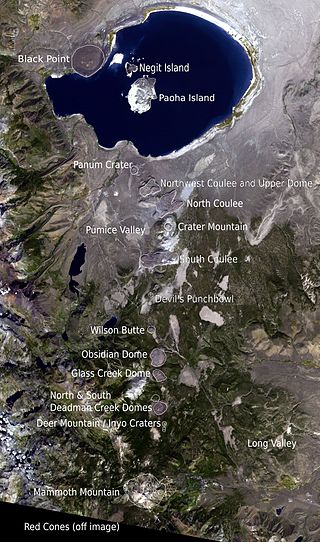
The Mono–Inyo Craters are a volcanic chain of craters, domes and lava flows in Mono County, Eastern California. The chain stretches 25 miles (40 km) from the northwest shore of Mono Lake to the south of Mammoth Mountain. The Mono Lake Volcanic Field forms the northernmost part of the chain and consists of two volcanic islands in the lake and one cinder cone volcano on its northwest shore. Most of the Mono Craters, which make up the bulk of the northern part of the Mono–Inyo chain, are phreatic volcanoes that have since been either plugged or over-topped by rhyolite domes and lava flows. The Inyo volcanic chain form much of the southern part of the chain and consist of phreatic explosion pits, and rhyolitic lava flows and domes. The southernmost part of the chain consists of fumaroles and explosion pits on Mammoth Mountain and a set of cinder cones south of the mountain; the latter are called the Red Cones.

Pacheco Pass, elevation 1,368 ft (417 m), is a low mountain pass located in the Diablo Range in southeastern Santa Clara County, California. It is the main route through the hills separating the Santa Clara Valley and the Central Valley.
The State Scenic Highway System in the U.S. state of California is a list of highways, mainly state highways, that have been designated by the California Department of Transportation (Caltrans) as scenic highways. They are marked by the state flower, a California poppy, inside either a rectangle for state-maintained highways or a pentagon for county highways.

Convict Lake is a lake located in Mono County, California, United States, situated in the Sherwin Range of the Sierra Nevada. It is known for its turquoise-blue water, the dramatic mountains that surround it, the trout fishing it affords, and its unusual history. The lake was renamed from its traditional Mono name by American settlers after an incident on September 23, 1871, in which a group of convicts escaped from prison in Carson City, Nevada, and took refuge near the lake. They were pursued by a posse, and after it caught up to the convicts, a shootout followed, in which a number of both posse members and convicts were killed or wounded. The remaining convicts who survived initially escaped but were eventually captured to be taken back to prison. They were lynched instead.

The Coso Volcanic Field is located in Inyo County, California, at the western edge of the Basin and Range geologic province and northern region of the Mojave Desert. The Fossil Falls are part of the Coso Field, created by the prehistoric Owens River. They are within the Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake and northeast of Little Lake and U.S. Route 395.

U.S. Route 395 (US 395) is a United States Numbered Highway, stretching from Hesperia, California to the Canadian border in Laurier, Washington. The California portion of US 395 is a 557-mile (896 km) route which traverses from Interstate 15 (I-15) in Hesperia, north to the Oregon state line in Modoc County near Goose Lake. The route clips into Nevada, serving the cities Carson City and Reno, before returning to California.

June Lake is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Mono County, California, United States. It is located against the southern rim of the Mono Basin, 12.5 miles (20 km) south of Lee Vining, at an elevation of 7,654 feet (2,333 m).

Obsidian Cliff, also known as 48YE433, was an important source of lithic materials for prehistoric peoples in Yellowstone National Park near Mammoth Hot Springs, Wyoming, United States. The cliff was named by Philetus Norris, the second park superintendent in 1878. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1996.

Benton is a census-designated place (CDP) in Mono County, California, United States. It includes the unincorporated communities of Benton and Benton Hot Springs and is 32 miles (51 km) north of the community of Bishop, at an elevation of 5,387 feet (1,642 m). The population of the CDP was 279 at the 2020 census.

The Grand Loop Road is a historic district which encompasses the primary road system in Yellowstone National Park. Much of the 140-mile (230 km) system was originally planned by Captain Hiram M. Chittenden of the US Army Corps of Engineers in the early days of the park, when it was under military administration. The Grand Loop Road provides access to the major features of the park, including the Upper, Midway and Lower geyser basins, Mammoth Hot Springs, Tower Fall, the Grand Canyon of the Yellowstone and Yellowstone Lake.

Mono Hot Springs is a summer resort and campground at a group of hot springs in Fresno County, central California. It is located within the Sierra National Forest, 70 miles (110 km) northeast of Fresno via California State Route 168.

Casa Diablo Hot Springs is a hot springs and active geothermal location, near Mammoth Lakes and the Eastern Sierra Nevada, in Mono County, eastern California.

The California Volcano Observatory (CalVO) is the volcano observatory that monitors the volcanic and geologic activity of California and Nevada. It is a part of the Volcano Hazards Program of the United States Geological Survey, a scientific agency of the United States government.
Roadside Heritage is a program designed to document and publicize the history, culture, and scientific background of the Eastern Sierra Nevada and the Owens Valley in the United States. It uses schoolchildren to interview scientists, Native Americans, and others and to record the interviews. These result in "audio stories" which can be downloaded from the website for use by travelers and others interested in the area.

The Mammoth Geothermal Complex is a complex of 4 geothermal power stations located at Casa Diablo Hot Springs about 3 miles (4.8 km) east of Mammoth Lakes, California. The complex is owned by Ormat and operated by its subsidiary Mammoth Pacific.
References
- Kathleen L. Hull (2001) Reasserting the Utility of Obsidian Hydration Dating: A Temperature-Dependent Empirical Approach to Practical Temporal Resolution with Archaeological Obsidians, Academic Press.
- C.Michael Hogan (2008) Morro Creek, The Megalithic Portal, ed. by A. Burnham
Coordinates: 37°34′59″N118°33′11″W / 37.58306°N 118.55306°W