Related Research Articles

The Sauk or Sac are a group of Native Americans of the Northeastern Woodlands, who lived primarily in the region of what is now Green Bay, Wisconsin, when first encountered by the French in 1667. Today they have three federally recognized tribes, often together with the Meskwaki (Fox), located in Iowa, Oklahoma, and Kansas.

The Algonquian languages are a subfamily of the Indigenous languages of the Americas and most of the languages in the Algic language family are included in the group. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from the orthographically similar Algonquin dialect of the Indigenous Ojibwe language (Chippewa), which is a senior member of the Algonquian language family. The term Algonquin has been suggested to derive from the Maliseet word elakómkwik, "they are our relatives/allies".
Algonquin is either a distinct Algonquian language closely related to the Ojibwe language or a particularly divergent Ojibwe dialect. It is spoken, alongside French and to some extent English, by the Algonquin First Nations of Quebec and Ontario. As of 2006, there were 2,680 Algonquin speakers, less than 10% of whom were monolingual. Algonquin is the language for which the entire Algonquian language subgroup is named; the similarity among the names often causes considerable confusion. Like many Native American languages, it is strongly verb-based, with most meaning being incorporated into verbs instead of using separate words for prepositions, tense, etc.

Ojibwe, also known as Ojibwa, Ojibway, Otchipwe, Ojibwemowin, or Anishinaabemowin, is an indigenous language of North America of the Algonquian language family. The language is characterized by a series of dialects that have local names and frequently local writing systems. There is no single dialect that is considered the most prestigious or most prominent, and no standard writing system that covers all dialects.
Indigenous peoples in Quebec total eleven distinct ethnic groups. The one Inuit community and ten First Nations communities number 141,915 people and account for approximately two per cent of the population of Quebec, Canada.

The Anishinaabe are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples present in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe, Odawa, Potawatomi, Mississaugas, Nipissing and Algonquin peoples. The Anishinaabe speak Anishinaabemowin, or Anishinaabe languages that belong to the Algonquian language family.

The Algonquians are one of the most populous and widespread North American native language groups. They historically were prominent along the Atlantic Coast and in the interior regions along Saint Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes. This grouping consists of the peoples who speak Algonquian languages.

Gitche Manitou means "Great Spirit" in several Algonquian languages. Christian missionaries have translated God as Gitche Manitou in scriptures and prayers in the Algonquian languages.
Potawatomi is a Central Algonquian language. It was historically spoken by the Pottawatomi people who lived around the Great Lakes in what are now Michigan and Wisconsin in the United States, and in southern Ontario in Canada. Federally recognized tribes in Michigan and Oklahoma are working to revive the language.
Innu-aimun or Montagnais is an Algonquian language spoken by over 10,000 Innu in Labrador and Quebec in Eastern Canada. It is a member of the Cree–Montagnais–Naskapi dialect continuum and is spoken in various dialects depending on the community.
Great Lakes Algonquian syllabics is a writing system for several Algonquian languages that emerged during the nineteenth century and whose existence was first noted in 1880. It was originally used near the Great Lakes: Fox, Sac, and Kickapoo, in addition to Potawatomi. Use of the script was subsequently extended to the Siouan language Ho-Chunk. Use of the Great Lakes script has also been attributed to speakers of the Ottawa dialect of the Ojibwe language, but supporting evidence is weak.

Fox is an Algonquian language, spoken by a thousand Meskwaki, Sauk, and Kickapoo in various locations in the Midwestern United States and in northern Mexico.

Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands include Native American tribes and First Nation bands residing in or originating from a cultural area encompassing the northeastern and Midwest United States and southeastern Canada. It is part of a broader grouping known as the Eastern Woodlands. The Northeastern Woodlands is divided into three major areas: the Coastal, Saint Lawrence Lowlands, and Great Lakes-Riverine zones.

Ojibwe is an indigenous language of North America from the Algonquian language family. Ojibwe is one of the largest Native American languages north of Mexico in terms of number of speakers and is characterized by a series of dialects, some of which differ significantly. The dialects of Ojibwe are spoken in Canada from southwestern Quebec, through Ontario, Manitoba and parts of Saskatchewan, with outlying communities in Alberta and British Columbia, and in the United States from Michigan through Wisconsin and Minnesota, with a number of communities in North Dakota and Montana, as well as migrant groups in Kansas and Oklahoma.
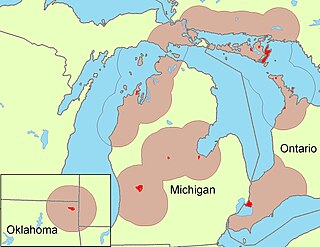
Ottawa or Odawa is a dialect of the Ojibwe language spoken by the Odawa people in southern Ontario in Canada, and northern Michigan in the United States. Descendants of migrant Ottawa speakers live in Kansas and Oklahoma. The first recorded meeting of Ottawa speakers and Europeans occurred in 1615 when a party of Ottawas encountered explorer Samuel de Champlain on the north shore of Georgian Bay. Ottawa is written in an alphabetic system using Latin letters, and is known to its speakers as Nishnaabemwin 'speaking the native language' or Daawaamwin 'speaking Ottawa'.
The Ojibwe language is spoken in a series of dialects occupying adjacent territories, forming a language complex in which mutual intelligibility between adjacent dialects may be comparatively high but declines between some non-adjacent dialects. Mutual intelligibility between some non-adjacent dialects, notably Ottawa, Severn Ojibwe, and Algonquin, is low enough that they could be considered distinct languages. There is no single dialect that is considered the most prestigious or most prominent, and no standard writing system that covers all dialects. The relative autonomy of the regional dialects of Ojibwe is associated with an absence of linguistic or political unity among Ojibwe-speaking groups.
The Ojibwe are a native people of North America.
Chippewa is an Algonquian language spoken from upper Michigan westward to North Dakota in the United States. It represents the southern component of the Ojibwe language.
Truman Michelson was a linguist and anthropologist who worked from 1910 until his death for the Bureau of American Ethnology at the Smithsonian Institution. He also held a position as ethnologist at George Washington University from 1917 until 1932.
References
- ↑ Costa, David J. (2003). The Miami-Illinois Language. University of Nebraska Press. p. 1. ISBN 0803215142.