Common Lisp (CL) is a dialect of the Lisp programming language, published in ANSI standard document ANSI INCITS 226-1994 (S20018). The Common Lisp HyperSpec, a hyperlinked HTML version, has been derived from the ANSI Common Lisp standard.
Zope is a family of free and open-source web application servers written in Python, and their associated online community. Zope stands for "Z Object Publishing Environment", and was the first system using the now common object publishing methodology for the Web. Zope has been called a Python killer app, an application that helped put Python in the spotlight.
In computer science, a continuation is an abstract representation of the control state of a computer program. A continuation implements (reifies) the program control state, i.e. the continuation is a data structure that represents the computational process at a given point in the process's execution; the created data structure can be accessed by the programming language, instead of being hidden in the runtime environment. Continuations are useful for encoding other control mechanisms in programming languages such as exceptions, generators, coroutines, and so on.
CLiki is an open source wiki application written in Common Lisp, that was under development from 2002 to 2005.

In computing, CLISP is an implementation of the programming language Common Lisp originally developed by Bruno Haible and Michael Stoll for the Atari ST. Today it supports the Unix and Microsoft Windows operating systems.

newLISP is a scripting language which is a dialect of the Lisp family of programming languages. It was designed and developed by Lutz Mueller. newLISP is free and open-source software released under the GNU General Public License, version 3 or later.
Embeddable Common Lisp (ECL) is a small implementation of the ANSI Common Lisp programming language that can be used stand-alone or embedded in extant applications written in C. It creates OS-native executables and libraries from Common Lisp code, and runs on most platforms that support a C compiler. The ECL runtime is a dynamically loadable library for use by applications. It is distributed as free and open-source software under a GNU Lesser Public License (LGPL) 2.1+.
Bigloo is a programming language, a dialect of the language Lisp, an implementation of the language Scheme. It is developed at the French IT research institute French Institute for Research in Computer Science and Automation (INRIA). It is oriented toward providing tools for effective and diverse code generation that can match the performance of hand-written C or C++. The Bigloo system contains a Scheme compiler that can generate C code and Java virtual machine (JVM) or .NET Framework (.NET) bytecode. As with other Lisp dialects, it contains an interpreter, also termed a read-eval-print loop (REPL). It is free and open-source software. The run-time system and libraries are released under a GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL). The compiler and programming tools are released under a GNU General Public License (GPL).
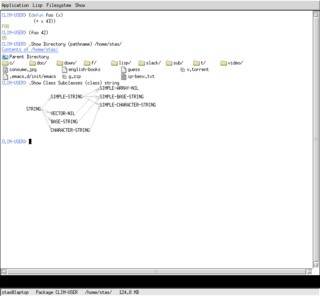
The Common Lisp Interface Manager (CLIM) is a Common Lisp-based programming interface for creating user interfaces, i.e., graphical user interfaces (GUIs). It provides an application programming interface (API) to user interface facilities for the programming language Lisp. It is a fully object-oriented programming user interface management system, using the Common Lisp Object System (CLOS) and is based on the mechanism of stream input and output. There are also facilities for output device independence. It is descended from the GUI system Dynamic Windows of Symbolics' Lisp machines between 1988 and 1993.
... you can check out Common Lisp Interface Manager (CLIM). A descendant of the Symbolics Lisp machines GUI framework, CLIM is powerful but complex. Although many commercial Common Lisp implementations actually support it, it doesn't seem to have seen a lot of use. But in the past couple years, an open-source implementation of CLIM, McCLIM – now hosted at Common-Lisp.net – has been picking up steam lately, so we may be on the verge of a CLIM renaissance. – From Practical Common Lisp

SLIME, the Superior Lisp Interaction Mode for Emacs, is an Emacs mode for developing Common Lisp applications. SLIME originates in an Emacs mode called SLIM written by Eric Marsden. It is developed as an open-source public domain software project by Luke Gorrie and Helmut Eller. Over 100 Lisp developers have contributed code to SLIME since the project was started in 2003. SLIME uses a backend called Swank that is loaded into Common Lisp.

Lift is a free and open-source web framework that is designed for the Scala programming language. It was originally created by David Pollak who was dissatisfied with certain aspects of the Ruby on Rails framework. Lift was launched as an open source project on 26 February 2007 under the Apache License 2.0. A commercially popular web platform often cited as being developed using Lift is Foursquare.
mod_lisp is an extension module for the Apache HTTP Server. It enables Apache to interface with application servers written in Common Lisp, making it possible to dynamically generate web pages and provide web applications with Common Lisp programs.

The .NET Framework is a software framework developed by Microsoft that runs primarily on Microsoft Windows. It includes a large class library called Framework Class Library (FCL) and provides language interoperability across several programming languages. Programs written for .NET Framework execute in a software environment named the Common Language Runtime (CLR). The CLR is an application virtual machine that provides services such as security, memory management, and exception handling. As such, computer code written using .NET Framework is called "managed code". FCL and CLR together constitute the .NET Framework.
AllegroGraph is a closed source triplestore which is designed to store RDF triples, a standard format for Linked Data. It also operates as a document store designed for storing, retrieving and managing document-oriented information, in JSON-LD format. AllegroGraph is currently in use in commercial projects and a US Department of Defense project. It is also the storage component for the TwitLogic project that is bringing the Semantic Web to Twitter data.

Flask is a micro web framework written in Python. It is classified as a microframework because it does not require particular tools or libraries. It has no database abstraction layer, form validation, or any other components where pre-existing third-party libraries provide common functions. However, Flask supports extensions that can add application features as if they were implemented in Flask itself. Extensions exist for object-relational mappers, form validation, upload handling, various open authentication technologies and several common framework related tools.
CL-HTTP is a web server, client and proxy written in Common Lisp. It is based on its own web application framework. It was written by John C. Mallery "in about 10 days" starting in 1994 on a Symbolics Lisp Machine. In the same year a port to Macintosh Common Lisp was done. In 1996 CL-HTTP became the first web server to support the HTTP 1.1 protocol. It runs on Unix, Linux, BSD variants, Mac OS X, Solaris, Symbolics Genera and Microsoft Windows.






