Metropolitan Manila, commonly shortened to Metro Manila and formally the National Capital Region, is the capital region and largest metropolitan area of the Philippines. Located on the eastern shore of Manila Bay, the region lies between the Central Luzon and Calabarzon regions. Encompassing an area of 636.00 km2 (245.56 sq mi) and with a population of 13,484,462 as of 2020, it consists of sixteen highly urbanized cities: Manila—the capital city—Caloocan, Las Piñas, Makati, Malabon, Mandaluyong, Marikina, Muntinlupa, Navotas, Parañaque, Pasay, Pasig, Quezon City, San Juan, Taguig, and Valenzuela, along with one independent municipality, Pateros. As the second most populous and the most densely populated region in the Philippines, it ranks as the 9th most populous metropolitan area in Asia and the 6th most populous urban area in the world.

Ermita is a district in central Manila, Philippines. It is a significant center of finance, education, culture, and commerce. Ermita serves as the civic center of Manila, bearing the seat of city government and a large portion of the area's employment, business, and entertainment activities.

Taguig, officially the City of Taguig, is the fifth-most populous city in the Philippines situated in eastern shores of Metro Manila, the national capital region. It is a center for culture, finance, technology, entertainment and media, academics, and the arts and fashion. The city hosts several embassies, making it an important center for the country's international diplomacy. As the home of Bonifacio Global City, major multinational corporations have their headquarters in the city, and it has the fourth largest skyline in the Philippines, with 289 high-rises, 80 of which exceed 100 m (328 ft).

The Philippine Revolution was a war of independence waged by the revolutionary organization Katipunan against the Spanish Empire from 1896 to 1898. It was the culmination of the 333-year colonial rule of Spain in the archipelago. The Philippines was one of the last major colonies of the Spanish Empire, which had already suffered a massive decline in the 1820s. Cuba rebelled in 1895, and in 1898, the United States intervened and the Spanish soon capitulated. In June, Philippine revolutionaries declared independence. However, it was not recognized by Spain, which sold the islands to the United States in the Treaty of Paris.

Rizal Park, also known as Luneta Park or simply Luneta, is a historic urban park located in Ermita, Manila. It is considered one of the largest urban parks in the Philippines, covering an area of 58 hectares. The site on where the park is situated was originally known as Bagumbayan during the Spanish colonial period. It is adjacent to the historic Walled City of Intramuros.
This is an overview of current and former national capital cities in the Philippines, spanning from the Spanish colonial period to the current Fifth Philippine Republic. The current capital city, Manila, has been the country's capital throughout most of its history and regained the title through a presidential order in 1976, with Metro Manila serving as the National Capital Region (NCR) since 1978.

The Philippine Centennial was a series of celebrations by the Philippine government to primarily commemorate the 100th anniversary of the proclamation of Philippine Independence on June 12, 1898.

Roxas Boulevard is a popular waterfront promenade in Metro Manila in the Philippines. The boulevard, which runs along the shores of Manila Bay, is well known for its sunsets and stretch of coconut trees. The divided roadway has become a trademark of Philippine tourism, famed for its yacht club, hotels, restaurants, commercial buildings and parks.

Ayala Malls is a retail subsidiary of real estate company Ayala Land, an affiliate of Ayala Corporation. Founded in 1988, Ayala Malls owns a chain of large shopping malls, all located in the Philippines. Ayala Malls is one of the largest shopping mall retailer in the Philippines, along with SM Supermalls and Robinsons Malls.

In Metro Manila, Philippines, tourism is a significant industry. In 2012, the city and the region welcomed 974,379 overnight visitors. Serving as the main gateway to the Philippines' numerous destinations, the city attracts mainly international tourists, with a total of 3,139,756 visitors in 2012. Global Blue ranks Manila as the eleventh 'Best Shopping Destination' in Asia. The city holds the tenth position in MasterCard's global top 20 fastest-growing cities for international visitors from 2009 to 2013.

The Battle of Manila of 1896 occurred in Manila in the Spanish colony of the Philippines during the Philippine Revolution. Katipunan under Andres Bonifacio attempted to take the city but the attempt failed, and Bonifacio retreated to the city's outskirts. The Battle of San Juan del Monte was joined a day later when Bonifacio attempted to capture the San Juan's powder magazine, but this too failed.

Bonifacio Drive is a road running approximately 1 kilometer (0.62 mi) in a north-south direction between Intramuros and the Port Area in Manila, Philippines. The boulevard is also designated as Radial Road 1 (R-1) of Manila's arterial road network, National Route 120 (N120) of the Philippine highway network, and an auxiliary route of Asian Highway 26 (AH26).

Circuit Makati is a riverfront redevelopment project by Ayala Land on the site of the former Santa Ana Race Track in Makati, Metro Manila, Philippines. The 21-hectare (52-acre) site located in the northwest portion of Makati, on the south bank of the Pasig River, is planned to contain a mixed-use entertainment complex which would include an indoor theater, a shopping mall, hotels and residential and office skyscrapers. It would also contain a football turf, skate park and an outdoor entertainment area. The development is envisioned to become the new entertainment district of Makati and the city's lifestyle hub.

The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the Philippine capital region of Metro Manila.

The Statue of the Sentinel of Freedom or the Lapu Lapu Monument is a monument to Lapulapu formerly located at the center of the Agrifina Circle at Rizal Park in Manila, Philippines.

The Agrifina Circle, officially the Teodoro F. Valencia Circle, is a traffic circle within the eastern portion of Rizal Park in Manila, Philippines. It has a diameter of 42 meters (138 ft).

The Makati Park and Garden, sometimes called Fort Bonifacio Riverside Park and Liwasang Bonifacio by local residents, is an urban riverfront park along the south bank of the Pasig River in Taguig, Philippines. As early as 1994, the city of Makati fully geared towards the implementation of its projects for the public, engaged with the services of an architectural firm to design the Liwasang Bonifacio. It was then in 1995 when the construction started until its completion in 1998. The park has an area of 35,433 square meters (381,400 sq ft) and its administration was assigned to the Department of Environmental Services who is responsible for the maintenance of the park. The park is open to the public and is designated by the city government of Makati as a safe place for students. In the aftermath of the 2021 Supreme Court decision, which was decided in favor of the City of Taguig gaining jurisdiction of Fort Bonifacio and the Embo barangays, ownership and management of the park has been disputed between the cities of Makati and Taguig. Subsequently, the City of Taguig issued a closure order citing the lack of permits to operate.
The Supreme Court of the Philippines was due to move to a proposed building to be built at the Bonifacio Capital District in Fort Bonifacio, Taguig, Metro Manila, but is now on hold.
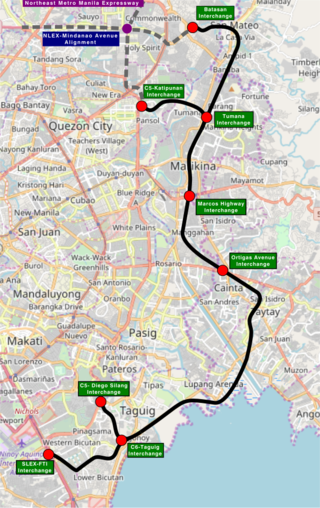
The Southeast Metro Manila Expressway (SEMME), also known as Skyway Stage 4, C-6 Expressway and formerly Metro Manila Expressway, is a proposed 32.664-kilometer (20.296 mi) tolled expressway running across eastern Metro Manila and western Rizal. The expressway will help decongest the existing roadways across Metro Manila, such as EDSA and Circumferential Road 5. The expressway is part of the larger Circumferential Road 6 project, expanding from the original C-6 currently passing from General Santos Avenue in Taguig up to Highway 2000 in Taytay, will expand to Cainta, Pasig, Marikina, San Mateo, and in Quezon City.

The Burnham Plan of Manila is a popular name for Report on proposed improvements at Manila and Manila, P.I., plan of proposed improvements, a 1905 report and map by Daniel Burnham and Pierce Anderson which detail the plan for the city of Manila. It proposed developments based on the characteristics of the city and is patterned after the cities of Naples, Paris, and Venice.